Calf pain: Cause, Symptoms, Diagnosis, Treatment, Exercise
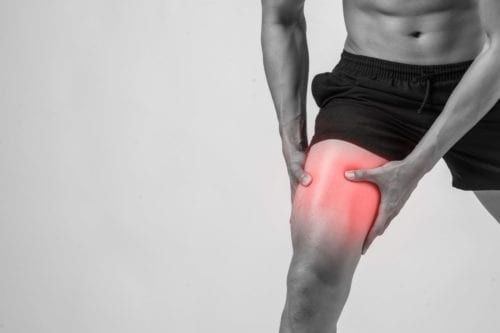
Calf Pain at the back part of the lower leg is occurs mostly due to overuse muscle pain or cramp or muscle strain. Although, in few cases calf muscle pain may be a symptom of serious conditions.
Table of Contents
What is the calf muscle?
- The calf muscle is comprised of two muscles — the gastrocnemius & the soleus.
- These two muscles are met at the tendon of the Achilles tendon, which is attached directly to the heel.
- For Any leg/foot motion uses in these muscles.
- The gastrocnemius muscle is just under the skin at the back of the lower leg.
- Because the gastrocnemius muscle is close to the skin’s surface, which is often seen for its outline.
- This muscle forms the bulk of the calf muscle.
- The soleus muscle is a wide or flat muscle that sits slightly deeper than the gastrocnemius muscle.
- This muscle starts at just below the knee joints so that it is running down to the lower leg & connects to the Achilles tendon above the heel.
- Soleus muscle injuries are less common because this muscle only crosses to the ankle joint.
What is calf pain?
- Pain in the calf muscle means the pain in the back part of the lower leg is usually do caused by the cramp/muscle strain. so that, sometimes this calf pain symptom of becomes the something of more serious.
- This Calf pain varies from the person to person, but it typically feels like dull, aching & sharp pain, so sometimes this pain is become tight & mostly in the back of the lower leg.
What causes the calf pain?
Cramp:
- Calf muscle pain is usually caused by cramps when the muscles are suddenly contracting.
- This cramp is might happen when any person is doing the new exercises.
- If the person is dehydrated & if the patient is deficient in some minerals.
- These calf muscle Cramps are normally gone away quite quickly by themselves.
- Cramps are also be triggered by dehydration, mineral deficiencies or muscle injuries.
- More serious cases of muscle cramps are:
- Alcoholism
- Diabetes
- Kidney failure
- Severe peripheral vascular disease
- Hypothyroidism
- In the more severe cases, the limited blood flow to parts of the body & other serious medical conditions is caused by muscle cramps.
Calf strain:
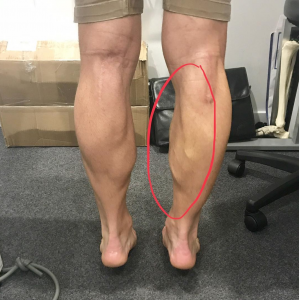
- The calf muscle is made up of 2 muscles which are called the gastrocnemius & the soleus.
- This calf muscle is met at the Achilles tendon which tendon is attached to the heel bone.
- Tearing/Overstretching either of these 2 calf muscles is known as a calf muscle strain.
- Normally person feels a sudden pain in the calf muscle, & it is may feel a pop, snap/tear.
- in the calf muscle strain patient is experiencing the following symptoms:
- Patient feel Sudden pain at the back of the leg.
- Patient feel the calf muscle is stiff & weak when the patient is walking.
- The patient is found too hard to rise onto the toes.
- Do the bruising onto the calf muscle after 1 or 2 days.
- The patient also feels the limited range of movement = ROM.
Achilles tendinitis:
- Achilles tendinitis is caused by overuse, stress or strain on the Achilles tendon.
- Common symptoms of Achilles tendinitis include inflammation of the tendon of the calf, pain in the back of the leg, swelling, & limited range of motion – ROM when flexing the foot.
- In Achilles tendinitis Simple home treatments such as to R.I.C.E. principle = rest, ice, compress, elevate is helpful.
