Iron-deficiency Anemia
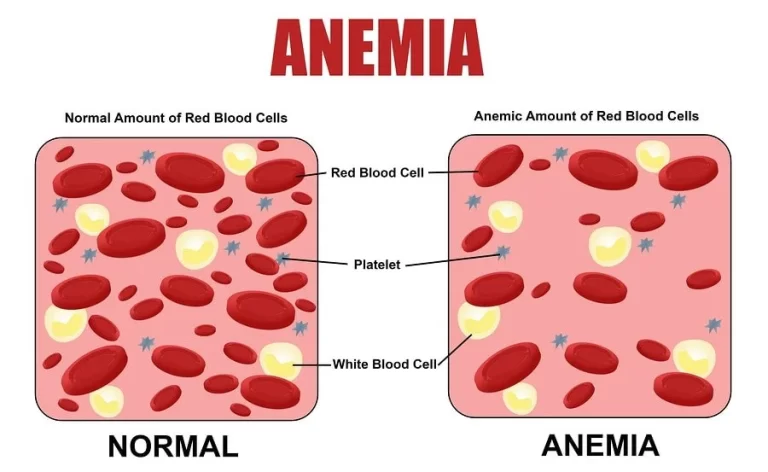
Introduction Iron-deficiency anemia is a prevalent medical condition characterized by a deficiency of iron in the body, leading to a reduction in the production of hemoglobin, a critical component of red blood cells. Hemoglobin plays a vital role in transporting oxygen from the lungs to various tissues and organs, and when its levels are insufficient,…