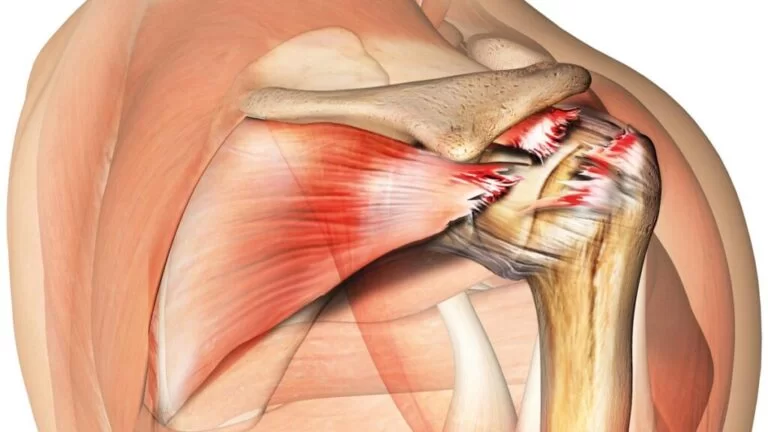
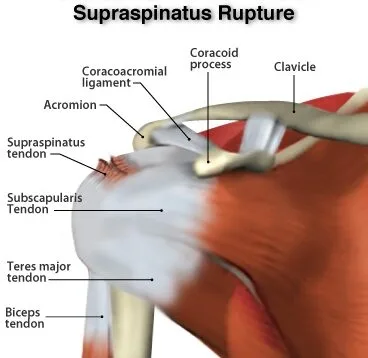
Infraspinatus tendon tear
Table of Contents
Introduction
An infraspinatus tendon tear is a common injury that can occur in the shoulder. The infraspinatus tendon is one of the four rotator cuff tendons that help stabilize and move the shoulder joint.
An infraspinatus tendon tear can be caused by a traumatic injury, such as a fall or direct blow to the shoulder, or by repetitive strain on the shoulder joint over time. Symptoms of an infraspinatus tendon tear can include pain, weakness, limited range of motion, and swelling or bruising around the shoulder joint.
Causes of Infraspinatus tendon tear
An infraspinatus tendon tear can occur due to various causes, including:
- Traumatic injury: A direct blow to the shoulder or a fall can cause an infraspinatus tendon tear.
- Repetitive strain: Repetitive overhead movements, such as those involved in throwing a ball, swimming, or weightlifting, can lead to overuse injuries and cause the tendon to tear over time.
- Age-related degeneration: As we age, our tendons become less elastic and more susceptible to degeneration, which can increase the risk of an infraspinatus tendon tear.
- Poor posture: Poor posture, such as hunching over a computer for long periods, can put stress on the shoulder joint and lead to a tear in the tendon.
- Weakness or imbalances in shoulder muscles: Weakness or imbalances in the muscles that support the shoulder joint can lead to overuse injuries and increase the risk of a tendon tear.
- Certain medical conditions: Certain medical conditions, such as diabetes and rheumatoid arthritis, can weaken the tendons and increase the risk of a tear.
It’s important to identify and address the underlying cause of an infraspinatus tendon tear to prevent further injury and promote proper healing.
Symptoms of Infraspinatus tendon tear
The symptoms of an infraspinatus tendon tear can vary depending on the severity of the injury. Some common symptoms include:
• Pain or tenderness in the back of the shoulder
• Weakness in the shoulder, particularly when lifting or reaching overhead
• Limited range of motion in shoulder joint movements
• A popping or clicking sensation when moving the shoulder joint
• Swelling and redness around the affected shoulder
Diagnosis
If you are experiencing symptoms of an infraspinatus tendon tear, it’s important to see a doctor for a proper diagnosis. Here are some of the common methods used to diagnose an infraspinatus tendon tear:
1. Physical exam: Your doctor will likely begin by conducting a physical exam, which may include moving your shoulder in different directions to check for pain, weakness, or limited range of motion. They may also press on different parts of your shoulder to check for tenderness.
• Special test for infraspinatus tendon
There are several special tests that can be performed during a physical exam to help diagnose an infraspinatus tendon tear. Here are some of the most commonly used special tests for shoulder injuries:
- Drop arm test: The drop arm test is a simple and reliable test for detecting a rotator cuff tear, including an infraspinatus tendon tear. During the test, the patient raises their arm to shoulder level and slowly lowers it to their side. If the arm drops suddenly, it can be a sign of a tear in the rotator cuff, including the infraspinatus tendon.
