Scarf Test (Cross Arm Adduction Test)
The scarf test is an important test that helps to examine the integrity of the acromioclavicular (AC) joint.
Table of Contents
Purpose
This is also famous as the cross-body adduction test, is to determine whether or not the acromioclavicular (AC) joint is in good condition.
Technique
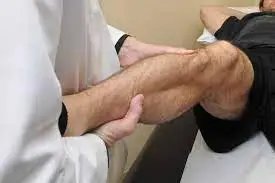
- The patient is passively brought into 90 degrees of forward flexion with their elbow also flexed to 90 degrees during the test. After that, the examiner moves the flexed arm horizontally across the patient’s body and brings the elbow toward the opposite shoulder.
- At the acromioclavicular joint, this position causes the medial acromial facet to be compressed against the distal clavicle.
Interpretation
- If the maneuver successfully reproduces the patient’s localized pain over the AC joint, this test is deemed positive.
- A positive test usually indicates either AC joint osteoarthritis or a ligamentous injury (such as a ligament sprain or joint separation) to the AC joint.
Validity
- The following factors determine this test’s diagnostic accuracy for AC joint pathology:
- Evidence Presently, research supports a special interpretation of a variety of physical examination tests to diagnose painful AC joint dysfunction. Sensitivity = 0.77 – 1.00 Specificity = 0.79 +LR = 3.67/-LR = 0.29 A summary is as follows:
Evidence
- Keeping away from painful AC joint dysfunction: Negative results from the cross-body adduction test, ACJ palpation tenderness, and the Paxinos sign.
- In the case of painful AC joint dysfunction: Positive results on the AC resisted extension, active compression, and cross-body adduction tests.
Differential Diagnoses
- The cross-body adduction maneuver may also reproduce pain in conditions like subacromial impingement and posterior capsule tightness.
- Additionally, a restricted range of motion is extremely uncommonly associated with AC joint pathology and is more likely to indicate adhesive capsulitis or glenohumeral arthritis.
FAQ
The acromioclavicular joint’s integrity can be assessed using the scarf test. Passively adduct the arm horizontally across the body, equidistant from the contralateral shoulder, to perform this test. If the patient experiences pain at the acromioclavicular joint, the test is positive.
AC Shear Test: The examiner should squeeze their hands together while cupping their hands over the shoulder with one heel on the clavicle and the other on the spine of the scapula. Interpretation:
A positive result indicates either abnormal movement or pain at the AC joint.
The AC joint compression test is the special shoulder test for AC joint separation. It is a straightforward test that your physical therapist or other healthcare provider may perform as part of your evaluation for shoulder pain or other issues.
Jobe lateral test. One of the most accurate tests for a rotator cuff injury is the Lateral Jobe Test, which may require assistance from an assistant once more. The supraspinatus muscle is also examined for weakness during this test.
Technique. The examiner performs the Speed’s Test by putting the patient’s arm in forearm supination, external rotation, full elbow extension, and flexion; The examiner then applies manual resistance in a downward direction.