Hypothyroidism
- Hypothyroidism is a usual condition where the thyroid does not create and release enough thyroid hormone into your bloodstream. This creates your metabolism slows down.
- Also known as underactive thyroid, hypothyroidism can make you feel tired, gain weight and be unable to tolerate cold temperatures. The important treatment for hypothyroidism is hormone replacement therapy.
Table of Contents
What is Hypothyroidism?
- Hypothyroidism is a condition where there is not enough thyroid hormone in your bloodstream and your metabolism slows down.
- Hypothyroidism happens when your thyroid does not create and relax enough thyroid hormone into your body. This creates your metabolism to slow down, affecting your entire body. Also known as underactive thyroid disease, hypothyroidism is fairly usual.
- When your thyroid levels are extremely low, this is known as myxedema.
A very serious condition, myxedema can cause serious symptoms, involving:
- A low body temperature
- Anemia
- Heart failure
- Confusion
- Coma.
- This serious type of hypothyroidism is life-threatening.
- As usual, hypothyroidism is a very treatable condition. It can be managed with regular medications and follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider (doctor).
How does my thyroid work?
- The thyroid gland is a little, butterfly-shaped organ located in the front of your neck just below the voice box (larynx). Picture the middle of the butterfly’s body riddled on your neck, with the wings hugging around your windpipe (trachea). The important job of the thyroid is to control your metabolism. Metabolism is the process that your body utilizes to transform food into energy your body uses to function. The thyroid makes the hormones T4 and T3 to control your metabolism. These hormones work throughout the body to tell the body’s cells how much energy to utilize. They look for your body temperature & heart rate (HR).
- When your thyroid works correctly, it is constantly making hormones, releasing them, and then making new hormones to replace what is been used. This retains your metabolism functioning and all of your body’s systems in check. The amount of thyroid hormones in the bloodstream is controlled by the pituitary gland, which is located in the center of the skull under the brain. When the pituitary gland senses either a reduce thyroid hormone or much, it adjusts its personal hormone (thyroid stimulating hormone, or TSH) & gives it the thyroid to stable out the amounts.
- If the amount of thyroid hormones is too high (hyperthyroidism) or too less (hypothyroidism), the entire body is impacted.
Who is affected by Hypothyroidism?
- Hypothyroidism can harm people of all ages, genders, and ethnicities. It is a common condition, particularly among women over age 60. Women are generally more likely to develop hypothyroidism later in menopause than earlier in life.
What is the difference between Hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism?
- In hypothyroidism, the thyroid does not create enough thyroid hormones.
- The various between hypothyroidism and hyperthyroidism is quantity. In hypothyroidism, the thyroid makes very small thyroid hormones. On the flip side, someone with hyperthyroidism has a thyroid that creates too much thyroid hormone. Hyperthyroidism includes higher levels of thyroid hormones, which makes your metabolism speed up. If you have hypothyroidism, your metabolism steadies down.
- Many things are the opposition between these 2 conditions. If you have hypothyroidism, you may have a hard time dealing with the cold. If you have hyperthyroidism, you may not control the heat. They are opposite high levels of thyroid function. Ideally, you should be in the middle. Treatments for both of these conditions work to acquire your thyroid function as close to that ground as possible.
What causes Hypothyroidism?
- Hypothyroidism can have a primary cause and a secondary cause. A primary cause is a condition that directly impacts the thyroid and causes it to make low levels of thyroid hormones. A secondary cause is something that causes the pituitary gland fails, which means it can not send thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to the thyroid to balance out the thyroid hormones.
- Primary causes of hypothyroidism are much more usual. The most common of these primary causes is an autoimmune condition known as Hashimoto’s disease. Also known as Hashimoto’s thyroiditis or chronic lymphocytic thyroiditis, this condition is hereditary (passed down through a family). In Hashimoto’s disease, the body’s immune system attacks and harms the thyroid. This prevents the thyroid from creating and releasing enough thyroid hormone.
The other primary causes of hypothyroidism can involve:
- Thyroiditis (inflammation of the thyroid),
- Cure of hyperthyroidism (surgical expulsion of the thyroid),
- Iodine deficiency (not having enough iodine — a mineral your thyroid uses to create hormones – in your body),
- Hereditary conditions (the medical condition passed down through your family),
- In some cases, thyroiditis can occur after a pregnancy (postpartum thyroiditis) or a viral illness.
What causes Hypothyroidism in pregnancy?
- In very cases, women with hypothyroidism during pregnancy have Hashimoto’s disease. This autoimmune disease causes the body’s immune system to attack and harm the thyroid. When that happens, the thyroid can not produce and release high enough levels of thyroid hormones, impacting the entire body. Pregnant people with hypothyroidism may feel very tired, have a difficult time dealing with cold temperatures, and experience muscle cramps.
