19 Best Exercises For Elbow Strain
Table of Contents
Introduction:
When the muscles or tendons surrounding the elbow joint are overextended or damaged, an elbow strain results. It is not the same as a sprain, which damages ligaments. Typically, elbow strains impact the flexor or extensor muscles that connect to the elbow joint.
Elbow pain can significantly impact day-to-day activities and overall quality of life. Elbow strain exercises improve flexibility, strength, and stability, all of which are important for managing elbow pain. However, choosing the right exercises based on each person’s needs and circumstances is essential for successful rehabilitation and pain management.
If you have elbow strain, Exercises For Elbow Strain are crucial. With exercise and a physiotherapist’s guidance, you can strengthen your arm muscles and regain a normal range of motion if you have elbow strains.
Causes:
Weakness or Unbalanced Muscles
- Weak grip muscles, shoulders, or forearms
- Elbow tendons and muscles excessively compensate
Wear and Tear Associated with Age
- Over time, tendons and muscles naturally degenerate.
- More prevalent in individuals over 40
Trauma or Unexpected Events
- A rapid blow, tumble, or arm twist may cause an acute strain.
- hitting a hand that is outstretched
- Suddenly catching a hefty thing
- Twisting of the arm in a contact sport
- Excessive elbow extension
Ergonomics and Poor Posture
- Long-term bad posture strains the muscles and tendons in the elbows.
- Causes the elbow to experience compensating strain.
- Increases muscle tiredness and decreases circulation.
Athletic Events
- High-risk sports include weightlifting, baseball, golf, and tennis.
- Swinging, throwing, or grabbing repeatedly
Improper Lifting Methods
- Performing improper form when lifting large objects
- Using the elbow rather than the bigger muscles
Repetitive Motions (Injuries from Overuse)
- The most frequent reason for elbow soreness is this.
- When the same muscles and tendons are used repeatedly without enough rest, small tears, inflammation, and pain result.
- Computer users, musicians, and individuals in physical labor are frequently impacted.
Signs and symptoms:
Feeling Sensitive to Touch
- Pressing on the elbow region may cause pain or sensitivity.
- Localized pain at the sites where muscles are inserted.
Pain That Radiates
- From the elbow, pain may radiate to the wrist and forearm.
Weakness of Muscles
- Significant decline in upper arm or forearm strength.
- Having trouble with things like carrying suitcases
- Holding onto things
- Opening doors or jars
Redness or Swelling
- Acute sprains or more severe strains can result in apparent swelling, soreness, and bruising around the joint, even though they are frequently not immediately noticeable.
Limited Range of Motion
- The elbow may become tight or difficult to fully bend (flex) or extend (straighten).
- Pronation and supination, or turning the palm up or down, might also be restricted.
Tightness or spasms in the muscles
- Particularly if the surrounding muscles are stretched during an activity, they may tighten or cramp.
- The wounded area may be protected by muscle guarding.
Advantages of elbow exercises:
Stop Re-Injury
- Strengthening and controlling the muscles surrounding the elbow aids in joint stability.
- Prepares the elbow to withstand sports or regular tasks without putting excessive stress on delicate tissues.
Lessen Pain Gradually
- Your body’s natural painkillers, endorphins, are released when you move.
- By correcting biomechanics, strengthening weak or unbalanced muscles can lessen chronic strain and pain.
Encourage Recovery and Healing
- Blood flow to the damaged area is increased by gentle movement.
- Improves the flow of nutrients and oxygen to help in tissue repair.
- Avoids the formation of scar tissue, which may restrict movement.
Prevents Stiffness
- Joints may become stiff after an injury.
- Stretching and range-of-motion exercises help in preserving or regaining the elbow and wrist’s capacity to fully bend, straighten, and rotate.
Enhanced Gripping
- Weak grip is a common sign of elbow strain.
- Certain exercises help in regaining the wrist and hand strength required for daily tasks, including gripping, lifting, and carrying goods.
