Broca’s Aphasia
Table of Contents
What is Broca’s aphasia?
- Aphasia is the decrease in the ability to understand speech or communicate utilizing language. It can happen when parts of the brain responsible for language become damaged.
- There are several various types of aphasia. Each and every type is classified as either fluent or non-fluent. Broca’s aphasia is the non-fluent type.
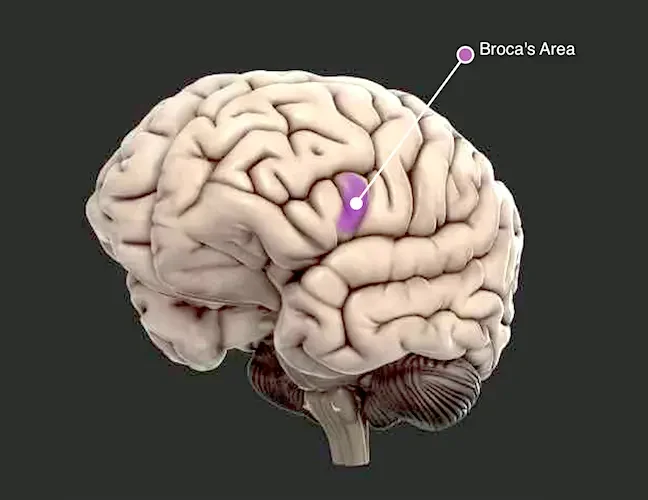
- Broca’s aphasia results from damage to an area of the brain called Broca’s area, which is located in the frontal lobe, usually on the left side. It is one of the areas of the brain responsible for speech and motor movement.
- It is named after Pierre Paul Broca, a French physician who discovered the part in 1861. Broca’s aphasia is referred to as expressive aphasia.
What are the symptoms of Broca’s aphasia?
- If you have Broca’s aphasia, you may be able to comprehend what’s being said yet be unable to speak fluently because your brain is not able to control the fluency of your speech.
- This may make you very frustrated, since you know what you want to say but can not get the words out the way you wish to.
Symptoms of Broca’s aphasia involve:
- poor or absent grammar,
- trouble forming complete sentences,
- omitting some words, such as “the,” “an,” “and,” and “is” (a person with Broca’s aphasia may say something such as “Cup, me” instead of “I want the cup”),
- more trouble using verbs than nouns correctly,
- trouble articulating sounds and words,
- trouble repeating what has been said by others,
- difficulty with writing sentences,
- trouble reading
- troubles with full comprehension,
- trouble following directions,
- frustration.
What are the causes of Broca’s aphasia?
- Any neurological condition that damages cells in the language part of the brain may result in aphasia. Brain cells die when blood flow or oxygen flow to a particular area of the brain is stopped or diminished.
Causes involve:
- stroke
- brain tumor
- injury to the brain, like from a severe blow to the head or gunshot, wound,
- infection in the brain,
- progressive neurological conditions, like Alzheimer’s disease.
What are the Diagnosing of Broca’s aphasia?
- If a stroke or other form of brain injury happens, a doctor will test for the symptoms of aphasia. If you or someone with a progressive neurological condition begins to show difficulty with speaking or language comprehension, a medical evaluation should be sought immediately.
- The doctor will talk with you to decide your ability to comprehend and communicate. If troubles with speech or comprehension are apparent or suspected, additional testing will be done.
- Diagnosis of Broca’s aphasia needs an MRI or CT scan. These tests assist determine the exact area of the brain that is affected, as well as the extent of the damage.
What is the treatment for Broca’s aphasia?
- Broca’s aphasia needs treatment with speech therapy. It is not expected to increase on its own.
- Speech therapy includes working with a speech-language pathologist, both in person or online, which can highly enhance progress. The more practice someone has speaking in a safe environment, the more such as they may be to continue trying to increase.
- Also, discovering a support group, book club, or another type of social setting with other people going through a similar thing can be very beneficial.
- Finally, if you have Broca’s aphasia, you can assist to accelerate your own progress by having verbal interactions with people you trust.
Here are certain techniques you can use:
- Try to control the noise level of the room you’re in to eliminate any unrequired distractions.
- It may seem silly at 1st, but use a mirror, and try practicing a few phrases, such as, “How are you?” & “What are you doing for holidays?” before you attend events. This may assist to build up your confidence level.
