Abdominal regions
- In anatomy and physiology, you will learn how to divide the abdomen into nine different regions & four different quadrants. If you plan to enter a healthcare profession like nursing, this is something you will use on the job when performing abdominal assessments (and while documenting).
- The abdomen refers to the region between the pelvis (pelvic brim) & the thorax (thoracic diaphragm) in vertebrates, involving humans.
- The abdomen can be divided into 9 areas or regions for the purpose of description.
Anatomical regions of the abdomen
- There are multiple anatomical areas within the abdomen, each of which contains specific contents & is bound by certain borders. These involve the abdominal cavity, Calot’s triangle, the peritoneum, the inguinal canal, & Hesselbach’s triangle.
- The muscles of the abdomen protect the vital organs underneath & provide structure for the spine. These Abdominal muscles assist the body bend at the waist.
Table of Contents
The Four Abdominal Quadrants
- First, let us take a look at the four quadrants, which are created by an intersecting horizontal (transverse) plane, also called the transumbilical plane, & a median (midsagittal) plane.
- The 4 quadrants are easy to remember because they consist of a left upper quadrant (LUQ), left lower quadrant (LLQ), right upper quadrant (RUQ), & right lower quadrant (RLQ).
Here are 2 important things to remember with these four quadrants:
- The navel (belly button) is the landmark you will use to visualize these quadrants while doing assessments. This is the point at which the 2 planes cross.
- The terms uses for “left or right” & “upper or lower” are always from the perspective of the anatomical position, not your perspective. Be careful not to mix up your right & left regions, as this is where most students make the mistake.
Major Organs in the Four Quadrants
Here are certain of the major organs that you will find in each of the four abdominal quadrants:
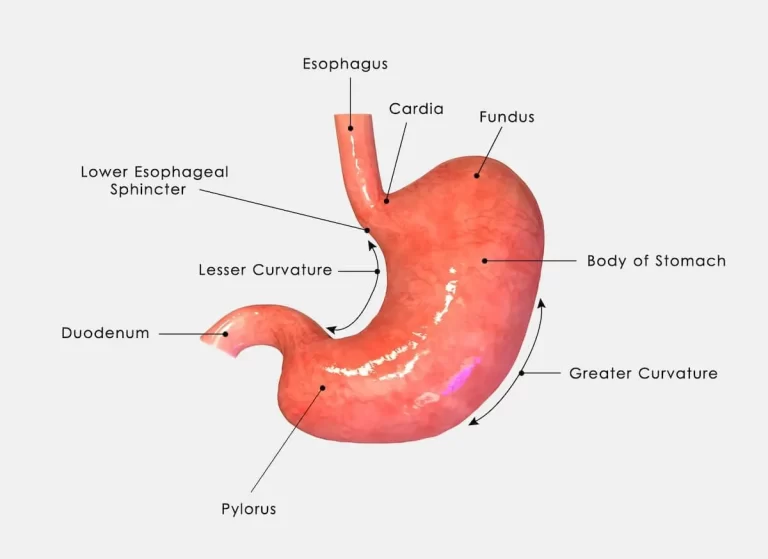
- Right Upper Quadrant: Liver, stomach, gallbladder, duodenum, right kidney, pancreas, & the right adrenal gland.
- Left Upper Quadrant: Liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen, & the left adrenal gland.
- Right Lower Quadrant: appendix, reproductive organs, & the right ureter.
- Left Lower Quadrant: left ureter, & the reproductive organs.
NOTE: All 4 quadrants contain portions of the small & large intestines.
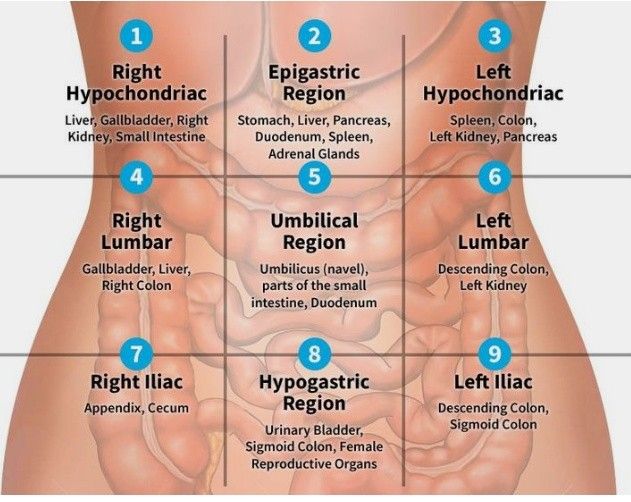
The Nine Abdominal Regions
- The nine abdominal regions divide the abdomen into even smaller sections by using 2 parasagittal planes that run down the middle of the clavicle bones (also called midclavicular planes) & two horizontal (transverse) planes.
- The superior transverse plane is called the subcostal plane, & it is located just under the ribs. The intertubercular plane is the inferior transverse plane, & it intersects the tubercles of the pelvis, running just the inferior to the navel.
- First, let’s cover the right & left columns, because they have the same exact name (distinguished by a left or right prefix), & they have named later the bones to which they are nearest. Remember, a huge tip for studying anatomy is to learn the usual prefixes and suffixes, as they will help you over & over again.
- Hypochondriac Regions (Left and Right): the word “hypo” means below or under. The prefix “chondritic” means cartilage, which is referring to the cartilage of the ribs. When we put them together, this is the abdominal region that is below the ribs. So you have a right & left hypochondriac region.
