Myalgic Encephalomyelitis (MF) / Chronic Fatigue Syndrome (CFS)
Table of Contents
Introduction
- Chronic fatigue syndrome, known as myalgic encephalomyelitis or ME/CFS, is a complicated disorder.
- It causes over-fatigue that lasts for at least 6 months. Symptoms worsen with physical or mental activity but do not fully improve with rest.
- The exact cause of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is unknown, However, there are so many views. Experts believe it might be triggered by a combination of many factors.
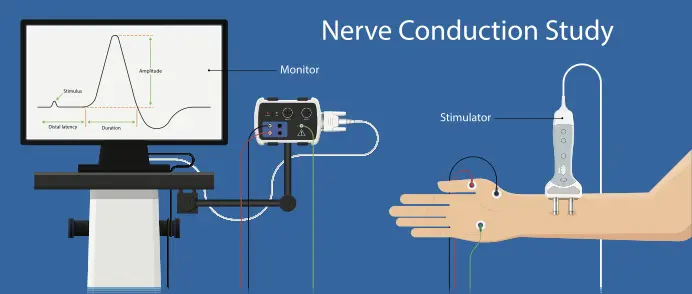
- There is no single test to verify a diagnosis of chronic fatigue syndrome. You may require different medical tests to rule out other health problems that have similar symptoms. Treatment for the condition attention on easing symptoms.
What are the symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome?
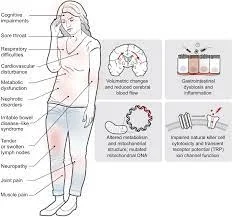
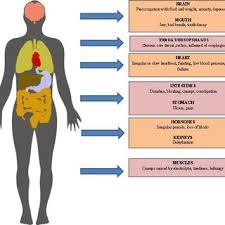
- Symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) can vary from person to person, and the severity of symptoms can change from day to day.
In addition to fatigue, symptoms may involve:
- Extreme exhaustion later physical or mental exercise,
- Difficulties with memory or thinking skills,
- Dizziness that bad with moving from lying down or sitting to standing,
- Muscle or joint pain,
- Unrefreshing sleep.
- Certain people with chronic fatigue syndrome have headaches, sore throats, or tender lymph nodes in the neck or armpits. People with the condition may become extra sensitive to light, sound, smells, food, and medicines.
When to see a doctor
- Fatigue can be a symptom of so many illnesses. In general, look to your doctor if you have persistent or excessive fatigue.
What are the causes of chronic fatigue syndrome?
- The cause of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is yet unknown.
A combination of factors may be involved, such as:
- Genetics: Chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) appears to run in some families, so certain people may be born with a higher likelihood of developing the disorder.
- Infections: Some people develop chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) symptoms after getting better from a viral or bacterial infection.
- Physical or emotional trauma: Certain people report that they experienced an injury, surgery, or significant emotional stress shortly before their symptoms began.
- Problems with energy usage: Certain people with chronic fatigue syndrome have problems converting the body’s fuel, primarily fats, and sugars, into energy.
What are the risk factors of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS)?
Factors that may improve your risk of chronic fatigue syndrome involve:
- Age: Chronic fatigue syndrome can happen at any age, but it most commonly affects young to middle-aged adults.
- Sex: Women are diagnosed with chronic fatigue syndrome much more often than men, yet it may be that women are simply more likely to report their symptoms to a doctor.
- Other medical problems: People who have a history of other complex medical problems, like fibromyalgia or postural orthostatic tachycardia syndrome, may be more likely to develop chronic fatigue syndrome.
What are the complications of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS)?
- Symptoms of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) can come and go and often are triggered by physical activity or emotional stress. This can create it difficult for people to maintain a regular work well worked or to even take care of themselves at home.
- Many people may be too weak to get out of bed at various points during their illness. Some may require to use of a wheelchair.
What is the diagnosis of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS)?
- There is no isolated test to confirm a diagnosis of chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS).
Symptoms can mimic those of so many other health problems, involving:
- Sleep disorders: Fatigue can be begun by sleep disorders. A sleep study can determine if your rest is being disturbed by disorders like obstructive sleep apnea, restless legs syndrome, or insomnia.
- Other medical problems: Fatigue is a usual symptom of several medical conditions, such as anemia, diabetes, and an underactive thyroid. Lab tests can detect your blood for evidence of some of the top suspects.
- Mental health issues: Fatigue is a symptom of a different of mental health problems, such as depression and anxiety. A counselor can assist determine if one of these problems is causing your fatigue.
- It is also common for people who have chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) to also have other health problems at a similar time, such as sleep disorders, irritable bowel syndrome, or fibromyalgia.
