What are the Quadrants of Abdominal Pain?
Table of Contents
Introduction
The quadrants of abdominal pain refer to four distinct regions within the abdomen that are used by medical professionals to pinpoint the source of abdominal discomfort and pain.
These quadrants, known as the right upper quadrant (RUQ), left upper quadrant (LUQ), right lower quadrant (RLQ), and left lower quadrant (LLQ), serve as a valuable anatomical framework for diagnosing and localizing the underlying causes of abdominal pain.
The common symptom of abdominal pain might have a variety of causes. The four quadrants of abdominal discomfort should be understood.
There are four areas of abdominal pain:
- Quadrant 1 is located in the upper right corner of the body, close to the bottom of the ribs and above the navel.
- Quadrant 2 is in the upper left corner, just beneath the ribs.
- Quadrant 3 is the bottom left side of the abdomen.
- Quadrant 4 refers to the lower right abdominal ache.
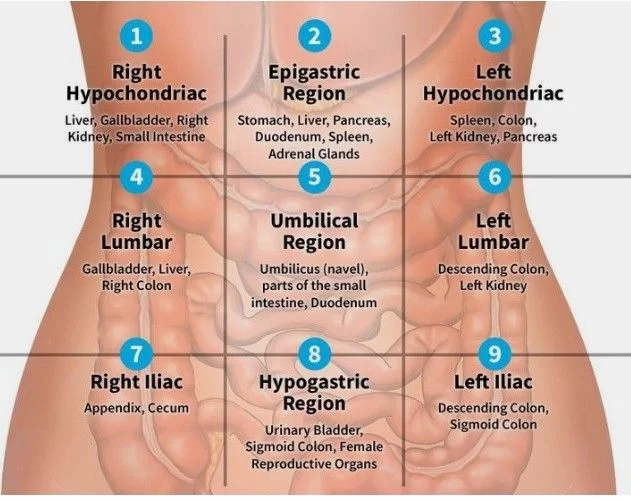
The Abdominal region is divided into four quadrants, each of which contains different organs. These quadrants are:
- Upper right quadrant: This quadrant contains the liver, gallbladder, and part of the pancreas.
- Upper left quadrant: This quadrant contains the stomach, spleen, and part of the pancreas.
- Lower right quadrant: This quadrant contains the appendix, cecum, and part of the small intestine.
- Lower left quadrant: This quadrant contains the sigmoid colon, rectum, and part of the small intestine.
The location of abdominal pain can help doctors diagnose the underlying cause. For example, pain in the upper right quadrant is often associated with liver or gallbladder problems, while pain in the lower right quadrant is often associated with appendicitis.
Here is a table that summarizes the organs in each quadrant of the abdomen.
| Quadrant | Organs |
| Upper right | Liver, gallbladder, pancreas |
| Upper left | Stomach, spleen, pancreas |
| Lower right | Appendix, cecum, small intestine |
| Lower left | Sigmoid colon, rectum, small intestine |
How Often Are Stomach Pains?
Almost everyone will eventually experience stomach pain. Typically, it needs to be more serious and resolves on its own. But it could also be an indication of a serious illness or even an emergency. Abdominal pain is the reason for 5% of trips to the emergency room.
Which Four Types of Stomach Discomfort are there?
Your doctor may want to focus on a particular area of your abdomen to understand the type of pain you’re having because your abdomen contains several functions. Specialists in the medical field commonly divide the abdomen into four quadrants. Inquiries may be made if your pain is localized.
- Upper and lower halves. Over the belly button is where upper abdominal pain is felt. It is below lower abdominal pain.
- You left side/right side. In the middle of your abdomen are your sternum and belly button.
What Does the Location of Stomach Pain Indicate?
- The location of your stomach ache is an important indicator, but it’s just one.
- It’s crucial to distinguish between upper and lower stomach pain when dealing with a case of abdominal discomfort. Numerous conditions, including heartburn, ulcers, and hiatal hernias, can result in upper stomach pain.
- In general, digestive issues including gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), constipation, or irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) are the primary causes of left-sided lower abdomen pain.
- The lower right side of your stomach will typically experience lower abdominal pain, which is typically more severe. Whether or not you have symptoms, the kind of symptoms you have, your age, your family history, and any pre-existing diseases you might have are a few of the contributing variables.
- Infection, menstrual pain, endometriosis, or even kidney stones can all result in lower abdomen pain.
- If you are experiencing blood in your stools, blood in your vomit, or have stopped having bowel motions, you must get emergency treatment for stomach pain.
What Causes Lead to Stomach Pain that is More Severe?
Abdominal discomfort can occasionally be a sign of a significant medical issue that needs to be treated. various types of pain may be caused by various organ involvement. For instance:
Right upper quadrant
Your liver, gallbladder, and bile ducts are in your upper right abdomen. Your back holds the right kidney. The start of your small and big intestines also passes through.
The most frequent cause of upper right abdomen pain is liver or gallbladder disease, such as:
- Hepatitis (autoimmune, viral, toxic, metabolic, or alcohol-related).
- Gallstones.
- Cholecystitis (inflammation of the gallbladder).
- stones, cancer, and bile duct obstructions.
- Bladder cancer.
- Carcinoma of the liver.
It might also be a specific issue with your right kidney, upper colon, or duodenum, such as a:
- A kidney infection.
- Renal stone.
- A duodenal ulcer.
- Blockage of the large bowel.
Left upper quadrant
Your stomach, pancreas, and spleen are located in your upper left abdomen. Right over your left kidney, towards the back of your abdominal cavity, is your heart and left lung.
Upper left abdomen discomfort may indicate:
- Pancreas inflammation, or pancreatitis.
- Carcinoma of the pancreas.
- Splenomegaly, or an enlarged spleen.
- Gastritis.
