Test for the Pathology related to the Radio-ulnar Joint
The radioulnar joint of the wrist is examined using these techniques.
When a patient complains of wrist pain in the joints, the therapist will do these physical exams.
Table of Contents
List of the test for the pathology related to the Radio-ulnar joint:
- Ulnar fovea sign test
- Ulnar impaction test
- Ulnar styloid triquetral impaction [ USTI ] provocation test
- Ulnomeniscotriquetral dorsal glide test
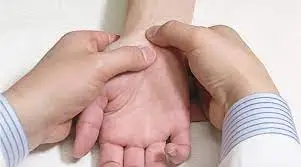
Ulnar fovea sign test:
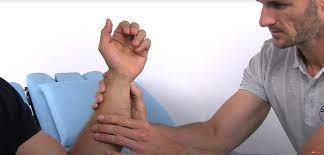
- Purpose= The ulnar fovea sign test is to evaluate the stability of the distal radioulnar joint.
- Technique: The subject performs the test while standing or sitting.
- The examiner puts a thumb or finger into the space or depression between the flexor carpi ulnaris tendon and the ulnar styloid process, which is located between the pisiforms and the anterior surface of the ulnar head.
- If the patient’s pain is repeated or the region is extremely painful in comparison to the unaffected side, the test is deemed positive.
- The distal radio ulnar and ulnotriquetral ligaments are commonly believed to be to blame for the discomfort.
When the distal radioulnar joint is stable, lunotriquetral ligament rips are frequently present, however when it is unstable, fovea disruptions are seen.
Ulnar impaction test
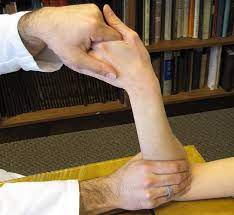
- Purpose =The ulnar impaction test of the ulnar impaction syndrome is checked by using this test.
- Technique= The patient is seated with the wrist in an ulnar deviation motion and the elbow flexed to 90 degrees.
With the aid of one hand, the therapist (examiner) secures the patient’s forearm while exerting an axial compression force across the fourth and fifth metacarpals. - Consequently, discomfort is a sign of a positive test and may be connected to an ulnar impaction syndrome or TFCC damage.
Ulnar styloid triquetral impaction [ USTI ] provocation test
![Ulnar styloid triquetral impaction [ USTI ] provocation test](https://samarpanphysioclinic.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/06/Ulnar-styloid-triquetral-impaction-USTI-provocation-test.jpg)
- Purpose = To determine when there is a pathological impaction, using this test.
- Technique=The patient is sitting in technique.
The patient’s wrist is extended, their forearm is pronated, and the examiner is holding their elbow with one hand. - The forearm is in a supinated posture while continuing the extension motion.
Results: Pain is present at the ulnar styloid indicating a positive test for pathological impaction.
Ulnomeniscotriquetral dorsal glide test:

- Purpose = The use of this test is done to determine whether TFCC pathology is present.
- Technique: The position of the patient is in sitting/standing with the arm pronated.
The proximal interphalangeal joint of the same hand’s index finger is placed on the pisotriquetral complex anteriorly, and the examiner inserts a thumb on the ulna dorsally. - The examiner [therapist] stresses the TFCC while posteriorly directed force is applied across the pisotriquetral complex while stabilizing the ulna.
- A positive test for TFCC pathology would result in excessive laxity or the patient experiencing discomfort when the posteriorly directed force is applied.