SPASTICITY IN QAUDRIPLEGIA
Table of Contents
What is spastic quadriplegia?
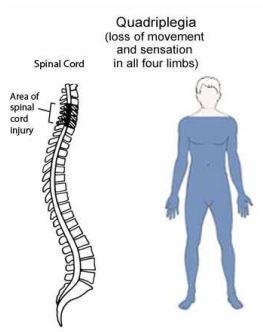
- Spastic quadriplegia usually displays equal involvement of both upper and lower extremities with severe involvement of the legs and arms and floppiness of the neck.
- In this condition, both the corticospinal and corticobulbar tracts are affected.

What are the Causes of spastic quadriplegia?
- Spastic quadriplegia is generally caused by brain damage either before birth, during, or shortly after.
- During 26 to 34 weeks of gestation, the white matter of an infant’s brain is very susceptible to damage.
- Lesions or holes in the white matter of the brain can lead to spastic quadriplegia.
- Some infections that have been linked to the development of spastic quadriplegia include meningitis, herpes, rubella, and encephalitis.
- Severe jaundice, can also lead to brain damage and spastic quadriplegia due to a buildup of bilirubin in the blood.
- Hypoxia, lack of oxygen to the brain, can also cause damage in the cerebral motor cortex and other brain regions.
Which are the Symptoms of spastic quadriplegia?
- Many experience contractures, which are defined as joints that cannot be stretched or moved.
- Clonus is another symptom that is characterized by alternating, rapid muscle contraction and relaxation.
- This presents itself as tremors and scissoring of the limbs.
- Distonia, or lasting muscle contractions and tightness, is also often experienced by those affected by spastic quadriplegia.
- These involuntary muscle contractions may affect the development of structural muscle around the hip and lead to hip dyslegia and dislocation, making it difficult to sit.
- Muscles that rapidly contract and release
- Muscle tightness and spasticity
- Difficulty walking and limbs scissoring
- Speech impediments/language disorder
- Seizures
- Cognitive disabilities
COMPLICATIONS :
- Since spastic quadriplegia can affect the child’s entire body, there is an increased risk of developing limb deformities.
- Spastic muscles continuously pulling on the bones and joints can cause issues over time, especially if not treated properly..
- People with spastic quadriplegia may have great difficulty swallowing, and this can lead to malnutrition or respiratory complications if food is aspirated.
- Poor coordination of facial muscles can also cause speech/language delays.
- They are also more likely to have cognitive and learning disabilities.
Diagnosis :
- Muscle tone is sometimes used to make the diagnosis for spastic quadriplegia as affected adult often appear to be either too stiff or too floppy.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) or a computed tomography scan (CT scan) may be used to locate the cause of the symptoms.
- These disorders must be non-progressive, non-transient, and not due to injury to the spinal cord.
DIFFERENT DIAGNOSIS :
Spastic Hypertonia :
- Spastic hypertonia, better known as spasticity, is one of the most common side effects of a spinal cord injury, with between 65% and 78% of spinal cord injury sufferers experiencing some degree of spasticity.

