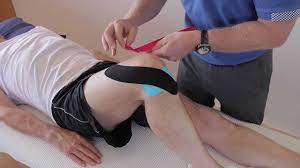
TAPPING TECHNIQUE FOR OA KNEE | KT Tape for Osteoarthritis of Knee joint
Table of Contents
Introduction
Tapping for osteoarthritis of the knee is the most effective technique to relieve knee pain. it is most popular technique also called kinesiology tape or kinesiology therapeutic tape, is an elastic cotton strip with an acrylic adhesive that is purported to ease pain and disability from athletic injuries and a variety of other physical disorders. Taping your knee can help stabilize it when you’re active and can give relief from pain.
- Kinesiological taping is a rehabilitative cum protective use of stretchable kinesiological tapes to provide a reduction of
- reduction in knee pain
- enhancing performance of knee
- preventing injuries to the knee
- support to the knee joint
- repositioning of structure
- stability of the knee and ligamentous correction.
- It facilitates the healing process while providing full ROM with support to the joint’s supportive structure as well as mobilization effects. osteoarthritis is most common in aged people. Pain in the knee is the most common symptom of osteoarthritis knee.
- Osteoarthritis of the knee (OA), also known as degenerative joint disease, is typically the result of wear and tear and progressive loss of articular cartilage. The most common complaint of patients is pain during walking or sitting to stand. Knee pain also may begin as mild discomfort, then slowly get worse.
- OA Knee can be divided into 2 types, primary and secondary:
- Primary degenerative joint disease – is articulary degeneration with no apparent underlying cause.
- Secondary degenerative joint disease – is the consequence of either associated abnormal concentration of force across the joint like post-traumatic causes or abnormal articulary cartilage tissue, like autoimmune disorder (RA).
- Osteoarthritis can be a painful, chronic joint disorder that primarily affects not only the knees but also the hands, hips, and spine. The intensity of the symptoms varies for each individual and often progresses slowly.
- Osteoarthritis is sometimes a progressive malady that can eventually lead to incapacity. The intensity of the clinical symptoms may vary for each individual.
- However, they typically become loads of severe, loads of frequent, and loads of weakening over time. the speed of progression together varies for each individual. Common clinical symptoms embrace knee pain that’s gradual in onset and worse with activity, knee stiffness, and swelling, pain once prolonged sitting or resting, and pain that worsens over time.
- Treatment for knee degenerative joint disease begins with conservative ways and progresses to surgical operation choices once conservative treatment fails. whereas medications will facilitate slow the progression of RA and different inflammatory conditions, no tried disease-modifying agents for the treatment of knee degenerative joint disease presently exist.
Anatomy of the Knee Joint
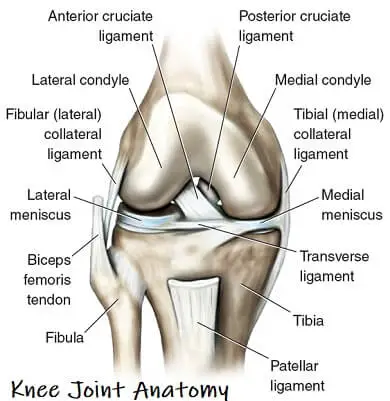
- The knee is the largest joint within the body and one of the foremost abraded. it’s created from four main things: bones, cartilage, ligaments, and tendons.
- Bones: 3 bones meet to create your knee joint: your leg bone (femur), shin (tibia), and kneecap (patella).
- Articulary cartilage: The ends of the leg bone and shin, and therefore the back of the patella are lined with articulary animal tissue. This slippery substance helps your knee bones glide swimmingly across one another as you bend or straighten your leg.
- Meniscus: 2 wedge-shaped items of meniscal animal tissue act as “shock absorbers” between your leg bone and shin. completely different from articulary animal tissue, the gristle is hard and rubbery to assist cushion and stabilizing the joint. once folks name torn animal tissue within the knee, they’re typically relating torn gristle.
- Ligaments: Bones are connected to alternative bones by ligaments. The four main ligaments in your knee act like robust ropes to carry the bones along and keep your knee stable.
- Collateral ligaments: These are found on the perimeters of your knee. The medial collateral ligament is on the within of your knee, and therefore the lateral collateral ligament is on the skin. They manage the sideways motion of your knee and brace it against uncommon movement.
- symmetric ligaments: These are found within your ginglymus. They cross one {another} to create an “X” with the anterior symmetric ligament before and the posterior symmetric ligament in the back. The symmetric ligaments manage the rear and forth motion of your knee.
- Tendons: Muscles are connected to bones by tendons. The extensor sinew connects the muscles within the front of your thigh to your patella. Stretching from your patella to your shin is the sesamoid bone sinew.
