Biceps muscle strain: Cause, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Exercise
Table of Contents
What is a Biceps muscle strain?
- A Biceps muscle strain is caused by excess strain on the shoulder due to overuse. The most common sign of a bicep muscle strain is a pain in the above elbow, which can lead to bruising, muscle spasms, or loss of mobility and strength.
- Some sports activities like swimming, tennis, or football require repetitive motion of the bicep in the shoulder or elbow that can lead to biceps muscle strains.
Where is the Biceps muscle located?
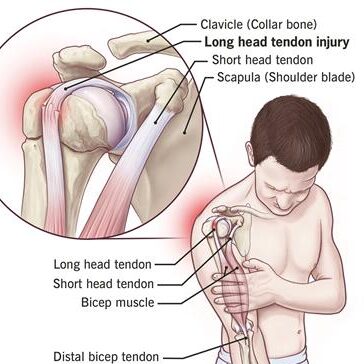
- It is located in the anterior compartment of the upper arm. The biceps includes a “short head” and a “long head” that work as one muscle also called Bicep Brachii muscle .
- The biceps is attached to the arm bones by strong connective tissues called tendons. The tendons that attach the biceps muscle to the shoulder joint in two-point are called the proximal biceps tendons.
- The tendon that attaches the biceps muscle to the forearm radius and ulna bone is called the distal biceps tendon. When the biceps contract, it pulls in the forearm up and external rotation.
- Origin: Short head: coracoid process of the scapula.
- Long head: supra glenoid tubercle
- Insertion: Radial tuberosity and bicipital aponeurosis into deep fascia on medium part of the forearm
- Artery: Brachial artery
- Nerve: Musculocutaneous nerve (C5–C7)
- Actions:Flexes elbow,
- Flexes and abducts the shoulder
- Supinates radioulnar joint in the forearm
- Antagonist: Triceps brachii muscle
What is the cause of biceps muscle strain?
An acute biceps muscle strain is one time your muscle tears quickly and unexpectedly. Muscle tears will be due either to injuries or trauma. this will respond to
- Not warming up properly before physical exercise
- Poor flexibility
- Poor exercise
- Overexertion and fatigue
- Weakness
- Acute injuries are generally the result of a single traumatic event and affect a macro-trauma to the muscle. There’s an articulate link between the cause and noticeable symptoms. They do contact sports similar to swimming, football, and tennis because of their dynamic and high collision nature. Moving or rotating the elbow in an unusual or unfamiliar way can lead to a strain.
- Overuse ( chronic or exercise-induced injuries) is subtler and generally done over a longer period. They result from repetitious micro-trauma to the muscle. Diagnosing is more challenging since there’s a less noticeable link between the cause of the injury and the symptoms
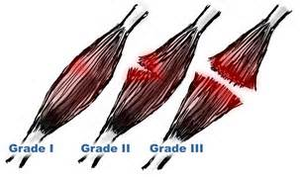
Biceps muscle strain is classified into three grade
- Grade 1: Biceps muscle strain is classified as a minor injury. It happens when the bicep muscles or tendons are overstretched, but you do not lose mobility or strength.
- Grade 2: The strain is moderate tearing in the biceps or tendons that causes some loss of mobility or strength.
- Grade 3: Strain is a complete rupture of the bicep muscle or tendons. If you have a grade 3 tear or strain, you may require surgery to repair muscle strain.
Signs and symptoms
Rely on the open intensity of the injury.
In delicate biceps, muscle strain could feel slightly stiff, however still versatile enough to be used.
- Unexpected pain in the front side of the arm.
- Pain or tenderness over the biceps muscle
- Snapping or popping sensation in your biceps
- Swelling and bruising in your biceps muscle.
- Limited movement of the biceps muscle
- Biceps muscle spasms
- Muscle weakness
- Muscle stiffness
Bicep muscle strain complications
Typically, complications with a bicep strain are rare. Complications that can occur include:
- Decreased range of motion
- Reduced muscle strength
- Pain and infection — if surgery is required to repair a strain
Risk factors
You are more likely to sustain a bicep strain risk if you:
- Participate in sports that require constant movement from the bicep, elbow, and shoulder. Examples are softball or baseball
- poor circulation
- Have a previous shoulder or upper-arm injuries
- Do not warm up before sports activities or exercises
Bicep strain diagnosis
Your doctor can diagnose a bicep strain during a physical examination.
- Medical history: to decide when symptoms began and potential activities that might have caused the sprain or strain.
- The doctor will also look for a swelling on the upper arm that indicates a bicep tear or strain. to confirm your diagnosis, your doctor may also instruct an X-ray or MRI.
Assessment
Subjective assessment
- History with associated symptoms
- Mechanism of injury
- Inciting trauma-direction and extent of injury force
- Repetitious trauma- defective postural related injuries
- Observation Strain injuries of the biceps may present with an obvious deformity similar to a bulge or defect in the muscle belly.
- Palpation
- Tenderness
- Swelling
Treatment
Medical Treatment
Biceps muscle strains infrequently require surgery still may be necessary for a complete rupture.
For immediate
- Nonsurgical, Conservative treatment maximum muscle strains do not demand surgery if the muscle is fully damaged doctors suggest surgery If there is a partial gash also the athlete can replace when they are effortless and have normal strength and movement. this generally occurs following anywhere from many weeks to many months of significant treatment and therapy. When the muscle is fully damaged, the athlete may advantage from surgical repair. e tone- care of a muscle strain.
- Some therapists suggest avoiding inimical pain medicines that can extend your threat of bleeding — similar to over-
the-counter (OTC) medicine (naproxen sodium (Aleve) aspirin and ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB), — during the first 48
hours after a muscle strain. Acetaminophen (Tylenol) and others can be helpful for pain relief during this period. A
physiotherapist can help you to increase the strength and stability of the injured joint or limb. Your doctor may suggest
that you stabilize with a brace. For some muscle injuries, biceps muscle sprint surgery may be called.
To prevent swelling and pain as first aid by following RICE principal
- R- rest
- I- ice for cooling
- C- compression tapping and splinting
- E- elevation
the R.I.C.E approach