- If the home treatment doesn’t work & pain becomes worse, in this situation important to see a doctor.
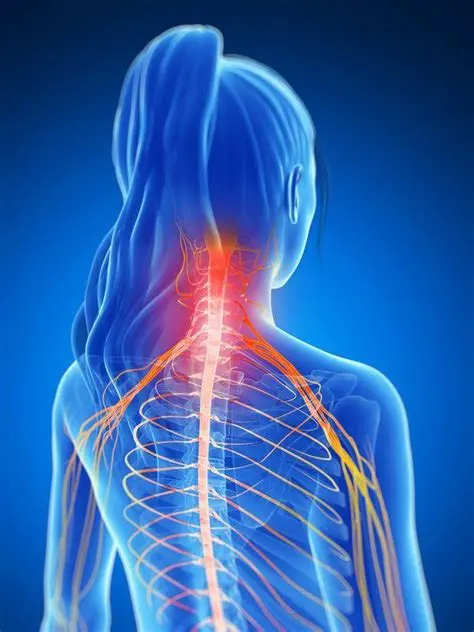
Sciatica pain:
- Sciatica is a result of the issues in the sciatic nerve, which controls the muscles in the lower leg & back of the knee joint.
- In this sciatic patient feel pain, numbness, & tingling in the lower back leg which is stretched down the leg onto the calf &other muscles.
- In more severe cases, surgery is necessary to treat sciatica.
Contusion:
- A contusion bruise, is the result of the trauma, like as to fall, cut & blow.
- The trauma causes the capillaries beneath the skin to burst, which is causes discoloration.
- Bruises are typically healed on their own.
Diabetic peripheral neuropathy = DPN:
- Diabetic peripheral neuropathy = DPN is a form of nerve damage which is given to that affects the feet, legs, arms & hands.
- This Diabetic peripheral neuropathy condition is a common complication of diabetes which is resulting from overexposure to high blood sugar, genetic factors & nerve inflammation.
- Other symptoms of DPN = Diabetic peripheral neuropathy include to :
- Muscle cramps
- Numbness
- Loss of balance and coordination
- Muscle weakness
- Sharp pain
- The impaired sensation which is then reduced to the ability to feel pain/temperature changes
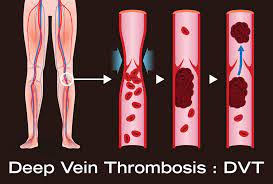
Deep vein thrombosis = DVT:
- Deep vein thrombosis =DVT is the result of a blood clot that is forming in the deep vein in the arm /leg, including the calf muscle. There are numerous factors & conditions which is cause DVT.
- Some conditions include sitting for long periods, medication complications & smoking.
- Symptoms of DVT = Deep vein thrombosis include:
- Swelling
- Skin discolouration
- The feeling of warmth in the calf
- Visible veins in the affected area
- Leg tenderness
- In this situation, contact the doctor immediately if they develop symptoms of DVT Deep vein thrombosis.
Compartment syndrome:
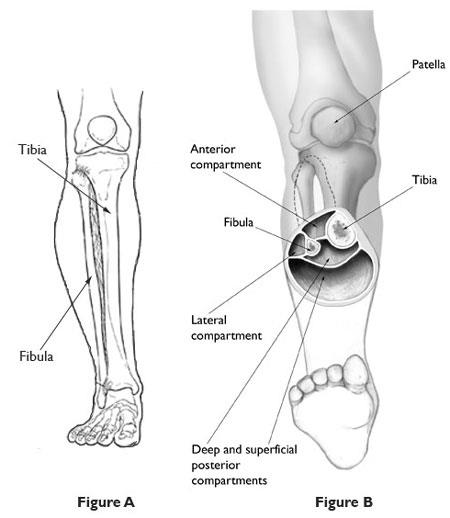
- Compartment syndrome is a serious condition that happens to a large amount of pressure builds up inside the muscle compartment.
- Typically, this occurs after the experienced major injury to the area, like the fracture /broken bone.