- Lumbar Regions (Left and Right): The word lumbar refers to the vertebrae in your lower back, which are the bones closest to the lumbar region. That is where this region gets its name.
- Iliac Region (Left and Right): The top of the hip bone has what is called an iliac crest, & that is the bone closest to the iliac region.
- That takes care of the left & right columns. Now, let’s see at the abdominal regions in the middle column. Unlike the regions on the left & right side columns, these regions are named later on their location relative to the stomach, not the bones.
- Epigastric Region: The word “epi” means above, or over, and “gastric” means stomach or belly. Therefore, this is the region over & above the belly.
- Umbilical Region: This is very easy to remember because the umbilical region contains your navel, which is also called the umbilicus. The navel is the landmark for the 4 quadrant points of intersection, and it can also assist you to remember that the umbilical region makes up the middle of the 9 abdominal regions.
- Hypogastric Region: We have already learned that hypo means “below,” & gastric refers to the stomach or belly. So when we put the two together, we know that the hypogastric region is the region under the belly.
- If you need a fast memory trick to keep these regions straight, remember that for the side columns, the names are the same from top to bottom: Hypochondriac, then Lumbar, & then Iliac (HLI). For the middle column, the regions are Epigastric, then Umbilical, & then Hypogastric (EUH). Remember this style: Hector Loves Isabel Every Unceasing Hour.
Organs in the Nine Abdominal Regions
- Now let’s take a look at certain of the major organs that you will find in each region. In most basic anatomy courses, professors probably do not expect you to memorize a list of the organs you will find in each region, yet try to get a general understanding of where the organs are located.
- Right Hypochondriac Region: You will find organs such as the liver, gallbladder, right kidney, and portions of the small & large intestines in this region.
- Epigastric Region: This region contains parts of the liver, as well as the stomach, pancreas, duodenum, spleen, & adrenal glands.
- Left Hypochondriac Region: This contains the spleen, large or small intestines, left kidney, pancreas, stomach, & tip of the liver.
- Right Lumbar Region: You will find portions of the ascending colon, small intestine, & right kidney in this region.
- Umbilical Region: Here you will find the duodenum, the small intestine, as well as the transverse colon.
- Left Lumbar Region: You will find parts of the descending colon, small intestine, & left kidney in this region.
- Right Iliac Region: Here you will find the appendix, cecum, ascending colon, & small intestine.
- Hypogastric Region: You will find the bladder, portions of the sigmoid colon, small intestine, & reproductive organs in this region.
- Left Iliac Region: You will find parts of the sigmoid colon, descending colon & small intestine in this region.
FAQs
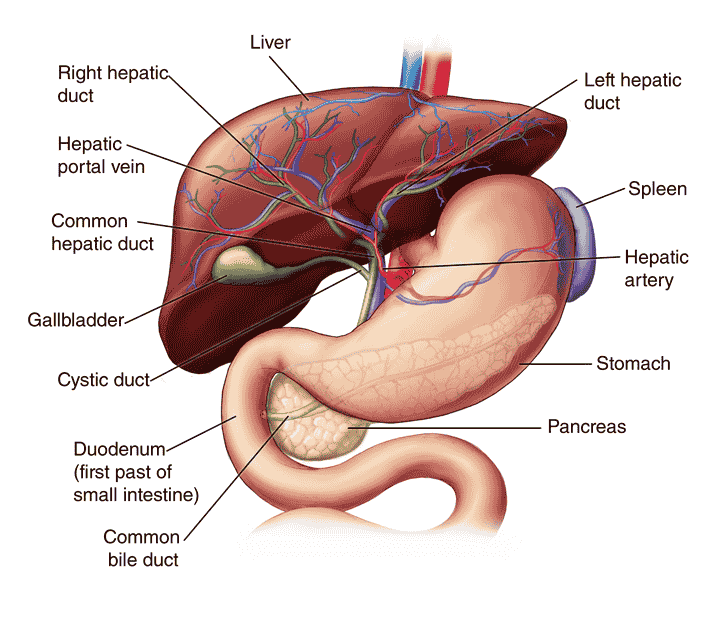
The Human Abdomen The Anatomy Of The Abdomen. The human abdomen is the part in the front of our body between the chest and the waistline. It is a cavity that contains many of the organs in the human body, including the liver, gallbladder, stomach, spleen, pancreas, kidneys, adrenal glands, and bowels.
Imagine the abdominal area divided into these nine regions.
Right, Upper Abdomen. It contains part of the liver, the gallbladder, and part of the right kidney deep inside towards the back It is where the pain of gallstones, hepatitis, costochondritis, myofascial trigger point pain, and upper thoracic nerve root pain, and some other conditions are felt.
Here are some of the major organs that you’ll find in each of the four abdominal quadrants: The right Upper Quadrant: Liver, stomach, gallbladder, duodenum, right kidney, pancreas, and the right adrenal gland. Left Upper Quadrant: Liver, stomach, pancreas, left kidney, spleen, and the left adrenal gland.
The navel (belly button) is the landmark you will use to visualize these quadrants while doing assessments. This is the point at which the 2 planes cross.
The terms uses for “left or right” & “upper or lower” are always from the perspective of the anatomical position, not your perspective. Be careful not to mix up your right & left regions, as this is where most students make the mistake.


5 Comments