symptoms :
- Sudden involuntary movements due to contracting of your muscles. Sometimes this results in jerking motions, but when the movement is in your bladder or rectum, it can cause you to lose control of your bowels.
- Hyperactive reflexes.
- This occurs when an action that would normally set off a reflex—such as pulling your hand away from a hot stove—produces a muscle spasm instead. After such a spasm, it can be difficult to relax your muscles.
- Involuntary muscle tightness. This can make it challenging to move or relax your muscles, and can undermine muscle health over time.
Physiotherapy examination:
- The patient includes an investigation of vital signs ( heart rate, respiratory rate, blood pressure, clubbing ) , signs of cardiac decompensation, and function of the cerebral hemispheres, cerebellum, cranial nerves , eyes and sensorimotor system.
- Spasticity mostly measured by Modified Ashworth Scale :
General examination:
- General appearance including posture , motor activity
Vital signs :
- Level of consciousness ,pulse , BP , look for pupil size , conjugate deviations of eyes, Meningeal signs.
- Neurocutaneous markers-
- Neurofibroma over the skin ( may have associated Tuberous sclerosis of brain )
- Sebaceous adenoma
- Sturge Weber Syndrome – facial nerve (port wine stain ) involving one half of face with upper eyelid – associated with atrophy and calcification of ipsilateral cerebral hemisphere.
- Lymphadenopathy
- Cyanosis
- Clubbing
- Shortening of hemiplegic limb – indicates it is dating from early childhood
- Irregular pulse of atrial fibrillation
Higher examination :
- A. Consciousness – Check level of altered sensorium. for this refer Glasgow Coma Scale
- B. Orientation -In time, place, space, person are tested.
- C. Memory-It includes Immediate memory, Recent memory, Remote memory. Check with relatives or friends of the patient if he is correct
- D. Intelligence
- E. Speech- Speech disturbances APHASIA may occur
- F. Emotion – Anxious / depressed / elated / swings of mood.
- G. Judgment
- H. Behaviour
- I. Presence of hallucination/dellusion/illusion
Spastic Quadriplegia Medical Treatment :
Anti-Spasticity Medicines commonly prescribed by Your doctors, following are the list of Medicines are as follows :
- Baclofen
- Tizanidine
- Dantrolene sodium
- Diazepam
- Clonazepam
- Gabapentin
Physiotherapy Treatment in spastic quadriplegia :
- Physiotherapists assess the Patients accordingly aim to provide adult the tools to be as independent as possible via flexibility exercises, stretching, and range-of-motion activities.
Physiotherapy especially when started early in life, is helpful in promoting normal motor development, and preventing deformity and contractures.
- It aims at reducing abnormal patterns of movement and posture and promoting the normal ones so as to enable to gain maximal functional independence.
- Re-inforcement of normal postural reflexes and
- Facilitation of normal movements.
The goal of physiotherapy therapy is to help individuals :
- Develop coordination
- Build strength
- Improve balance
- Maintain flexibility
- Optimize physical functioning levels
- Maximize independence
- Overcoming physical limitations
- Expanding the range of joint motion
- Building and maintaining muscle tone
- Increasing recreational capabilities
- Identifying alternate ways to perform everyday tasks
- Fostering independence
- Decreasing the likelihood of contractures, bone deformity
- Providing sensory stimulation
- Increasing fitness Increasing flexibility
- Improving posture Improving gait
Icing Helps reduce spasticity :
- Efferent and afferent neurotransmission is reduced through prolonged use of ice
- which is effective for the reduction of spasticity. In order to achieve this, the muscle spindles need to be cooled requiring that ice is applied until there is no longer an excessive reflex response to stretching.
Heat decrease spasticity :
- Sometimes heat or ice can be used to temporarily relax a spastic muscle.
- Warm baths or swimming pools can also help to relax a spastic muscle.
Weight bearing Exercise help spasticity :
- Any weight bearing of the upper extremity either at the wall, table, or floor helps sends signals to the brain that reminds it the arm is still there.
- Strengthening can improve spasticity in two ways.
- By strengthening the antagonist (opposing) muscle, it can help inhibit the reaction of the spastic muscle.
The most commonly indicated treatments for spasticity, in descending order, were positioning, prolonged muscle stretching, splinting, motor-level stimulation, other treatment modalities, vibration, transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS), traction, and prolonged icing.
The largest benefit of therapy to the qaudruplegia with spasticity is in the treatment of problematic conditions when they occur, including:
- Muscle atrophy or tightening
- Loss in joint range of motion
- Muscle spasticity Pain in muscles and joints
- Joint inflammation Contractures (muscle rigidity)
- Minimizing pain and discomfort
Exercises often include the use of equipment, such as:
- Weights Exercise machines
- Bands Rollers
- Balance balls
- Heat and cold packs
- Ultrasound technology
- Adaptive equipment including braces, splints, walkers, orthotics, wheelchairs and even computers will be used in therapy; therapists will modify the equipment as needed.
- The therapist will also play an instructive role in this regard for spastic qaudruplegia teaching them how to use the equipment.
- Performing stretching exercises daily.
- Prolonged stretching can make muscles longer, helping to decrease spasticity and prevent contracture.
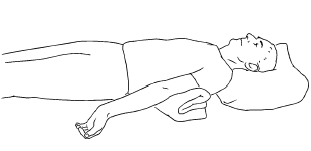
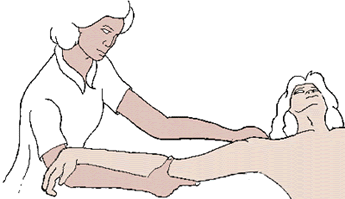

- Splinting, casting, and bracing. These methods are used to maintain range of motion and flexibility.
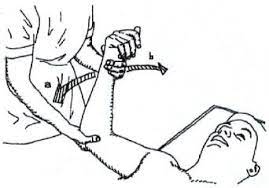
- Agonist & antagonist work together to produce smooth coordinate movement.
- Hamstring will undergoing stretch = Antagonist
- Quadriceps will extend knee with contraction = Agonist
- Physiotherapy is important for supporting people with spastic managing spactic qaudriplegia symptoms related to movement, posture, and balance.
- Physiotherapy can help improve motor skills and prevent movement problems from worsening over time.

- It can also allow spastic with to gain more independence with daily activities.
PREVENT HYPOTENSION:
Tilt Table Exercise:

- REDUCE HYPO-TENSION
CONTRACTURE PREVENTION :
MANIPULATION MOBILIZATION
PREVENT BED SORE
- Quadruped pt. have been bed ridden so air bed prevent pressure sore.




2 Comments