- External Rotation Lag Sign: This test is performed by having the patient place their arm at their side with the elbow bent to 90 degrees and the palm facing up. The examiner then holds the patient’s wrist and asks them to externally rotate their arm while resisting the examiner’s pressure. If the patient is unable to hold the position, it can indicate a tear in the infraspinatus tendon.
- Infraspinatus Test: In this test, the patient’s arm is held at the side with the elbow bent to 90 degrees and the palm facing down. The examiner then applies resistance to the back of the patient’s hand while the patient tries to externally rotate their arm. Pain or weakness during the test can be a sign of an infraspinatus tendon tear.
- Hornblower’s Sign: This test is performed by having the patient place their arm at their side with the elbow bent to 90 degrees and the palm facing down. The examiner then asks the patient to internally rotate their arm against resistance. Inability to perform this movement can be a sign of an infraspinatus tendon tear.
2. Imaging tests: Imaging tests such as X-rays, MRIs (Magnetic Resonance Imaging), or ultrasounds can help identify any structural abnormalities, including a tear in the infraspinatus tendon. These tests can provide a detailed view of the shoulder joint and help your doctor determine the severity of the injury.
3. Electromyography (EMG): An EMG test can be used to evaluate the electrical activity of the muscles and nerves in the shoulder, which can help to determine the extent of the injury and how well the muscles are functioning.
4. Diagnostic injection: A diagnostic injection of a local anesthetic into the shoulder joint can help determine if the pain is coming from the infraspinatus tendon or another area of the shoulder.
Treatment of Infraspinatus tendon tear
The treatment for an infraspinatus tendon tear will depend on the severity of the tear. For mild tears, non-surgical treatment options may be recommended. For more severe tears, surgery may be necessary.
Non-surgical Treatment
1. Rest and Ice: Resting the shoulder and applying ice to the affected area can help reduce pain and inflammation.
2. Physical therapy: Physical therapy can help strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve shoulder stability. A physical therapist can create an exercise program that is tailored to your specific injury.
3. Medications: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) may be recommended to manage pain and reduce inflammation.
4. Corticosteroid Injection: A corticosteroid injection may be recommended to reduce inflammation and pain in the shoulder. However, these injections should be used with caution, as they can weaken the tendon and increase the risk of further injury.
Surgical Treatment
Surgery may be recommended for more severe infraspinatus tendon tears. The type of surgery performed will depend on the severity and location of the tear. Common surgical procedures include:
Arthroscopic Surgery: This minimally invasive surgery involves making small incisions in the shoulder and using a camera and small instruments to repair the tendon.
Open surgery: This involves making a larger incision in the shoulder to directly access the torn tendon.
Tendon Transfer: In some cases, a tendon from another part of the body may be used to replace the torn infraspinatus tendon.
After surgery, a period of rest and physical therapy is necessary to ensure proper healing and recovery.
Physiotherapy Treatment in Infraspinatus tendon tear
Phase-wise physiotherapy management for an infraspinatus tendon tear typically involves a progressive approach to rehabilitation, focusing on pain reduction, inflammation control, and gradual restoration of shoulder function. Here are the typical phases of physiotherapy management for an infraspinatus tendon tear:
- Phase 1: Acute Phase
- This phase focuses on reducing pain and inflammation, protecting the shoulder joint from further injury, and maintaining joint mobility. Treatment may include rest, ice or heat therapy, ultrasound, and gentle range-of-motion exercises.
- Phase 2: Subacute Phase
- This phase involves regaining the shoulder range of motion, strengthening the rotator cuff muscles, and improving shoulder blade control. Treatment may include range-of-motion exercises, shoulder blade stabilization exercises, and isometric strengthening exercises.
- Phase 3: Strengthening Phase
- This phase focuses on improving the strength and endurance of the rotator cuff muscles, shoulder blade muscles, and other shoulder muscles. Treatment may include resistance training exercises, such as external rotation with a resistance band, scapular retraction, and shoulder abduction with weights.
- Phase 4: Return to Activity
- This phase involves gradually returning to functional activities and sports-specific movements. Treatment may include sport-specific training and exercises that simulate the demands of the individual’s sport or activity.
It is important to note that the duration and progression of each phase of physiotherapy management may vary depending on the individual’s age, health, and severity of the infraspinatus tendon tear. A physiotherapist can help design a personalized treatment plan and monitor progress throughout each phase of rehabilitation.
How to Prevent Infraspinatus tendon tear?