- Gastric ulcer.
- Reflux of bile.
- Digestive cancer.
- A kidney infection.
- Renal stone.
If your chest is the source of the pain, it could come from:
- Heartburn.
- Angina.
- Chest pain that is not cardiac.
- Chest pains.
- Pericarditis.
- Pneumonia.
- Pleurisy.
- Embolism in the lungs.
Your lower belly is where the majority of your small and large intestines are situated. Lower abdomen pain is more frequently brought on by gastrointestinal (GI) diseases. Additionally, your uterus, ovaries, or ureters can be involved.
Among the abdominal causes are:
- Bowel irritability syndrome.
- Dyspepsia with function.
- Bowel inflammation (Crohn’s, ulcerative colitis).
- Obstruction of the large or small intestine.
- Small-bowel cancer.
- Bowel cancer.
- Aneurysm of the abdominal aorta.
- Peritonitis.
- lymphadenitis of the mesentery.
- Mesenteric (intestinal) ischemia syndrome.
- Hernia.
- Renal stones.
Possible causes of pain referred from the pelvic organs include:
- Endometriosis.
- Cysts on an ovary.
- Inflammation of the pelvis.
- Ectopic conception.
- Breast cancer.
Left lower quadrant
The most common causes of pain in the lower left abdomen are diverticulosis and diverticulitis of the colon. Diverticula, which are tiny openings in the gut wall, can appear anywhere in your colon, although they typically start in the bottom left corner.
Lower right quadrant
If you have persistent lower right stomach pain, your appendix can be to blame. The reason could be appendiceal irritation or, less frequently, appendiceal cancer.
General pain
Other common causes of stomach ache are as follows:
- Pain from stress (psychosomatic).
- hypersensitivity in the organs.
- Bloating in the abdomen.
- traumatizing wounds.
- strained abdominal muscles.
- Shingles.
What Other Symptoms are Related to Abdominal Pain?
An abdominal ache may feel dull or gnawing, or it may be painful, stabbing, burning, twisting, cramping, or burning.
Along with the pain, other symptoms could also be present, such as abdominal discomfort, bloating, constipation, wind (flatulence, farting, or belching), fever, heartburn, nausea, vomiting, fever, dehydration, or loss of appetite.
A doctor may be able to determine the source of your stomach discomfort if you describe the pattern and location of your symptoms to them. Among these reasons are:
- Peptic ulcer – This condition causes frequent upper abdominal pain that feels like a knife and travels through to the back.
- Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD) – This condition is characterized by a persistent, central burning sensation that usually starts under the breastbone and may climb to the top. It can be followed by belching.
- Appendicitis – The pain typically begins close to the navel (belly button), and then descends to the lower right abdomen as it becomes more persistent.
- Gallstones or gallbladder irritation – The discomfort is felt in the upper right belly, back, or right shoulder.
- Lower abdominal discomfort – Also known as ‘lower stomach pain,’ it is most likely caused by your colon.
- Period pain – It is typically described as a dull, cramping discomfort felt low down that may radiate to the back.
Treatment:
Some types of abdominal pain may be avoided with the adoption of these measures:
- Consume a lot of water every day.
- Eat more often and in smaller portions.
- Regularly moving around.
- Eat fewer meals that cause gas.
- Make sure your meals are fiber-rich and well-balanced. Eat lots of fruits and vegetables.
Prevention Of Stomach Pain
Consuming a balanced diet:
Ensure that the rice is completely white. Brown or black rice can be challenging to digest, especially if your stomach is disturbed. White rice is a starchy, low-fiber food that can firm up your stools and halt the occasional diarrhea that comes along with stomach issues.
Consuming fewer food items:
Mini meals can aid with blood sugar regulation, vitamin absorption, and appetite suppression throughout the day. Smaller meals help with digestion and prevent you from experiencing abdominal aches.
Summary:
Abdominal pain can be categorized into four main quadrants, each representing a specific region of the abdomen. The right upper quadrant typically houses the liver, gallbladder, and parts of the small intestine, and pain in this area can be indicative of issues like gallstones or liver disease. The left upper quadrant contains the spleen and the stomach, with pain possibly pointing to gastritis or splenic disorders.
The right lower quadrant is home to the appendix and portions of the large intestine, making pain here a concern for appendicitis or gastrointestinal problems. Finally, the left lower quadrant encompasses the descending colon and is often associated with conditions like diverticulitis or irritable bowel syndrome. Understanding which quadrant the pain originates from can aid healthcare professionals in diagnosing and treating the underlying cause effectively.
FAQs
Why is it important to identify the location of abdominal pain in a specific quadrant?
Identifying the location of abdominal pain is crucial for diagnosing and treating medical conditions. Different organs and structures are located in each quadrant, and pain in a specific quadrant can be a clue to the underlying cause. For example, right lower quadrant pain may be a sign of appendicitis, while left upper quadrant pain could indicate a problem with the spleen.
What should I do if I experience severe abdominal pain in any quadrant?
You must seek medical care right away if you have severe or chronic stomach pain. Abdominal pain can be a symptom of various conditions, some of which may require immediate treatment.
Are there any home remedies for relieving mild abdominal pain?
Mild abdominal pain caused by indigestion or gas may be relieved with over-the-counter antacids, gentle massaging of the abdomen, and rest. However, if the discomfort continues or gets worse, you should see a doctor.
When should I require medical treatment for abdominal pain?
If you experience severe or persistent abdominal pain, especially if it is accompanied by other symptoms such as fever, vomiting blood, or blood in the stool, you should seek immediate medical attention. Abdominal pain can be a sign of a serious medical condition that requires prompt evaluation and treatment.
References:
Professional, C. C. M. (n.d.). Abdominal Pain. Cleveland Clinic. https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/symptoms/4167-abdominal-pain