What are Spasticity and Rigidity?
Table of Contents
Spasticity & Rigidity
- Spasticity is a lesion of the pyramidal tract or damage to corticospinal tracts.
- Rigidity is a lesion of extrapyramidal tracts, commonly the basal ganglia, and also a lesion of the mesencephalon and spinal cord.
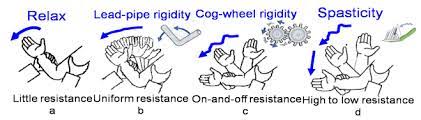
COMPARISON OF SPASTICITY & RIGIDITY :
| NO. | SPASTICITY | RIGIDITY |
| 1 | Spasticity is a condition in which there is an abnormal increase in muscle tone or stiffness of muscle. | Rigidity is a hypertonic state characterized by constant resistance throughout range of motion . |
| 2 | Incresed muscles tone due to damage to pyramidal tracts. | Incresed muscles tone due to damage to extrapyramidal tracts. |
| 3 | It depends upon velocity & amplitude. | It independents upon velocity & amplitude. |
| 4 | Mainly affect antigravity muscles | Both flexors & extensors are affected. |
| 5 | Best assessed by repid movt. | Detectable with very slow movt. |
| 6 | Hypertoniya _ claps knife type of rigidity . | Hypertoniya _ cog wheel & lead pipe type of rigidity. |
| 7 | Clonus present . | Clonus absent . |
| 8 | Increase in gamma activity | Increase in alpha & gamma activity . |
| 9 | No tremors | Static tremors. |
| 10 | Hyperreflexia | Normal reflexia . |
| 11 | Stretch sensetive . | Not stretch sensetive . |
| 12 | Ex. Chonic UMNL . | Ex. Parkinsonism. |

SPASTICITY :
- Also known muscle stiffness , hypertonia
- It is upper moter neuron lesion .
- It is velocity dependent .
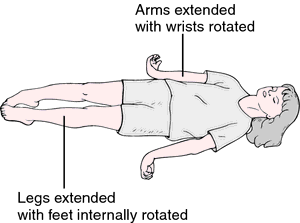
- More tone in initial part of movement – “Clasp knife spasticity” .

Lead pipe spasticity :
- Spasticity is characterized by abnormally high muscle tone, which often asymmetrically affects antagonistic muscle groups.
- It is present in flexors and extensor muscle groups equally, giving rise to a uniform quality in all directions often described as “lead pipe” rigidity.
Causes :
- Stroke
- Spinal cord compression
- Motor neuron disease
- Head injury
- Multiple sclerosis
SYMPTOMS :
- Spasticity start mild stiffness or tightening of muscles to painful and uncontrollable spasms.
- Muscle stiffness
- Muscle spasms
- Abnormal posture
- Exaggerated deep tendon reflexes
- Clonus
- hypertonicity – increased muscle tone
- Involuntary crossing of the legs
- Muscle and joint deformities
- Muscle fatigue
- Contractures
- Inhibition of longitudinal muscle growth
- Inhibition of protein synthesis in muscle cells
- Bone and joint deformities
Complications :
- Urinary tract infections (UTI)
- Chronic constipation
- Fever or other systemic illnesses
- Pressure sores
- Frozen joints
Testing & Diagnosis:
- A physiotherapy examination with neurological testing will be done to test for spasticity and the severity of it.
- Imaging such as magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can provide more information.
MEDICAL TREATMENT :
Anti-spasticity medicine are used to reduce spasticity – mostly your doctor prescribed according to grade of spasticity. following most commonly used medicine.
- Baclofen
- Tizanidine
- Dantrolene sodium
- Diazepam
- Clonazepam
- Gabapentin
RIGIDITY :

- upper motor neuron facilitation.
- Rigidity is a hypertonic state characterized by constant resistance throughout range of motion that is independent of the velocity of movement.
- In parkinsonian rigidity, tendon jerks are usually normal.
Causes :
- Muscle rigidity is often triggered by stress.
- Polymyalgia rheumatica is a common condition that causes pain and stiffness in older adults.
- Unexplained weight loss and fatigue.
- In parkinsonism pt. reduced dopamine levels are thought to disrupt the balance between the muscles which extend and relax for each movement .
Symptoms :
- Stiff and/or inflexible muscles.
- Pain and muscle cramps.
- Difficulty turning when walking, turning in bed and getting out of a chair or bed.
- The combination of tremor & incresed tone is consider to be at the origin to cog wheel rigidity .
- Rigidity may be associated joint pain .
Two types of rigidity:
1) Cogwheel rigidity :

- Muscular rigidity in which passive movement of the limbs elicits ratchet-like start-and stop movements through the range of motion of a joint (as of the elbow) .
2) Lead pipe rigidity :