- Symptoms of compartment syndrome :
- Severe pain which is not improving after rest/medication
- A noticeable bulge in the affected muscle
- Trouble moving the affected area
- Numbness
Arterial claudication:
- A person is experiencing calf pain due to the narrowing/blockages in the arteries which are supplied in the blood flow into the legs. it is known as arterial claudication.
- Arterial claudication is caused to pain while walking, so movement is required for blood to flow into the lower legs.
- If the blood is present in the difficulty for moving due to the narrowing – claudication for to a person which is an experience to calf pain.
- A person with arterial claudication is experiencing no discomfort at rest, but the patient is present the pain after too few minutes of walking.
Neurogenic claudication:
- Neurogenic claudication occurs when the nerves are going to the legs are pinched so that affecting the ability to communicate with the lower legs.
- Neurogenic claudication condition is due to spinal stenosis.
- This Neurogenic claudication condition occurs when the bones in the spinal column are narrow so that placing extra pressure on the nerves.
- Sciatica pain is one example of neurogenic claudication.
- In the symptoms of neurogenic claudication is :
- Pain after prolonged standing
- Pain is usually improved when the person leans forward at the waist
- Pain while walking
- A person is also experiencing calf pain in the neurogenic claudication even at rest.
- Patient is also feel the pain which is occurs in the thighs, buttocks or lower back,
Plantar fasciitis:
- Plantar fasciitis is a condition that affects the tissue of the plantar fascia & located on the bottom of the foot.
- When the calf muscles are too tight, a person is more likely to experience plantar fascia because the calf muscles do not support the foot.
- The most common symptoms of plantar fasciitis are foot pain when waking & difficulty in flexing the foot.
Varicose veins:
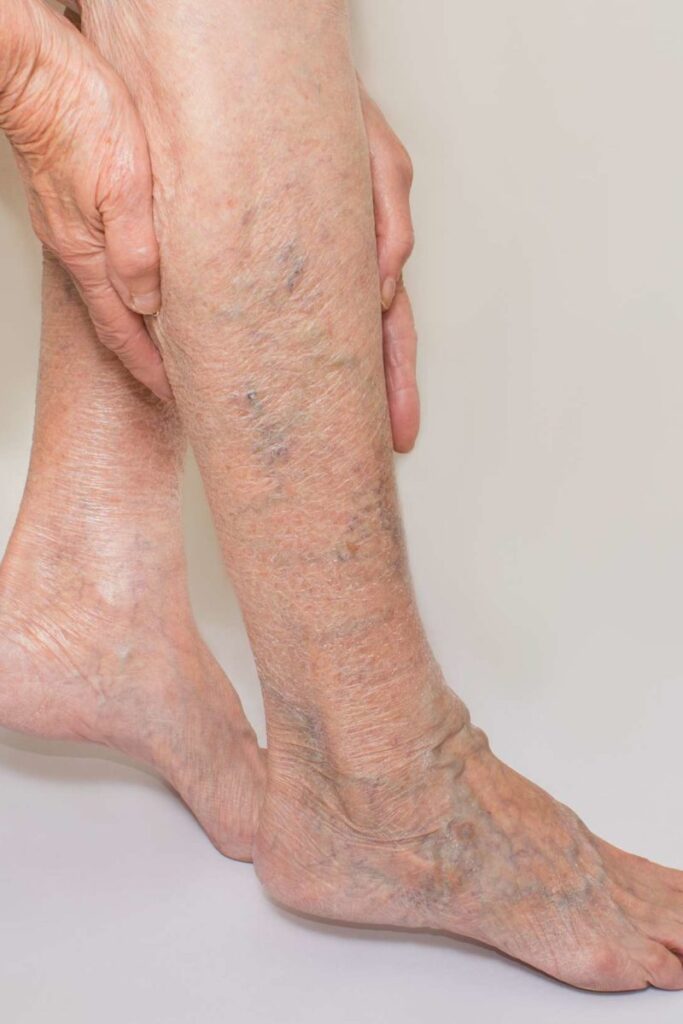
- Varicose veins are enlarged veins that often bulge from the legs & it looks like cords.
