Ehlers-Danlos syndrome
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome is a group of inherited conditions that harm connective tissues that support organs and other tissues throughout the body.
Table of Contents
What is Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a group of conditions that harm the joined tissues in the body. These tissues involve cartilage, bone, fat, and blood. They support organs and other tissue throughout the body.
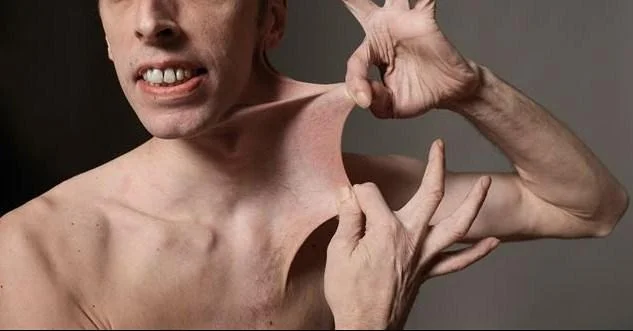
- Doctors classify Ehlers-Danlos syndrome into 13 (Thirteen) types based on their most notable features and the portion of the body where symptoms look. People with the most common type have symptoms involving very loose joints and fragile skin that tears easily.
- Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) can be genetic, meaning it is passed join family members. An estimated 1 in 5,000-20,000 people have the most usual Ehlers-Danlos syndrome type.
What are the symptoms of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
Each and every type of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) has its own symptoms. The most usual type of condition is Ehlers-Danlos hypermobility, or hypermobile Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS).
Its symptoms involve:
- Hypermobile (overly flexible) joints,
- Unstable joints,
- Soft skin that is thinner and stretches more than common,
- Excessive bruising.
What causes Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
A defect in collagen (proteins that add flexibility and strength to connective tissue) because by Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). People with the disorder have a faulty gene that leads to fragile collagen or not enough normal collagen in their tissues. These defects can affect the connective tissue’s ability to support muscles, organs, and other tissues.
How do doctors diagnose Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
Doctors use your family history and so many tests to diagnose Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
Your diagnosis may include:
- Genetic testing: The most usual way to identify the condition is to look for a faulty gene.
- Biopsy: In certain cases, a doctor will use a test known as a biopsy. In this test, the doctor removes a sample of skin and examines it below a microscope to look for signs of the condition, such as specific genes and gene mutations (abnormalities).
- Physical exam: During a physical exam, doctors can look at how much the skin stretches and how far the joints can move.
- Imaging: Tests that provide images of the inside of the body can assist doctors identify abnormalities including heart function problems and curved bones. These tests involve X-rays and computerized tomography (CT) scans.
What are the common treatments for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
- Treatment for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) aims to cure dangerous complications. It can also assist in protecting the joints, skin, and other tissues from injuries. An individual’s treatment depends on many factors, involving the type of the disorder and its symptoms.
- To protect the skin, doctors recommend utilizing sunscreen and mild soaps. Taking extra Vitamin C can assist reduce bruising. Physical therapy (exercises to strengthen the muscles supporting the joints) can assist cure joint injuries. Braces also help stabilize joints.
- Because blood vessels are weak, doctors will monitor people with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and may use medication to assist retain blood pressure (BP) decrease and stable.
- Dislocated joints and other joint injuries are usual among people with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome.
For this reason, doctors recommend they avoid:
- Strenuous (heavy) lifting,
- High-impact exercise where the body pains the ground,
- Contact sports.
Physiotherapy Treatment
Physiotherapists play a main role in management through exercise prescription and patient education for many of these conditions. Each physical therapy plan of care must be specially made for the patient depending upon the subtype of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) and the signs and symptoms of that patient.
As usual, physical therapy intervention focuses on decreasing the patient’s disability from a multidirectional clear:
- Aerobic exercise program: consisting of aerobic conditioning combined with a decreased resistance, high repetition resistive training program to promote increased joint stability by improving usual resting muscle tone.
- Strength exercise program: to keep away recurrent joint subluxations/dislocations due to improved muscle tone and to counteract the presence of excessive joint, ligament, tendon, and muscle laxity.
- Assistive devices: to supply loading relief to lower extremity joints during ambulation and weight-bearing activities.
- Bracing: to promote improved joint stability and decrease the likelihood of joint subluxation/dislocation.
- Pain management techniques: to mark soft tissue, myofascial, and chronic joint pain associated with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS).
- Myofascial release (MFR) techniques.
- Pain relief (immediate – several hours).
Can Ehlers-Danlos syndrome be prevented?
Because it is genetic, you cannot cure Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS).
What is the viewpoint of people with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
The viewpoint for people with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome turns on the type of the condition and the individual’s symptoms. Most forms of the condition do not harm life expectancy.
What are the usual complications or side effects of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
- The complications of certain types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome can be life-threatening. Certain types, involving vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, can cause blood vessels to rupture (tear). When this happens, it can conduct to dangerous internal bleeding and stroke.
- People with these types of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome have a higher risk of organ rupture. Most usually, the intestines or a pregnant woman’s uterus may tear.
- The complications of other kinds of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome turn on the type.
These complications can involve:
- Problems with the valves that push blood via the heart,
- Severe spine curvature,
- Thinning of corneas in the eyes,
- Bowed (curved) limbs,
- Defects of the teeth and gums.
How can people best live with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome?
Doctors can assist you treat symptoms with physical therapy and, if needed, pain management. Observing Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) through day-to-day doctor visits is the better way to ensure the condition does not stand in the way of happening a healthy routine life.
FAQs
loose, unstable joints that dislocate easily, stretchy skin, weak skin that can part away easily, especially on the forehead, knees, shins, and elbows, smooth, velvety skin that bruises lightly.
The median life expectancy for individuals with vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is through 48 years. Patients with kyphoscoliotic Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) — whose hallmark is a sideways curvature of the spine in combination with a hunched back — may have a decreased life expectancy.
Because the condition is genetic, there is no prevention for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). Treatment for Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) will concentrate on reducing stress on the aorta and other arteries and managing cadaverous and joint troubles and any pain connected with them.
Extremely loose joints, stretchy or weak skin, and a family history of Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) are sometimes sufficient to make a diagnosis. Genetic tests over a sampling of your blood can confirm the opinion in infrequent forms of Ehlers-Danlos pattern (EDS) and assist prevent other issues.
Vascular Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) pattern can weaken your heart’s largest artery (aorta), or the arteries to another segment of your body. A rupture of any of these greater blood vessels can be fatal. The vascular type can loosen the walls of the uterus or large intestines — which may tear.
Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) is a group of hereditary connective tissue disorders that shows clinically with skin hyperelasticity, hypermobility of joints, atrophic scarring, and fragility of blood vessels.
I was queried recently to describe what my body feels along with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS). I related the feeling of being tenderized with a mallet total of my body. Not enough to break bones, yet hard enough to leave bruises. This is my daily experience even along with the aid of ache meds.
Yes, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) can make you appear younger. Patients with Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) do not have any wrinkles as the collagen is furthermore stretchy. This makes their skin soft and youthful.
Although any physician can diagnose Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS), complicating factors may bear consultation with a geneticist. The goal is to genetically confirm Ehlers-Danlos syndrome (EDS) or rule out other conditions.


5 Comments