- Since the knee joint is tri-compartmental, there are numerous attainable patterns of knee OA. In general, we have a tendency to see knee OA chiefly as a disorder of the TFJ and picture-taking investigations tend to focus solely on the antero -posterior X-ray, while not exploration of the PFJ involvement within the OA method has become a lot of apparent since the redoubled use of lateral and skyline X-rays. In truth, the PFJ is one of the foremost normally affected compartments. Although osteophytes alone aren’t uncomfortable to diagnose OA, a better frequency of picture-taking osteophytes within the PFJ compared with the TFJ compartment has been discomfort.
Causes of OA Knee
- The most common explanation for degenerative arthritis of the knee is age. virtually everybody can eventually develop a point of degenerative arthritis. However, many factors increase the danger of developing the vital inflammatory disease at associate earlier age.
- 1. Age: the power of gristle to heal decreases as someone gets older.
- 2. Weight: Weight will increase pressure on all the joints, particularly the knees. each pound of weight you gain adds three to four pounds of additional weight on your knees.
- 3. Heredity: This includes genetic mutations which may create someone additional seemingly to develop degenerative arthritis of the knee. it should even be thanks to familial abnormalities within the form of the bones that surround the genu.
- 4. Gender: girls ages fifty-five and older square measure additional seemingly than men to develop degenerative arthritis of the knee.
- 5. Repetitive stress injuries: These square measure sometimes a result of the sort of job someone has. folks with bound occupations that embody a great deal of activity that will stress the joint, like kneeling, squatting, or lifting serious weights (55 pounds or more), square measure additional seemingly to develop degenerative arthritis of the knee thanks to the constant pressure on the joint.
- 6. Athletics: Athletes concerned in football, tennis, or long-distance running could also be at higher risk for developing degenerative arthritis of the knee. meaning athletes ought to take precautions to avoid injury. However, it is important to notice that regular moderate exercise strengthens joints and might decrease the danger of degenerative arthritis. In fact, weak muscles around the knee will result in degenerative arthritis.
- 7. Other sicknesses: People with arthritis, the second most typical kind of inflammatory disease, are additional seemingly to develop degenerative arthritis. people with bound metabolic disorders, like hemochromatosis or excess somatotrophic hormone, additionally run the next risk of degenerative arthritis.
Symptoms of OA Knee
- Symptoms of osteoarthritis of the knee may include:
- pain that increases when you are active, but gets a little better with rest
- swelling
- the feeling of warmth in the joint
- stiffness in the knee, especially in the morning or when you have been sitting for a while
- decrease in mobility of the knee, making it difficult to get in and out of chairs or cars, use the stairs, or walk
- creaking, crackly sound that is heard when the knee moves
- abnormal gait pattern
- difficulties in sit to stand
Risk factors of OA knee:
- Old age
- female gender
- overweight (obesity)
- knee injury,
- repetitive use of joints
- bone density
- muscle weakness
- joint laxity
- poor posture
- family history
- certain occupations,
- other medical conditions like Rheumatoid inflammatory disease, diabetes, gout, pseudogout, and an underactive thyroid.
Grades of OA Knee
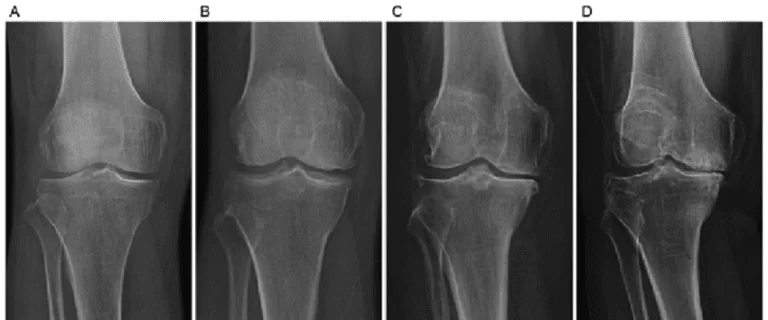
Grade 0: this can be the “normal” knee health
Grade 1: terribly minor bone spur growth and isn’t experiencing any pain or discomfort.
Grade 2: this can be the stage where individuals can expertise symptoms for the primary time. they’re going to have pain when an extended day of walking and can sense a bigger stiffness within the joint. it’s a gentle stage of the condition, however, X-rays can already reveal bigger bone spur growth. The gristle can possibly stay at a healthy size.
Grade 3: Moderate OA. Frequent pain throughout the movement and joint stiffness also will be an additional gift, particularly when sitting for long periods and in the morning. The gristle between the bones shows obvious harm, and therefore the house between the bones is obtaining smaller.
Grade 4: this can be the foremost severe stage of OA. The joint house between the bones is going to be dramatically reduced, the gristle can virtually be fully gone and therefore the secretion is going to be diminished. This stage is generally related to high levels of pain and discomfort throughout walking or moving the joint.
Types of Knee Tape
The two main forms of tape are effective in numerous studies.
- Rigid tape: this sort does not stretch. It’s designed to assist keep a neighborhood from moving.