- a varicose vein is developed when the damaged valves in the person’s veins which is allowed blood from to backflow.
- Factors that contribute to the varicose veins include:
- Pregnancy
- Lack of physical activity
- Hormone fluctuations
- Age
- Obesity
- A family history of the varicose veins
- The varicose vein is most commonly appear in the legs & it is causing pain, cramping, throbbing, & aching.
Other factors which are become to cause of calf muscle pain :
- If the use of certain medications, including cholesterol-lowering drugs.
- Short/tight calf muscles
- If in the patient present Diseases like as hypothyroidism, kidney disease, liver disease, diabetes /peripheral artery disease = PAD.
- If the presence of Edema – swelling due to fluid build-up in the patient’s lower leg.
- Pregnancy.
- In the patient Low electrolytes due to dehydration/dialysis means a procedure to clean the blood.
- Heat exhaustion.
- Patient do the Smoking/using the tobacco products.
What are symptoms of the calf pain?
- Swelling around the calf area
- Co lour = Unusual coolness/pale color seen in the calf muscle
- Patient feel the tingling/numbness in the calf, muscle & leg
- Patient feel the weakness in the leg
- Fluid retention in the patient
- Redness, warmth & tenderness of the calf muscle
- If any of these symptoms is feel severe, please contact & visit the doctor.
Who gets the calf muscle pain?
- Anyone gets calf muscle pain.
- It is more common in the athletes & people who do the exercise &put the excess stress on the calf muscles.
- People over the age of 65 are also at a higher risk of lower leg pain due to muscle weakness, certain health conditions or if they’ve been inactive.
When does the patient go to the doctor?
- The calf muscle is swollen.
- The calf muscle is unusual to cool/pale
- Patient’s leg is tingly or numb
- Patient’s leg is weak
- Patient feel they have fluid retention
- Patient’s calf muscle is red, warm & tender
- Both legs of the patient are swollen.
- The patient is feeling the breathing problems
- The calf muscle is painful during/after the walking
- If in the patient is present the painful varicose veins
- In the medical attention is straight away if the patient’s symptoms of the DVT & occurs the recently been to sitting for a long time, like as in the flight.
Other signs which are seen in the person & called for the emergency treatment of calf pain include to:
- In the patient presence of fever greater than the 100°F
- In the patient feel the swollen leg when they do pale/cool into the touch
- In the patient presence of sudden extreme swelling in the affected legs
What is Diagnosis of the calf pain?
- A doctor which is carried out a physical examination to determine whether to pull/strain muscle which is the main problem in the patient.
- If the doctor finds the issue in the patient more severe, that doctor is checking the musculoskeletal ultrasound scan.
- Ultrasound can identify the following:
- Diabetic neuropathy
- Achilles tendinitis
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Arterial claudication
- Plantar fascia
- Musculoskeletal ultrasound is provided to guidance regarding injection therapy.
How is the calf muscle pain treated?

- If the patient present of muscle cramp that does gently stretch & do the massage on the calf muscle.
- If the patient presents the calf strain /Achilles tendinitis, so first use the ‘RICE’ method of treatment for the calf muscle :
- R -Rest = Rest the area of the calf muscle.
- I – Ice = Ice is applied in the area of calf pain for 20 minutes & the ice application using the covered ice pack/bag of the frozen peas.
- C – compression = Compress the area of calf pain with the help or use of the bandage but if the patient fell the pain is worse than before pain, so that loosen the bandage.
- E – elevation = Elevate the affected lower leg by sitting/lying down with the use of the pillows so that the affected leg is stay above the level of the heart.
- Use the Soft cast & boot to immobilize the lower leg in the case of strain/tear.
How is treated of vascular calf muscle pain?
- When the calf muscle pain is the result of the claudication, must flow these treatments:
- Do the Diet modification to reduce the intake of sodium (salt), saturated fat, cholesterol & sugar.
- Do the Exercise.
- Take the Medications to manage the BP – high blood pressure, cholesterol & diabetes.
- Take to Medication to prevent/treat blood clots.
- Take to Medications to improve blood flow in both legs.