Capacity to Handle Stress
- The main cause of the pain is eventually lessened by strengthening the muscles and tendons, which makes them stronger in resistance to the repetitive tension that initially produced the strain.
Restore Your Range of Motion
- Exercises help in restoring flexibility and reducing stiffness.
- Become stronger at fully rotating, bending, and extending your elbow.
Enhance Tendon and Muscle Strength
- The muscles that support the elbow joint, the forearm, biceps, triceps, and wrist, are the focus of strengthening workouts.
- Improves muscular coordination, which lessens the strain on the damaged area.
Improvement of Joint Awareness and Proprioception
- By enhancing neuromuscular coordination, certain workouts enable your brain to better understand joint movement and position.
- Lessens the possibility of incorrect or dangerous motions that could make the injury worse.
Before starting an exercise program, take these precautions:
Before starting any exercise program, it’s important to consider a few safety measures to guarantee your well-being and the advantages. Consult your physician or physiotherapist to determine which exercises are most suitable for your specific problem.
You should listen to your body and avoid pushing yourself above your limits. Exercise often causes mild pain, but if the pain gets worse, it can be an indication that you’re pushing yourself too hard. Start with low-impact exercises to gradually progress to more challenging ones once you can tolerate greater pain.
To prevent more injuries, it’s critical to maintain proper form and technique. Get guidance from a qualified professional if you’re unsure about how to perform an exercise routine. Warm up before beginning any activity to better prepare your joints and muscles for the workout.
Exercises For Elbow Strain:
Stretches and range-of-motion exercises can help your elbow joint become more flexible, less stiff, and have a wider range of motion.
The following is a list of the best exercises for elbow pain.
Wrist flexion
- This is an activity that must be done while sitting.
- Hold a lightweight dumbbell in your hand, a tiny dumbbell.
- Make a right-angle bend in the elbow.
- With the palm pointing upward, move the hand outward.
- Raise your wrist toward your body.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- After that, release gradually.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
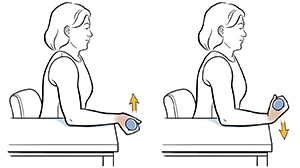
Wrist extension
- You must sit in a chair for this exercise.
- Your elbow should be resting on the table while you hold a two-pound dumbbell upright.
- You can straighten your wrist by bending it away from your body and pointing it downward.
- If you find this exercise too difficult, don’t use any weight.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
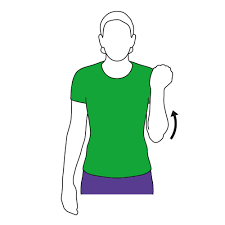
Elbow band
- Take a straight stance.
- To one side, lower the arm.
- Bend the arm slowly upward until the hand is as comfortable as possible near the shoulder.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Let go of your hand.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
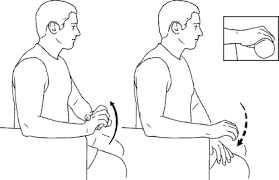
Wrist Turn
- Make a right-angle bend in the elbow.
- Place the palm outward.
- Slowly rotate the wrist such that the thumb is facing the ceiling.
- Continue slowly rotating the wrist until the palm is down.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Return to the initial position slowly.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
Supination & Pronation of the Forearm
- Maintain a 90-degree angle with your arm when seated in a chair.
- You can rest your hand on your thigh by placing your forearm on it.
- Get a light dumbbell.
- With it held vertically, use it like a hammer.
- Slowly twist your hand inward with the palm facing down.
- Allow the dumbbell’s weight to assist with the movement.
- With your palm towards the ceiling, slowly rotate your hand outward.
- Make sure the motion is controlled and smooth.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
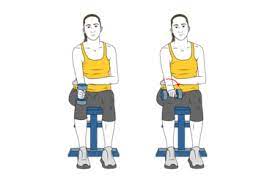
Biceps Curl
- Choose a comfortable standing position to begin.