- Lead-pipe rigidity is a type of movement disorder, a hypokinesia that pertains to decreased bodily movements.
Different between lead pipe rigidity & cogwheel rigidity :
- Lead pipe rigidity is defined as a constant resistance to motion throughout the entire range of movement.
- Cogwheel rigidity refers to resistance that stops and starts as the limb is moved through its range of motion.
PHYSIOTHERAPY TREATMENT IN SPASTICITY :
Physiotherapy especially when started early in life, is helpful in promoting normal motor development, and preventing deformity and contractures.
- It aims at reducing abnormal patterns of movement and posture and promoting the normal ones so as to enable to gain maximal functional independence.
- Re-inforcement of normal postural reflexes and
- Facilitation of normal movements.
Heat decrease spasticity
- Sometimes heat or ice can be used to temporarily relax a spastic muscle.
- Warm baths or swimming pools can also help to relax a spastic muscle.
The goal of physiotherapy treatment to reduce your spasticity are :
- Develop co-ordination
- Build strength of opposite group muscles
- Improve balance
- Maintain flexibility – stretching of spastic group of muscles
- Optimize physical functioning levels
- Maximize independence
- Overcoming physical limitations
- Expanding range of joint motion
- Building and maintaining muscle tone
- Increasing recreational capabilities
- Identifying alternate ways to perform everyday tasks
- Fostering independence
- Decreasing the likelihood of contractures, bone deformity
- Providing sensory stimulation
- Increasing fitness Increasing flexibility
- Improving posture Improving gait
Weight bearing exercise to help reduce spasticity :
- Any weight bearing of the upper extremity either at the wall, table, or floor helps sends signals to the brain that reminds it the arm is still there.
- Strengthening can improve spasticity in two ways. By strengthening the antagonist (opposing) muscle, it can help inhibit the reaction of the spastic muscle.
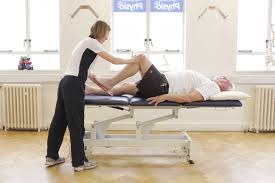
The largest benefit of therapy to the quadriplegia with spasticity is in the treatment of problematic conditions when they occur, including:
- Muscle atrophy or tightening
- Loss in joint range of motion
- Muscle spasticity Pain in muscles and joints
- Joint inflammation Contractures (muscle rigidity)
- Minimizing pain and discomfort
Exercises often include the use of equipment, such as:
- Weights Exercise machines
- Bands Rollers
- Balance balls
- Heat and cold packs
- Ultrasound technology
- Adaptive equipment including braces, splints, walkers, orthotics, wheelchairs, and even computers will be used in therapy; therapists will modify the equipment as needed.
- The therapist will also play an instructive role in this regard for spastic qaudruplegia teaching them how to use the equipment.
Icing reduces spasticity

- Efferent and afferent neurotransmission is reduced through prolonged use of ice, which is effective for the reduction of spasticity.
- In order to achieve this, the muscle spindles need to be cooled requiring that ice is applied until there is no longer an excessive reflex response to stretching.

- Orthosis prevent the contracture.

Physiotherapy Treatment in rigidity :
- Applying a warm compress or heating pad to the affected muscle to help relax rigid muscles.
- Gently stretching your stiff muscle to help relax it.
- Avoiding strenuous activity that may trigger the muscle to become rigid again.
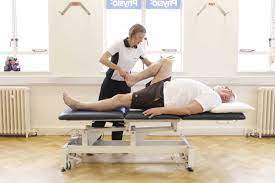
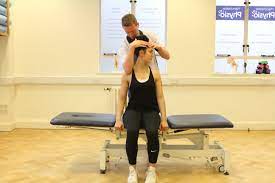

- Gental rocking exercise , rotational exercise in slow & rhythamic pattern.
- Rhythmic initiation technique in which movt progress passive to active assisted and active movt.
- In supine : slow side to side head rotation .
- In hooklying : lower trunk rotation .
- In side lying : upper & lower trunk rotation .

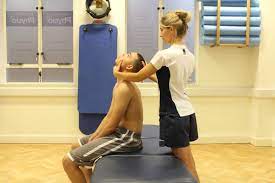
- Relaxation & stretching exercise


Balance Training:
Develop high-level eccentric strength dynamic neuromuscular efficiency & reactive joint stabilization.
Balance training programs aim to:
- Strengthen balance control in everyday activities leading to improved fall-related self-efficacy, reduced fear of falling, and increased walking speed
- Improve physical function
- Improve the quality of life

Gait training:
- The exercises involve improving motion in your lower extremity joints, improving strength and balance, and mimicking the repetitive nature of your legs that occur while walking.
Gait Training Exercises
- Walking on a treadmill.
- Lifting your legs.
- Sitting down.
- Standing up.
- Stepping over objects.



4 Comments