Ulnocarpal Stress Test
Table of Contents
Introduction
The Ulnocarpal Stress Test also known as the ulnar carpal stress test, is a medical exam used to assess the integrity and stability of the wrist’s triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC). The TFCC is a group of ligaments and cartilage that support and stabilize the wrist joint.
The test is normally performed by a healthcare expert, such as an orthopedic surgeon or a physical therapist, and is usually recommended when a patient complains of wrist discomfort, limited range of motion, or a history of a severe wrist injury. The test aids in the diagnosis of disorders such as TFCC rips, ligament damage, and other wrist joint issues.
How is the Ulnocarpal Stress Test Performed?
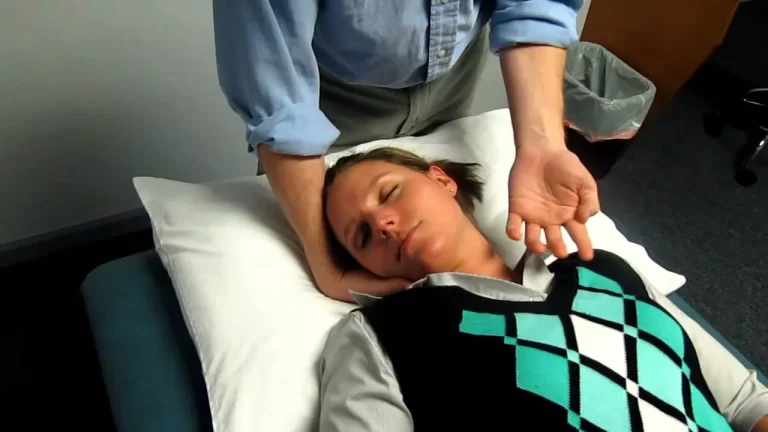
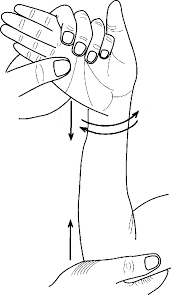
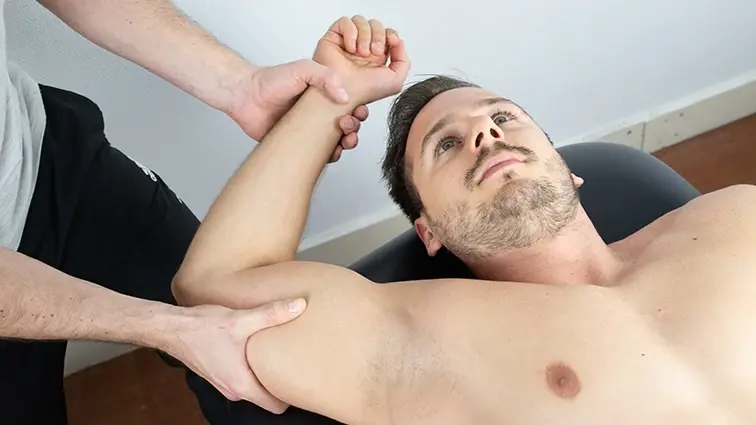
The ulnocarpal stress test is done as follows:
The patient is either lying or sitting comfortably.
The examiner uses one hand to stabilize the forearm and wrist of the affected hand while the other hand applies force to the ulnar side of the wrist.
Stress is directed in a way that tends to reproduce or exaggerate the patient’s symptoms.
To check the stability of the TFCC and the wrist joint, the examiner may move the wrist through various ranges of motion while applying stress.
If the patient suffers discomfort or an increase in symptoms during the test, this might indicate a TFCC damage or instability. It is important to note, however, that this test is only one component of the overall clinical evaluation, and the healthcare provider will consider the patient’s history, physical examination findings, and possibly other diagnostic tests (such as imaging studies like MRI) to arrive at an accurate diagnosis.
If you have any wrist discomfort or concerns, it is critical that you get expert medical guidance, as self-diagnosis and self-treatment might lead to more difficulties. Only a skilled healthcare expert can offer you with an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan tailored to your individual situation.
What is the purpose of the Ulnocarpal stress test?
In a medical examination, the ulnocarpal stress test is used for the following purposes:
The major goal of the ulnocarpal stress test is to assess the integrity and stability of the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC) in the wrist. The TFCC is an important structure that helps in the stabilization of the wrist joint and offers support to the ulnar side of the wrist.
Diagnosis of TFCC Injuries: The test is frequently used to identify TFCC injuries such as tears, sprains, or degenerative changes. Trauma, overuse, or wear and tear can all cause TFCC problems.
Ligament Instability: The test may be helpful in the identification of ligament instability in the wrist joint, particularly on the ulnar side. Wrist discomfort and impaired functional ability might result from ligament injuries or laxity in this location.
Differential Diagnosis: The ulnocarpal stress test distinguishes TFCC injuries from other wrist pathologies with similar presentations, such as carpal tunnel syndrome, arthritis, or other ligament injuries, by recreating or increasing the patient’s symptoms.
Treatment Planning: The results of the tests, when combined with additional clinical findings and diagnostic testing, can assist in the development of a suitable treatment plan. Treatment options for TFCC injuries may include conservative measures (rest, physical therapy, splinting), medication, or even surgical intervention if conservative procedures are ineffective.
Follow-up Evaluation: If the patient has previously been diagnosed with a TFCC injury, the ulnocarpal stress test can be utilized to monitor healing progress and assess the effectiveness of the selected treatment plan.
Conclusion
Overall, the ulnocarpal stress test is a valuable tool in the diagnosis of wrist injuries and discomfort, especially when TFCC involvement is suspected. However, keep in mind that the exam is only one component of a thorough clinical evaluation. A combination of history-taking, physical examination, imaging examinations (e.g., MRI), and the experience of a skilled healthcare practitioner is required for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
FAQ
What is the cause of Ulnocarpal impaction?
Ulnar impaction syndrome, also known as ulnar abutment syndrome, ulnocarpal impaction, or loading, is a painful degenerative wrist ailment caused by the ulnar head colliding with the ulnar-sided carpus, causing damage to the triangular fibrocartilage complex (TFCC).
What causes Ulnocarpal abutment syndrome?
Ulnar abutment syndrome (ulnocarpal impaction) can cause ulnar-sided wrist discomfort in athletes. Excessive load transmission between the triangular fibrocartilage complex and ulnocarpal joints causes this disorder, which is characterized by degenerative alterations.
How do you treat ulnocarpal abutment?
Hand – Ulnocarpal Abutment Syndrome – Orthobullets
For individuals with minor symptoms, treatment may involve a trial of rest and splinting. Depending on the severity of the symptoms, surgical ulnar shortening operations are recommended.
What are the special tests for TFCC?
These are some examples:
The TFCC compression test reproduces symptoms by placing the forearm in a neutral posture with ulnar deviation.
The TFCC stress test reproduces symptoms by exerting a force across the ulna with the wrist in ulnar deviation.
Press test: The patient raises himself out of a chair with their wrists outstretched.
Reference
Clinic, M. P. (2023, August 3). Ulnocarpal Stress Test. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/ulnocarpal-stress-test/
Ulnar Impaction Syndrome. (n.d.). Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Ulnar_Impaction_Syndrome
TFCC Stress Test – WikiSM (Sports Medicine Wiki). (n.d.). https://wikism.org/TFCC_Stress_Test