- Thyroid hormones are the main to fetal development. These hormones assist develop the brain and nervous system. If you have hypothyroidism, it is important to manage your thyroid levels during pregnancy. If the fetus does not obtain enough thyroid hormone during development, the brain does not make correctly & there could be issues later. Untreated or insufficiently treated hypothyroidism during pregnancy may lead to complications such as miscarriage or preterm labor.
Does birth control affect my thyroid?
- When you are working on birth control pills, estrogen & progesterone inner of pills can kill your thyroid-binding proteins. This improves your levels. If you have hypothyroidism, the dose of your medications will need to be increased while you are using birth control pills. Once you stop using birth control pills, the dosage will require to be lowered.
Can Hypothyroidism cause erectile dysfunction?
- In certain cases, there can a connection between untreated hypothyroidism and erectile dysfunction. When your hypothyroidism is caused by an issue with the pituitary gland, you can have decreased testosterone levels. Treating hypothyroidism can often assist with erectile dysfunction if it was directly caused by hormone imbalance.
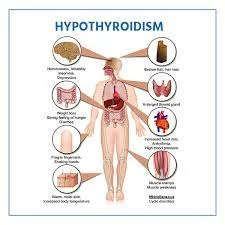
What are the symptoms of Hypothyroidism?
- The symptoms of hypothyroidism commonly develop slowly over time – sometimes years.
They can involve:
- Feeling tired (fatigue)
- Experiencing numbness & tingling in your hands
- Having constipation
- Gaining weight
- Experiencing soreness throughout your body (can involve muscle weakness)
- Having higher than normal blood cholesterol levels
- Feeling depressed
- Being unable to tolerate cold temperatures
- Having dry, coarse skin and hair
- Experiencing a decrease in sexual interest
- Having frequent and heavy menstrual periods
- Seeing physical changes in your face (involving drooping eyelids, as well as puffiness in the eyes and face)
- Having your voice become lower and hoarser
- Feeling more forgetful (“brain fog”).
Will Hypothyroidism make me gain weight?
- If your hypothyroidism is not treated, you could acquire weight. Once you are treating a condition, weight should begin to lower. However, you will still require to watch your calories and exercise to lose weight. Talk to your healthcare provider about weight decrease and ways to develop a diet that works for you.
How is Hypothyroidism diagnosed?
- It can actually be hard to diagnose hypothyroidism because the symptoms can easily be confused with other conditions. If you have any of the symptoms of hypothyroidism, tell to your healthcare provider (doctor). The main way to diagnose hypothyroidism is a blood test known as the thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) test. Your healthcare provider (doctor) may also order blood tests for conditions such as Hashimoto’s disease. If the thyroid is enlarged, your provider (doctor) may be able to sense it during a physical exam during an appointment.
How is Hypothyroidism treated?
- In most cases, hypothyroidism is cured by replacing the amount of hormone that your thyroid is no longer creating. This is commonly done with medication. One medication that is commonly used is known as levothyroxine. Get orally, this medication improves the amount of thyroid hormone your body produces, evening out your levels.
- Hypothyroidism is a manageable disease. However, you will require to continuously take medication to normalize the number of hormones in your body for the rest of your life. With careful management and follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider (doctor) to make your treatment is working properly, you can lead a normal and healthy life.
Physiotherapy Treatment for Hypothyroidism
- Developing an exercise program for a patient with Hypothyroidism can assist in many ways. First, it assists to rebuild activity tolerance, increase muscle strength, and reduce apathy secondary to the decreased metabolism caused by the disorder. Exercise to assist correct such problems should only be implemented once the patient has begun hormone replacement therapy, otherwise, the issues cannot be resolved. Improving the patient’s exercise tolerance can also be extremely helpful for patients who are severely constipated from the disorder. It assists to increase peristaltic activity and overall metabolism. Because many patients with hypothyroidism have co-morbid heart conditions, improving aerobic activity can have effects on the cardiovascular health of patients & reduce risk factors for cardiac events.
Other issues possibly addressed involve:
- Encourage the patient to utilize moisturizer if the skin is dry,
- Educate the patient on conformity with thyroid hormone therapy,
- Encourage the patient to follow up with mental health nurse since depression is usual in hypothyroidism.
What happens if Hypothyroidism is not treated?
- Hypothyroidism can become a severe and life-threatening medical condition if you do not get treatment from the healthcare provider.