Preventing an infraspinatus tendon tear involves taking steps to maintain shoulder health and minimize the risk of injury. Some effective prevention strategies include:
• Maintaining good posture and shoulder mechanics during activities
• Performing regular shoulder strengthening exercises
• Warm up before engaging in physical activity.
• Avoiding overuse and repetitive movements
• Listening to the body and taking breaks when necessary
Conclusion
An infraspinatus tendon tear can be a painful and debilitating injury, but with proper diagnosis and treatment, individuals can recover and return to their normal activities. Taking preventive measures, such as maintaining good shoulder health and using proper mechanics during activities, can also help to reduce the risk of developing an infraspinatus tendon tear.
FAQs
Where is the pain coming from in the infraspinatus?
The infraspinatus muscle is located in the shoulder blade region, specifically on the posterior (back) surface of the scapula bone. Pain from the infraspinatus muscle may be felt in the shoulder, upper back, or down the arm, depending on the severity and location of the injury or strain. Common symptoms of infraspinatus pain include limited range of motion in the shoulder, difficulty lifting or moving the arm, and pain that worsens with certain movements or activities. If you are experiencing persistent or severe pain, it is recommended that you consult with a healthcare professional for an accurate diagnosis and an appropriate treatment plan.
What exercise works the infraspinatus?
There are a number of exercises that can target and strengthen the infraspinatus muscle, including:
1. External rotation with resistance band: Place a resistance band around a stable object at waist height, hold the other end with your elbow bent at 90 degrees, and rotate your arm away from your body.
2. Seated dumbbell external rotation: Sit on a bench with a dumbbell in one hand, bend your elbow 90 degrees, and rotate your arm away from your body.
3. Inverted rows: Lie underneath a suspension trainer or a bar, grasp the handles or the bar with an overhand grip, and pull your body towards the bar while keeping your elbows close to your body.
4. Face pulls: Attach a resistance band to a stationary object at chest height, hold the band with both hands and pull the band towards your face while squeezing your shoulder blades together.
It is important to use proper form and start with a lightweight or resistance band to avoid injury. If you are experiencing pain or discomfort during these exercises, it is recommended that you stop and consult with a healthcare professional.What is the function of the infraspinatus?
The infraspinatus is one of the four muscles that make up the rotator cuff in the shoulder. Its main function is to externally rotate the arm and stabilize the shoulder joint during arm movements. The infraspinatus muscle is responsible for rotating the arm outward, away from the body, and is involved in a wide range of movements, including reaching, throwing, and lifting objects. It also helps to keep the head of the humerus (upper arm bone) stable within the glenoid cavity (shoulder joint socket) during arm movements. In addition to its role in shoulder movement and stability, the infraspinatus also plays a role in maintaining a proper posture of the shoulder blade and upper back. Overall, the infraspinatus muscle is an important contributor to healthy shoulder function and overall upper-body mobility.
How long does an infraspinatus tendon tear take to heal?
The healing time for an infraspinatus tear can vary depending on the severity of the injury and the individual’s overall health and healing ability. In general, a mild tear may take a few weeks to a few months to heal, while a more severe tear may take several months to a year or more to fully heal.
During the initial phase of healing, it is important to rest the affected area, avoid activities that may aggravate the injury, and engage in physical therapy or other rehabilitation exercises to strengthen the surrounding muscles and promote healing. Ice, compression, and anti-inflammatory medications may also be used to reduce pain and swelling.
If the tear is severe or does not respond to conservative treatment, surgery may be necessary to repair the muscle. Recovery from surgery may take several months, and physical therapy is often required to restore strength, flexibility, and range of motion to the shoulder.What are two warning signs of an infraspinatus tear?
Here are two warning signs of an infraspinatus tear:
1. Pain: Pain is a common symptom of a rotator cuff tear, and it may be felt in the shoulder or upper arm. The pain may be sudden and intense, or it may develop gradually over time. The pain may also be worse at night, especially when lying on the affected shoulder.
2. Weakness: Weakness or a feeling of weakness in the shoulder or arm is another warning sign of a rotator cuff tear. You may find it difficult to lift or move your arm, especially when trying to reach overhead or perform activities that involve the shoulder. Weakness can be a sign of a partial or complete tear in the rotator cuff, and it may be accompanied by a popping or clicking sensation in the shoulder joint.
Other symptoms of a rotator cuff tear may include a limited range of motion, stiffness, and swelling in the shoulder. If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, it is recommended that you seek medical attention to determine the cause of your discomfort and receive appropriate treatment.



One Comment