- In fact, there are so many overlapping symptoms between chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia that certain researchers consider the two disorders to be different aspects of the same disease.
Diagnostic criteria
Guidelines proposed by the United States (US) Institute of Medicine define the fatigue associated with chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) as being:
- So serious that it interferes with the ability to engage in pre-illness activities,
- Of latest or definite onset,
- Not considerably alleviated by rest,
- Bad by physical, mental, or emotional exertion.
To meet the Institute of Medicine’s diagnostic criteria for chronic fatigue syndrome, a person would also require to experience at least one of these 2 symptoms:
- Problems with memory, focus, and concentration.
- Dizziness that bad with moving from lying down or sitting to standing.
- These symptoms must last for at least 6 months and occur at least half the time at moderate, substantial, or severe intensity.
What is the treatment of chronic fatigue syndrome (CSF)?
- There is no cure for chronic fatigue syndrome. Treatment concentrates on symptom relief. The most disruptive and disabling symptoms should be addressed 1st.
Medications
- Some problems associated with chronic fatigue syndrome (CSF) can be improved with certain medicines.
Examples involve:
- Pain: If medicines such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and naproxen sodium (Aleve) do not help enough, prescription drugs sometimes used to treat fibromyalgia might be options for you. These involve pregabalin (Lyrica), duloxetine (Cymbalta), amitriptyline, or gabapentin (Neurontin).
- Orthostatic intolerance: Certain people with chronic fatigue syndrome (CSF), particularly adolescents, feel faint or nauseated when they stand or sit upright. Medications to regulate blood pressure or heart rhythms may be assisted.
- Depression: Many people with long-term health problems, like chronic fatigue syndrome, are also depressed. Treating your depression can create it easier for you to cope with the problems associated with having a chronic disease. Low doses of certain antidepressants also can help improve sleep and relieve pain.
Pacing for post-exertional malaise
- People with chronic fatigue syndrome (CSF) have worsening of their symptoms after physical, mental, or emotional effort. This is known as post-exertional malaise. It commonly begins within 12 to 24 hours after the activity, and it can last for days or weeks.
- People who have post-exertional malaise sometimes struggle to find a good balance between activity and rest. The goal is to last active without overdoing it. This is also known as pacing.
- The goal of pacing is to decrease post-exertional malaise, rather than getting back to the similar activity level you had when you were healthy. As you improve, you may be able to safely capture more activity without triggering post-exertional malaise.
- It may assist to keep a daily diary of your activities and symptoms, so you can track how much activity is too much for you.
Addressing sleep problems
- Lack of sleep can create other symptoms more difficult to deal with. Your healthcare team might suggest keeping away caffeine or changing your bedtime routine.
- Sleep apnea can be managed by using a machine that delivers air pressure through a mask while you sleep.
FAQs
Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is a severe, long-term illness that affects many body systems. People with Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) are often not able to do their usual activities. At times, Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) may confine them to bed. People with Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) have severe fatigue and sleep problems.
There is no preventative or approved treatment for myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS). However, certain symptoms can be treated or managed. Treating these symptoms might provide relief for some patients with Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) but not others.
There is no test for myalgic encephalomyelitis or chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), yet there are clear guidelines to help doctors diagnose the condition. A GP should query you about your medical history and give you a physical examination.
Myalgic encephalomyelitis (ME) or chronic fatigue syndrome (CFS) is a long-term (chronic) neurological condition that harms the nervous and immune systems. People with Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) experience severe pain and fatigue associated with post-exertional malaise (PEM).
Myalgic Encephalomyelitis or Chronic fatigue syndrome (ME or CFS) can run in families. It is possible that certain people inherit a risk for it from one of their parents, such as inheriting a defect in how a particular gene is built.
Chronic fatigue syndrome is characterized by profound tiredness. Symptoms sometimes worsen with physical or mental activity. In addition to severe fatigue, symptoms involve light sensitivity, headache, muscle and joint pain, difficulty concentrating mood swings, and depression.
For some people with Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS), however, symptoms can get worse over time. It appears that while the majority of people with Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) partially recover, only a few fully recover, while others experience a cycle of recovery and relapse.
Initially relaxed passive movement and gradual progress to active exercise then gradually progress to strength training. Floor-based strength exercises can counteract the de-conditioning of muscles that happens when individuals go through prolonged periods without exercise.
It is possible that Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) is caused by a change in the person’s immune system and the way it responds to infection or stress. Myalgic encephalomyelitis/chronic fatigue syndrome (ME/CFS) shares some features of autoimmune illnesses (diseases in which the immune system attacks healthy tissues in own body, such as rheumatoid arthritis).

One Comment