If you are not treated, your symptoms can become more serious and can involve:
- Developing mental health problems,
- Having trouble breathing,
- Not being to maintain a normal body temperature,
- Having heart problems,
- Creating a goiter (enlargement of the thyroid gland),
- You can also develop a serious medical condition known as myxedema coma. This can happen when hypothyroidism is not treated.
Will I have a similar dose of medication for Hypothyroidism my entire life?
- The dose of your medication can actually exchange over time. At various points in your life, you may need to have the amount of medication changed so that it manages your symptoms. This could occur because of things such as weight gain or weight loss. Your levels will require to monitored throughout your life to make sure your medication is working correctly.
Can Hypothyroidism be prevented?
- Hypothyroidism cannot be cured. The good way to cure developing a serious form of the condition or having the symptoms impact your life in a serious way is to watch for signs of hypothyroidism. If you experience any of the symptoms of hypothyroidism, the good thing to do is tell your healthcare provider (doctor). Hypothyroidism is very manageable if you catch it quickly and start treatment.
Are there any foods I can eat to assist my Hypothyroidism?
- Most of the foods in western diets include iodine, so you do not have to worry about your diet. Iodine is a mineral that assists your thyroid to produce hormones. One idea is that if you have decreased levels of thyroid hormone, eating foods rich in iodine could help increase your hormone levels. The most reliable way to improve your hormone levels is with a prescription medication from your healthcare provider. Do not try any latest diets without talking to your provider 1st. It is important to always have a conversation before starting the latest diet, especially if you have a medical condition such as hypothyroidism.
Foods that are high in iodine involve:
- Eggs,
- Dairy products,
- Meat, poultry, and seafood,
- Edible seaweed,
- Iodized salt.
- Work with your healthcare provider (work) or a nutritionist (a healthcare provider who specializes in food) to craft a meal plan. Your food is your fuel. Making sure you are eating foods that will assist your body, along with taking your medications as instructed by your healthcare provider (doctor), can keep you healthy over time. People with a thyroid condition should not consume big amounts of iodine because the effect may be paradoxical (self-contradictory).
Can Hypothyroidism go away on its own?
- In certain mild cases, you may not have symptoms of hypothyroidism or the symptoms may fade over time. In other cases, the symptoms of hypothyroidism will go away shortly later you start treatment. For those with particularly decreased levels of thyroid hormones, hypothyroidism is a life-long condition that will need to be managed with medication on a regular schedule.
FAQs
An underactive thyroid is a lifelong condition, so you will usually require to take levothyroxine for the rest of your life.
Hashimoto’s disease, an autoimmune disorder, is the most usual cause of hypothyroidism. With this disease, your immune system harms the thyroid. The thyroid becomes inflamed and can not make enough thyroid hormones.
Radiation therapy to the neck area.
Radioactive iodine treatment.
Use of certain medications.
Thyroid surgery.
Too little iodine in the diet.
Pregnancy.
Problems with the thyroid at birth.
Pituitary gland damage or disorder.
Hypothyroidism is a condition where there is not enough thyroid hormone in your bloodstream and your metabolism slows down. Hypothyroidism happens when your thyroid does not create and relax enough thyroid hormone in your body. This creates your metabolism to slow down, affecting your entire body.
Hypothyroidism can conduct to a higher risk of heart disease and heart failure. That is mainly because people with an underactive thyroid tend to develop high levels of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol — the “bad” cholesterol.
Thyroid and diet factsheet
eat at least 5 portions of a differ of fruit and vegetables every day.
base meals on greater fiber starchy foods like potatoes, rice, or pasta.
have certain dairy or dairy alternatives.
eat certain beans, pulses, fish, eggs, meat, and other protein.
For mild cases of hypothyroidism, not all patients require treatment. Occasionally, the condition may resolve without treatment. Follow-up appointments are the main to monitor hypothyroidism over time, however. If hypothyroidism does not go away on its own within several months, then treatment is necessary.
Thyroid diseases are lifelong, yet treatable conditions. However, if untreated, thyroid disease can cause increased cholesterol levels and subsequent heart disease, infertility, muscle weakness, osteoporosis, and, in extreme cases, coma or death. Treatment to balance your hormone levels is simple & not very much expensive.
Treatment for this condition aims to decrease and normalize thyroid hormone production. Sometimes, treatment can cause the levels of your thyroid hormone to remain decreased permanently. This often happens after treatment with radioactive iodine. If your whole thyroid gland is removed due to thyroid problems, you will develop hypothyroidism.
Hypothyroidism happens when your thyroid does not create and relax enough thyroid hormone in your body. This makes your metabolism slow down, affecting your whole body. Also known as underactive thyroid disease, hypothyroidism is fairly usual. When your thyroid levels are extremely low, this is known as myxedema.

32 Comments