- Rest. keep down from activities that cause pain, swelling, or discomfort. do not avoid all physical activity.
- Ice. although you’re seeking medical facilities, ice Loosen the wrap if the ache will extend, place| the world| the area} becomes numb or swelling goes on below the wrapped space. quickly. Use Associate in Nursing associate ice pack or slush tub of ice and water for fifteen to twenty minutes each time and reprise every two to three hours. In contrast, you’re awake for the first few days once the injury.
- Compression. to help stop swelling, compress loosen the serape if the pain will increase, space| the world| the realm} becomes numb or swelling goes on below the wrapped area. with an associate degree girth until the swelling stops. don’t wrap it too tightly else, you would maybe interfere with circulation. Begin wrapping at the highest farthest from your heart. Loosen the wrap if the pain will increase, space| the world| the realm} becomes numb or swelling goes on below the wrapped area. Loosen the serape if the pain will increase, space| the world| the realm} becomes numb or swelling goes on below the wrapped area.Loosen the serape if the pain will increase, space| the world| the realm} becomes numb or swelling goes on below the wrapped area.
- Elevation. Elevate the leg on high of your heart’s extent, significantly at night time, that allows gravity to help reduce swelling.
Physiotherapy treatment
The aim of activity treatment is
- Relieve biceps muscle pain
- Reduce muscle swelling
- Increases biceps muscle strengths.
- Improve full mobility of the ligament and corresponding joint
- Restore patient’s confidence
- Restore the patient’s whole functional activity
Physiotherapy rehabilitation can be started after 48 hours of injury, For the first few days give an electric modality give to relieve swelling and pain
- Ultrasound
- Ultrasound has been used about tissue healing
- Increases blood circulation and mobility.
- To reduce swelling and pain
- Cryotherapy
- Inflammation and swelling can be reduced by applying cryotherapy in form of ice packs, and cold water baths to the affected area. Continuous application of cold several times a day for 15-30 minutes at a time is recommended.
- TENS
- Trans cutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS) may be able to help reduce pain and muscle spasms.
Rehabilitation program
Acute stage(grade-1)
- First few days
- Ice pack,
- Electric modality
- Active movement of biceps muscle
- Biceps muscle stretching
- After week
- Strengthening exercise
Chronic stage(grade-2&3)
Phase one- one week after injury
- Ice pack , three times per day
- Compression
- Active exercise: elbow flexion
- Biceps stretching
Phase two- after 3 to 12 week(strengthening exercise)

Bicep curl (self-applied resistance): Curl one arm toward your shoulder while at the same time stretching to push it back down with your other arm. Compress your biceps at the top of the rep and hold the compression for another. Lower your hand back down to your sides while simultaneously trying to push it back upward with your spare arm. Switch arms and 3-5 sets of 10-15 repetitions per arm.

Static arm curl: Hold a pair of weights by your sides. Curl one weight up — so that your elbow is flexion and put down and hold it there. Immediately perform 5 regular ( full range of movement) curls with your other arm. Switch over so that the arm that was working isometrically is now doing curls. Repeat this process two further times so that each arm has done 10 ringlets and two lots of 5-alternate holes. Perform 3-4 sets in totality.
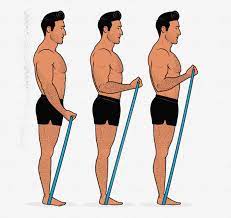
Single Arm Resistance Band Bicep Curl: Pick a resistance band, place it under your feet from one side and hold the other side tightly with your right hand. Stand upright, and keep the band tight or loose adjusting to your strength. Keep your elbows straight and attach to your sides. That’s the starting position. Now, pull the band toward your shoulders until your bicep muscles got fully attached. Pause for a sec, and then bring your arm back to the rest. That’s one repetition. Do as many reps as you can. Recommended 3 sets of 10 reps each. Avoid moving your elbows back while curling your arm, as it will make your exercise easier and less effective.
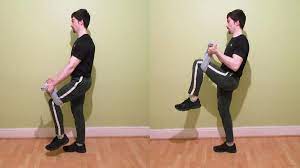
- Towel curl: Stand up straight and lift one leg. put down a towel under that leg and hold the ends of the towel in your hands. Curl the towel toward your chest by flexing your elbow. Keep lifting until your forearms and biceps make touch Hold the contraction for a second and then back down your leg. Perform 3-5 sets of 20-50 reps.

- Door frame holds: Stand in the middle of a door frame. Turn sideways so that you are facing one side of the door frame. Grab the door frame with one hand (two if you are weaker) and shuffle your feet forward. band your torso back so that your elbow is fully extended. Pull yourself near the door frame by flexing your biceps. Keep going until your forearms press right up touching your biceps. Hold this contracted for 30 seconds, and then repeat with your other arm. Do 3-5 sets per arm.
Preventive measures
- warm up before some exercise or sporting activity
- Stretch after exercising or playing sports
- Avoid immediate intense strength training and build strength gradually
- Do regular stretching and strengthening exercises for your sports activity , fitness, or work exertion, as a part of your overall physical activities
- An exercise program can help to minimize your danger of muscle strains.
- Try to be in a shape to play your sport; do not play your sport to get in shape.
- If you have a physically demanding occupation, regular exercise can help to help injuries.
- Follow a healthy diet and an exercise program to maintain a healthy weight. The overweight can put added pressure on the muscles, making muscle strains again probable to do.


One Comment