- Now grasp something light, such as dumbbells.
- Next, maintain a straight upper arm position.
- The weight at your elbow should then be raised.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Return your arm to the ground slowly.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

The band pulls apart
- Place your arms at chest height in front of you and stand erect.
- Take a band in each hand, leaving a little space in it.
- Make sure your palms are facing down.
- As you extend your arms to your sides, maintain a straight posture.
- Avoid allowing your shoulders to rise towards your ears and maintain your arms at chest height.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

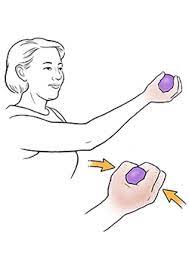
Ball squeeze
- Get started by standing on the floor.
- Make a fist with your fingers while holding a tennis ball in your hand.
- Hold it firmly in your hand for a few minutes.
- Then, when you squeeze the ball next, gently.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
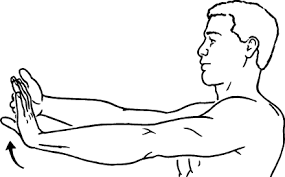
Wrist flexor stretch
- Take a straight stance.
- Then lift your arm directly in front of you.
- Then, palm up.
- Using your other hand, gently push your fingertips back to the ground.
- Maintaining a straight elbow, extend your forearm.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
Wrist extensor stretch
- Start by settling into the chair’s seated position.
- Then put out your arm.
- Next, palm down.
- Apply mild pressure to the fingers and back of your hand with your other hand.
- You should tense the upper half of your forearm.
- Keep your elbow straight.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

Isometric Wrist Flexion
- Your elbows should be at your sides, relaxed.
- Make a fist out of your affected hand and take the stance.
- No movement can be made while you press down into your palm or a level surface with your affected wrist!
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

Isometric wrist extension
- Your elbows should be relaxed and at your sides.
- Place your unaffected hand over the wrist that is affected.
- Apply pressure to it.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

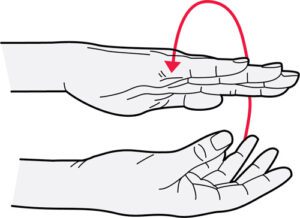
Wrist circle
- First, locate a comfortable place to stand or sit on the floor.
- Make fists with your hands, holding them shoulder-high.
- As you keep your elbow position the same, rotate your wrists to the left, flexing them upward.
- After that, move them to the right.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

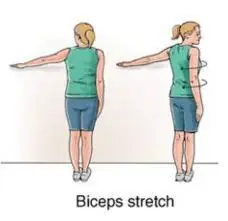
Biceps stretch
- Get started by standing on the floor.
- Press the palm of your left hand against a wall.
- Turn your body slowly away from the wall.
- Your arm, shoulder, and chest should all feel stretched.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
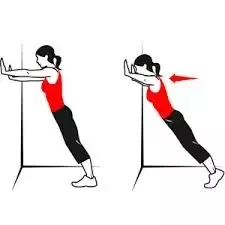
Wall Push-Ups
- Your feet should be a few feet away from a wall.
- Put your hands on the wall at chest height, lean forward, and keep your arms and legs straight.
- Your arms ought to be able to bear some of your weight.
- As you progressively bend your elbows, lower your chest towards the wall.
- When the body and head are almost touching the wall, stop.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.
Towel twist
- Start on the floor in a standing position.
- Hold a loosely rolled towel by its length with one hand at both ends.
- Keep your posture relaxed.
- Similar to how you would remove water, you can twist the towel in various ways with your hands.
- Continue in this direction for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

Reverse biceps Curls
- Your feet should be shoulder-width apart when you stand upright.
- Use an overhand grip with both hands to hold the weights.
- Your arms should be hanging out at your sides.
- Hold your elbows near your chest.
- Maintain a straight back and use your core.
- Curl at the elbows to curl the weights upward.
- Concentrate on lifting with your upper arms and forearms.
