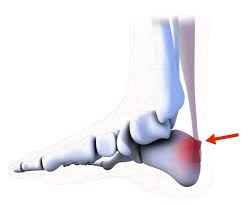
HAG-LUND ‘S SYNDROME
DEFINATION : Haglund’s syndrome is a constellation of soft tissue and bony abnormalities and represents one cause of retro-calcaneal pain consisting of inflammation of the regional soft tissues, e.g., retro-calcaneal bursitis, superficial tendo Achilles bursitis, and thickening and/or inflammation of the Achilles tendon, associate Haglund’s syndrome is a cause of retrocalcaneal pain. The clinical diagnosis of…