- Given up to smoking & tobacco products.
Will the calf pain need surgery?
- Most people don’t need surgery for calf muscle pain.
- In rare cases, people need surgery in the situation of torn calf muscles, blood clots & blocked arteries in the calf.
What is common physiotherapy exercises for calf pain?
- Calf raises exercise
- Step-Ups
- Ankle pump exercise
- Downward-Facing Dog yoga
- Calf stretches

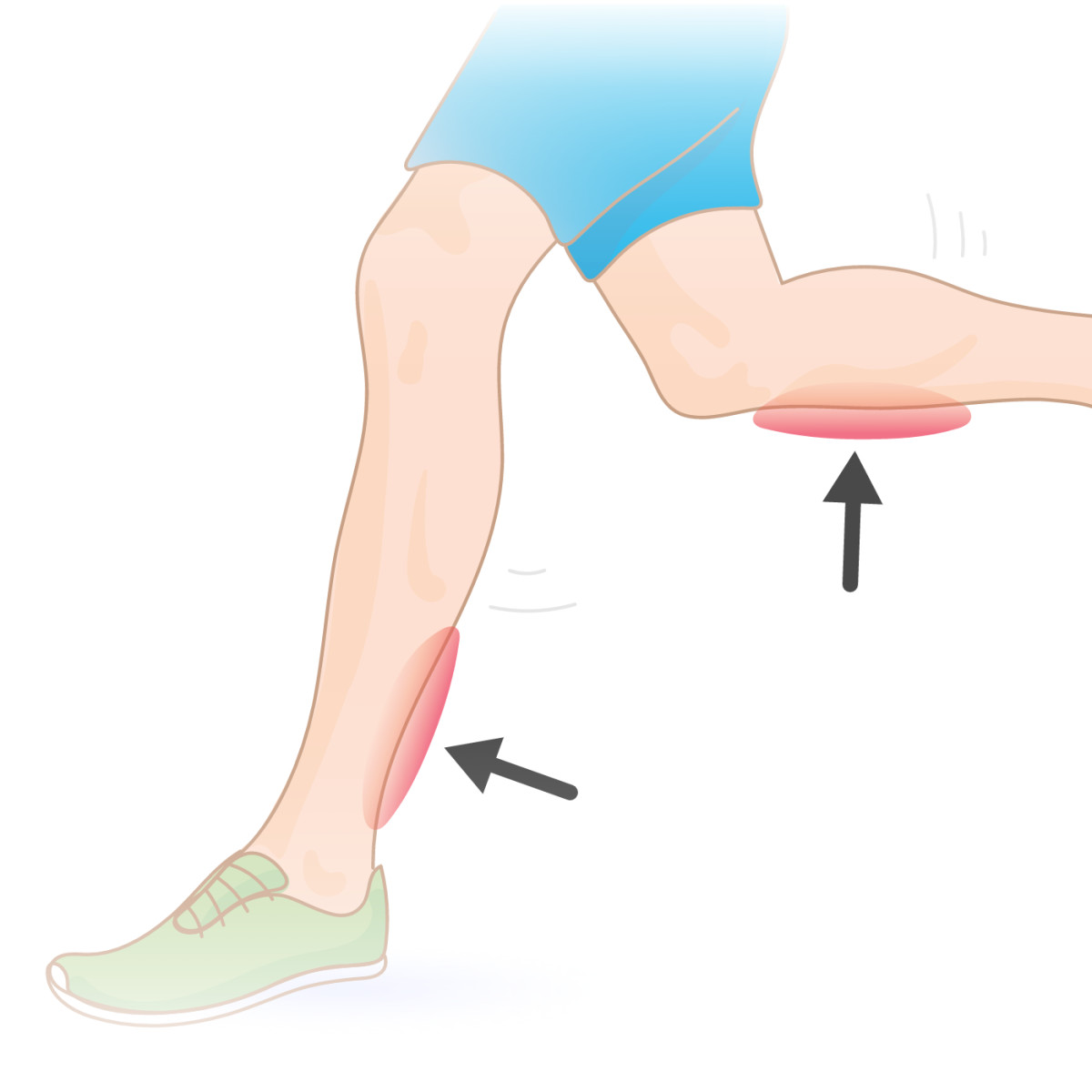
Calf stretch :
- The starting position of the patient is the standing position.