- Throughout the exercise, keep your palms down.
- Increase the weight until your forearms are at shoulder level or almost horizontal.
- Avoid swinging or using force; instead, move carefully and slowly.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

Resistance band Lateral arm raises
- Your feet should be hip-width apart as you stand upright.
- To anchor it, place the resistance band’s middle beneath your feet.
- Keep both hands by your sides.
- Grasp one end of the band in both your hands.
- Turn your palms inward.
- Maintain a small bend in your elbows.
- Keep your back straight and use your core.
- Breathe out while slowly raising your arms to the sides, keeping them almost straight.
- Your arms should be parallel to the floor when you raise them.
- Keep your wrists in a neutral position.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Take a breath and carefully return your arms to their initial position.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

Resistance Band Triceps extensions
- You should stand with your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Hold the resistance band with one end in each hand.
- One foot should be placed on the center of the band to secure it to the ground.
- Raise your hands over your head with your elbows near your ears, then bend them so that they are behind your head.
- With the palms facing the ceiling.
- Maintain a taut core and a straight back.
- Elbows shouldn’t be overly extended; they should point forward or slightly out.
- As you slowly raise your arms and straighten your elbows, release your breath.
- The upper arms should remain motionless; just move at the elbow joint.
- Do not forcefully lock out your elbows, but rather fully extend your arms at the top.
- Hold this position for a few seconds.
- Breathe in as you controllably return your hands to the initial position behind your head.
- Then return to your neutral position.
- Then relax.
- Repeat this exercise 5-10 times.

What precautions should be considered when working out?
First, a medical clearance is needed.
- See a doctor before starting a new exercise regimen.
- Look for any restrictions.
Get warm and cool.
- Warming up gently increases circulation and stimulates the muscles and nerves.
- Cooling reduces inflammation and prevents stiffness.
Avoid making painful motions.
- If you experience severe or persistent pain when exercising, you should stop right away.
- An intense, pinching, or pulling sensation indicates overuse or poor technique.
Prevent the Affected Limb from Tiring
- Poor form, unstable joints, and nerve strain are all made more likely by muscle weakness.
- Limit the number of repetitions and take a break in between sets.
- Consider practicing interval training while taking frequent rests.
Make a Small Step Forward
- Do range-of-motion (ROM) exercises first, then weight-bearing and strengthening exercises.
- When flexing or extending your wrists, in particular, avoid moving too fast, rapidly, or jerkily.
Gradually Overcome Opposition
- To begin adding resistance, start with a light weight or band.
- Make progress only once you can perform the exercise with perfect form, total control, and no pain.
- Repetitions should be increased before resistance is increased.
Pay attention to your posture and position.
- Unbalance during exercise might strain the corrective muscles and nerves.
- Pay close attention to scapular stability, neutral spine, and shoulder position.
- Use mirrors or the advice of a professional to fix your posture.
Take Regular Breaths
- Holding your breath puts undue strain on your body.
- Breathe evenly and calmly throughout the exercise to help with muscle relaxation.
When did you stop working out?
You must stop exercising or modify your regimen to prevent worsening the injury or postponing its recovery.
Joint or Sharp Pain
- If you get shoulder, elbow, or neck pain, stop immediately.
- Be mindful of your body; muscle weakness is not the same as pain.
Following a Task, Swelling
- Little swelling is normal in the beginning, but if it gets significantly worse after exercising, comes back after it has gone away, or is followed by warmth or redness, your body may be reacting to overuse or reinjury.
- Resuming should only happen under supervision and when the oedema has decreased.
Shortness of breath or dizziness
- Keep a watch out for lightheadedness, especially when working out your upper body.
- It may be a result of excessive exercise or bad breathing technique.
Decrease in Strength or Grip
- If the injured arm begins to feel weak, unstable, or uncoordinated, stop right away.
- Nerve dysfunction may worsen if this is ignored.
Atrophy of Muscles or Ineffectiveness
- Doing repetition correctly is impossible.