- Elastic tape: this sort, conjointly referred to as kinesio tape, is intended to be a similar weight and thickness as your skin. It’s manufactured from stretchable cotton with adhesive on one aspect. this is often the bright-colored tape you have most likely seen on athletes throughout races and games. Kinesio tape offers stability however with a wider variety of motion than rigid tape. Keeping a joint from moving will generally build it stiffer.
Methods for tape for OA Knee:
1. The McConnell recording technique:

- This methodology uses rigid tape to align the kneecap (or patella) to ease the pain. you will be ready to use it for knee degenerative joint disease, patellofemoral pain syndrome (otherwise known as runner’s knee), and chondromalacia patella (when the tissue behind your kneecap is damaged).
- You’ll need a roll of 2-inch-wide adhesive gauze to defend your skin and a roll of 1 1/2-inch-wide rigid athletic tape.
- Sit together with your leg slightly bent and extended before you.
- Cut a combination of things of adhesive gauze and place them across your kneecap to defend your skin.
- Start the strip of the rigid tape inside the center of the kneecap and pull it over the kneecap toward the inner region of your knee.
- Push the soft tissue on your inner knee toward the kneecap.
- Secure the tape to the inner facet of the kneecap.
2. Kinesio taping technique:
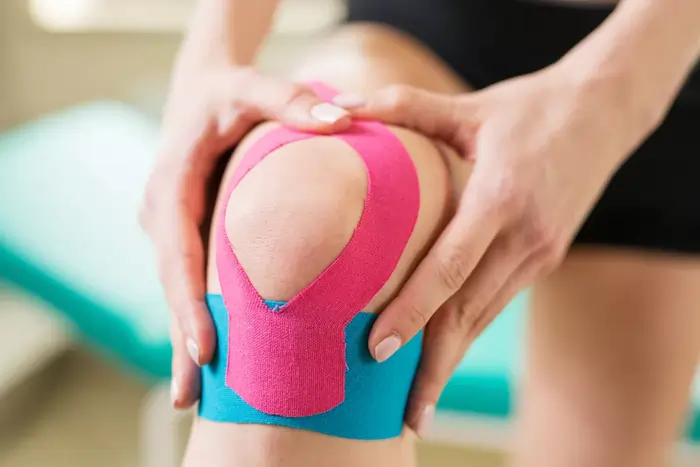
- This methodology used tons of versatile elastic tape to support your knee allowing an honest variety of motion. you’ll need a pair of pre-cut Y strips and a couple of pre-cut I strips. Rub the tape to activate the adhesive once you assail each strip.
- Sit throughout a chair in conjunction with your knee bent. placed on an all-time low in a neighborhood of the fashioned piece of tape starting at mid-thigh.
- Slightly stretch one tail of the fashioned tape and around one side of the kneecap, coming back to the center below the kneecap.
- Repeat with the other tail on the other side of your kneecap. The kneecap got to be closed in.
- Take the other piece of fashioned tape and place it on an all-time low 0.5, starting several inches below the kneecap.
- Slightly stretch one tail of the fashioned tape and apply it around the kneecap, ending on the skin of the other strip.
- Repeat with the other tail on the other side of your kneecap. Place the middle of the first I strip below the kneecap.
- Straighten your knee slightly and continue applying the strip upward on either side of the thigh, outside of the Y strips.
- Repeat with the second I strip placed slightly but the first.
- These are entirely a pair of ways in which of the numerous. Your doctor or healer can assist you in understanding the only methodology to help in conjunction with your issues.
How to remove KT?
- So presently you’ve got your tape on and you’ve gotten that additional support throughout your chosen sporting activity, it’s time to need it off, so enable the United States to ease the tactic of removing physiology tape for you. the foremost effective tip we are going to provide once it involves removing your physiology tape is to peel the skin from the tape, not the tape from the skin.
- But in terms of the actual methodology, 1st ensure you’re removing the tape in an equivalent direction as a result of the expansion of the hair below it, and despite you’re doing don’t rip the tape off kind of a plaster!
- Start slowly, folding the corners of the sting back bit by bit, guaranteeing that you’re birth the removed tape on the rear of the applied tape, as opposition propulsion the tape on top of and aloof from your arm.
- As you’re scraping the tape, hold your skin down beside your completely different hand and either regulator it or pull it gently among the opposite means of the tape.
- This helps the skin and so the tape to separate heaps expeditiously but with no discomfort.
- If the tape has been applied over an awfully furred region of the body, it helps to maneuver on the tape as you are peeling it off, as a result of the pressure helps avoid a lot of pain.
- It’s knowing have shaved the realm before applying the tape but, as this isn’t frequently smart, taking this precaution square measure reaching to be necessary to some.
- want a bit of additional assistance? Apply oil directly onto the tape, rub it in, and wait around 10 to 20 minutes before removing it slowly. This will facilitate the reduction of the viscousness of the tape and make it easier to induce obviate.