- The patient is Stand facing the wall.
- Then Place the hands on the wall.
- Move to the one foot of the patient’s back as far as the patient do to comfortably.
- Then do the Toes on to both feet for to facing forward, heels flat & with to a slight bend into the knee joint.
- After that Lean through the wall.
- In the position, the patient feels the calf muscle stretches.
- Hold this position for 30 seconds & do the 3 times in 1 session.
- Do the 3 sessions per day.
Downward-Facing Dog yoga :

- In the Starting phase on to the hands & knees.
- Then Press into the hands as to the lift of the hips joint toward the ceiling.
- Then Drop to the head down to bring the ears into the line with the upper arms / to the chin into the toward of to the chest.
- Then Bend to the knees to tilt the pelvis slightly as to the forward.
- Move to the body through of to any variations for the feel of to the appropriate.
- Then Hold to this pose for up to 1 minute.
- In this holding, position Patient feels to stretch into the back leg.
- This position Hold for 30 seconds.
- Repeat this stretching exercise or the 3 times.
- Do the 3 sessions per day.

Calf Raises :
- The starting position for the exercise is the standing position.
- In the Standing position facing the back of the chair.
- The patient is Also used to backing off to the couch or a wall bar at the gym for support.
- This exercise is also done on the stairs.
- Then holding to the Bannister with to the heels.
- After that hanging off to the edge of this step.
- Then Slowly raise to the heels as high as possible then lower in starting position.
- This exercise position Hold for 10 seconds.
- Then Repeat this exercise 10 times in 1 session.
- This exercise Do in the 3 sessions per day.
Step-Ups :

- The starting position for the exercise is the standing position.
- Then Place one Of foot on a platform/step bench & the lowest step on a staircase.
- In the standing position Keep straight to the pelvis level.
- After that bend to the knee joint & slowly lower to the opposite foot onto the floor.
- Then Lightly touch the toe onto the floor& rise to back up in the starting position.
- Repeat this exercise 10 times in one session.
- This exercise Do in the 3 sessions per day.

Ankle pump exercise :
- The patient is sitting/supine with to back straight against a chair.
- Then legs are extended and spread slightly apart.
- After that point the toes up so that soles are too flat.
- Then Pretend to press down onto the gas pedal for to automobile and point the toes to down means return in starting position.
- When the patient feels the stretch so that this position Hold for 3 to 5 seconds.
- After that Slowly return to the toes which lie perpendicular to the floor.
- Then Repeat this exercise 10-15 times in one session.
- This exercise is Do the 3 sessions per day.
What is Home remedies for calf pain relief?
- Treatment methods for calf pain is depending on the cause of pain, but most of the causes are addressed at home. For the calf muscle pain is caused by overuse & mild-to-moderate trauma, but here are present to few tips:
- The patient can take to anti-inflammatory medicines to relieve pain & bring down the swelling.
- After 48 hours, start stretching & strengthening the calf muscle, like doing heel raises & calf stretches. but Don’t return to full physical activity till the pain & tenderness is gone, move the ankle & knee joint properly,& return the calf muscle strength.
Can a person prevent form calf pain?
- Always do the stretch before & after exercise to repair & strengthen the calf muscle.
- Don’t over-exercise & build up gradually if the starting something new.
- Drink plenty of water to avoid cramps in the calf muscle.
- Magnesium supplements of water have been preventing cramps in some people, mostly in pregnant women,
- If the presence of diabetes in the patient, so that keep the blood sugar levels under to control for to prevent of the diabetic neuropathy.
- OTC medication = Calf pain is also be soothed with the common pain in relievers like ibuprofen/naproxen.
- Stretching = Light stretching is help to ease the calf pain.
- This stretching is applied After the symptoms is slightly decreased, so that stretch the calf muscles.


4 Comments