- Muscles feel weakened or tired.
Numbness, tingling, or burning
- These are signs of nerve compression or overstimulation.
- Stop immediately and rest.
- If it persists, consult with your doctor.
Persistent Pain After Exercise
- If the pain lasts longer than 48 to 72 hours after your workout, and there are no signs that it is improving, think about taking a break and seeing a doctor or a physiotherapist.
Which workouts should you avoid doing if you have an elbow strain?
Exercises involving grasping, pulling, pushing, or repeated arm action should be avoided if you have an elbow strain since they put excessive stress on the muscles, tendons, and ligaments surrounding the elbow joint.
Depending on how severe the strain is, you should limit or refrain from the following activities and movements while you recover:
Heavy Bicep Curls
- Particularly when using heavy dumbbells or barbells
- Requires a lot of elbow flexion and strains the biceps tendon.
- Avoid curls with a supinated grip (palms up) as they put more strain on the damaged area.
Gripping-Heavy Workouts
- Deadlifts
- Farmer’s carries
- Kettlebell swings
- Battle ropes
- These can tear elbow tendons and stress the forearm muscles.
Bench Press or Push-Ups
- The elbow joint is compressed and strained during full-body weight push-ups or bench presses.
- Includes narrow-grip, incline, and chest presses.
Chin-ups and pull-ups
- Pulling exercises with high loads that put a lot of strain on the flexors in the forearm and elbow
- Because they activate the biceps, chin-ups are particularly difficult.
Rows (Barbell, Cable, or Dumbbell)
- Any type of rowing, such as sitting cable rows or bent-over rows, engages the forearm and elbow flexor muscles.
- Because of the repeated pulling motion, it could worsen the strain or prolong the healing.
Sports-Related Movements
- Boxing, throwing, and racket sports
- Activities that require strong extension/flexion and repetitive elbow motion
- Should be stopped until the pain goes away and your strength returns.
When to Consult a Physician:
- Pain lasts longer than two to three weeks.
- You feel a major weakness, tingling, or numbness.
- The elbow seems unstable or damaged.
- It is impossible to move the joint.
Summary:
A frequent injury that can be caused by overuse, unexpected trauma, or repetitive actions involving the arm and wrist is elbow strain. Whether you work as a laborer, an athlete, or spend a lot of time typing at a desk, elbow strain might interfere with your day-to-day activities. With the right care and rehabilitation, you can totally heal and regain your strength and flexibility, especially with targeted exercises.
If you experience elbow joint pain, it may be quite difficult to perform simple tasks like lifting, gripping, or even extending your arm. The elbow joint’s intricate anatomy is made up of cartilage, ligaments, tendons, and muscles.
Keeping an active lifestyle is essential; make an effort to engage in the right kinds of exercise every day. Start carefully and work your way up to more activity. It may be challenging to cope with elbow joint pain, but with the right exercises and methods, you can lessen pain and improve mobility.
Elbow strains require patience, care, and consistency to heal. You can strengthen the muscles that support your elbow, improve range of motion, and lessen pain by introducing the proper exercises gradually. Be mindful of your body’s needs, avoid hurrying your recovery, and take medical advice when necessary. To maintain elbow health over the long term, regular exercise and preventive steps are essential.
FAQ:
How much time does it take to heal from a strained elbow?
With rest and simple workouts, mild strains can heal in 1-2 weeks.
It could take four to eight weeks or more to treat moderate to severe strains, particularly if physiotherapy is needed. The reason, intensity, and level of treatment compliance all affect recovery time.
Following a strain, should I move or rest my elbow?
For 48–72 hours, start by resting to lower inflammation.
Then, if there isn’t any severe pain, begin mild mobility exercises.
Stiffness and delayed healing might result from prolonged immobility.
I have an elbow strain; can I still exercise?
Sure, but only once the severe pain has passed.
Before moving on to strengthening activities, begin with mild range-of-motion and stretching exercises.