- Keep trying! Remember that improvement can continue for so many years.
- Go at your own pace; just create sure to keep going.
- Supporting someone with Broca’s aphasia.
- If you care about someone who has this condition, remember that they are just as intelligent as before. Be understanding, as they may sense frustrated about their latest situation.
- Try to have patience and involve them in the life of your family or circle of friends. Keep them in the loop by involving them actively in conversations & by looking directly at them rather than talking around them.
Other tips for communication involve:
- Keep your sentences simple and short, but do not speak to them as if they’re a child.
- Re call that their interests have not changed, only their ability to talk about them.
- Ask lots of yes and no questions, or questions that need very simple answers.
- Utilize gestures or props to get your point across.
- Fold in simple interactions, like sitting quietly in nature, where you can enjoy each other’s presence without speaking too much.
Physiotherapy treatment
- Physiotherapists get to manage patients with neurological conditions that may and sometime conduct to aphasia. It is important to be knowledgeable about the condition and its types to aid appropriate referral if or when identified by the physiotherapist in the course of patient care and to optimize interaction with patients.
Can you prevent Broca’s aphasia?
- There is no 1 method for preventing Broca’s aphasia or any type of aphasia. One way to try to prevent it is by decreasing your risk of having a stroke.
- This may need lifestyle changes, such as quitting smoking if you smoke and losing weight if you are overweight. Quitting smoking or alcohol is often difficult, but a doctor can assist build a plan that works for you.
- Medications that decrease blood pressure and cholesterol can also assist. Speak with a doctor about your stroke risk and about lifestyle changes you can create to decrease it.
- It is important to safeguard your head during sports and other activities, such as riding a motorcycle. Wearing a helmet can assist to prevent the types of brain injuries that can conduct to aphasia.
Outlook
- People with Broca’s aphasia sometimes make significant improvements in their ability to speak over time. The extent of the harm, its cause, and your overall health and age are all factors that may impact recovery.
- Improvement in speech may start within days, weeks, or months of the injury. Improvements may constantly be seen for years afterward.
FAQs
Symptoms of Broca’s aphasia involve poor or absent grammar. difficulty forming complete sentences. omitting certain words, such as “the,” “an,” “and,” and “is” (a person with Broca’s aphasia may say something such as “Cup, me” instead of “I want the cup”).
Wernicke’s aphasia causes you to speak in a together “word salad” that others can not understand. Broca’s aphasia leaves you with limited language. You might only be able to say single words or very few sentences. Yet others can commonly understand what you mean.
They sometimes omit small words, such as “is,” “and” and “the.” For example, a person with Broca’s aphasia may tell, “Walk the dog,” meaning, “I will take the dog for a walk,” or “book 2 tables,” for “There are 2 books on the table.” People with Broca’s aphasia commonly understand the speech of others fairly well.
Broca’s aphasia is known as non-fluent aphasia. Speech is effortful and sounds rather stilted, with most utterances limited to four words or less. A person with Broca’s aphasia relies mostly on important keywords (nouns and verbs) to communicate their message.
Broca’s aphasia outcomes from injury to speech and language brain areas such as the left hemisphere inferior frontal gyrus, among others. Such damage is often a result of a stroke yet may also occur due to brain trauma.
New research looks that Broca’s area, located in the frontal cortex and shown here in color, plans the process of speech by interacting with the temporal cortex, where sensory information is processed, & the motor cortex, which controls movements of the mouth.
Broca’s aphasia is the outcome of damage to a specific language region in the frontal lobe of the brain known as Broca’s area. It is not a trouble with the muscles, the throat, or the mouth. Broca’s area is one of so many language parts of the brain.
Writing in Broca’s aphasia seems to be impaired analogously to speech output, yet reading ability may be only mildly impaired; writing will exhibit misspellings, letter omissions, poor formation of letters, and agrammatism.
It can be affected by apraxia, yet people with Broca’s aphasia can typically repeat 1 to 4 words. Same to speech production, people with more severe aphasia will say fewer sounds or words, whereas people with moderate Broca’s aphasia will repeat up to 4 to 5 words.
Writing in Broca’s aphasia tends to be impaired analogously to speech output, yet reading ability may be only mildly impaired; writing will exhibit misspellings, letter omissions, poor formation of letters, & agrammatism.



2 Comments