Stay away from activities that worsen symptoms or cause pain.
Which factors are most frequently responsible for elbow strains?
Motions that are repeated, like typing or lifting
Baseball, golf, tennis, and other sports
Poor posture or ergonomics,
unexpected trauma, or overwork
Can strained elbows result in long-term harm?
If correctly and promptly handled, it is not typically.
Ignoring symptoms or resuming intense activity too soon might result in long-term weakness, muscular imbalances, or chronic tendinopathy.
Is it possible to stop elbow strain from happening again?
Yes, by regularly engaging in flexibility and strength training. Developing technique in physical labor or sports. Taking regular breaks when performing repetitive chores. Using supports or ergonomic tools.
Will exercising worsen my elbow strain?
Indeed, activities can worsen symptoms if they are initiated too soon or performed improperly.
Avoid exercises that result in popping, swelling, or severe pain.
Always begin with smooth movements and minimal resistance.
How frequently ought I to perform these exercises?
Usually, two or three times a day to increase mobility and stretch.
Depending on tolerance and the level of recovery, strengthening exercises can be performed three to four times each week.
Rest days are always necessary for muscular recovery, particularly when strengthening.
If I have an elbow strain, can I still lift weights?
Not in the acute stage.
You can begin using very light weights and concentrate on controlled motions after the initial healing period.
Increase weight gradually only if it is pain-free and under a doctor’s supervision.
References:
- April 25, 2025, DMediaWeb. Improve your injured elbow with these seven physical therapy exercises. Fort Worth Hand Center. Exercises for Physical Therapy for Injured Elbows: https://fortworthhandcenter.com/orthopedic
- Elbow-related exercises. (undated). Exercises for Healthy Joints/Elbow Exercises. Versus Arthritis. https://versusarthritis.org/about-arthritis/exercising-with-arthritis/
- Cadman, B. (January 29, 2025). There are eight tennis elbow exercises. The article 322746 can be found at https://www.medicalnewstoday.com.
- Freutel, N. (2025, February 13). Five tennis elbow rehabilitation exercises. Healthline. Tennis elbow rehabilitation https://www.healthline.com/health/fitness-exercise
- By S. Physio (n.d.-c). The Top 5 Elbow Pain Exercises by Surrey Physio. The Surrey Physio. https://www.surreyphysio.co.uk/top-5/top-5-exercises-for-elbow-pain/
- Y. SportsMed (2022, Oct. 24). Toronto physiotherapists | Yorkville Sports Medicine Clinic | The Top 7 Tennis Elbow Pain Relief Exercises. Toronto physiotherapists | Yorkville Sports Medicine Clinic. https://www.yorkvillesportsmed.com/blog/the-7-best-sports-medicine-related elbow exercises
- Image 11, Physiotherapist Shrey Vazir. October 11, 2024. The 3 Essential Exercises for People Over 60 with Sciatica [Video]. YouTube. -MRj3ukHUaM https://www.youtube.com/watch?v
- Image 12, Pxc_Dev. (2020). tennis elbow rehabilitation exercises. Sports Medicine Information. Tennis elbow rehabilitation exercises: https://sportsmedinfo.sg/treatment/
- Image 17, June 19, 2022: DMoose.Reversee curls, reverse arm curls, and reverse bicep curls. AfmBOoo9ZDH6yFwOOer71UPg4bGP2QphXyg9aPn_xiwYGVFRl248GQNI https://www.dmoose.com/blogs/biceps/reverse-bicep-curls-reverse-arm-curl-reverse-curl?srsltid=Afm
- Image 18, Lift Manual. April 24, 2023. Band Lateral Raise: Overview, Advantages, and Structure. Band-lateral-raise: https://liftmanual.com/
- Image 19, On February 21, 2025, Cpt. C. F., and Cpt. C. F., How to perform tricep extensions with a resistance band. Chris Freytag suggests getting healthy. The resistance band tricep extension: https://gethealthyu.com/





