Obturator internus syndrome : Physiotherapy Treatment
Obturator internus syndrome is a disorder that affects the inner thigh. It is most common in women who are pregnant or obese.
The condition is caused by a problem with the muscles and tendons in your pelvis. The obturator internus muscle is one of several muscles that make up your Hip region.
The obturator internus muscle is one of the four muscles that make up the obturator foramen. Normally, the obturator internus muscle is covered by the obturator membrane called Obturator internus bursa. The obturator membrane attaches to the bone in the pelvis. As the muscle contracts, it moves the thigh bone forward.
Table of Contents
Anatomy of Obturator internus:
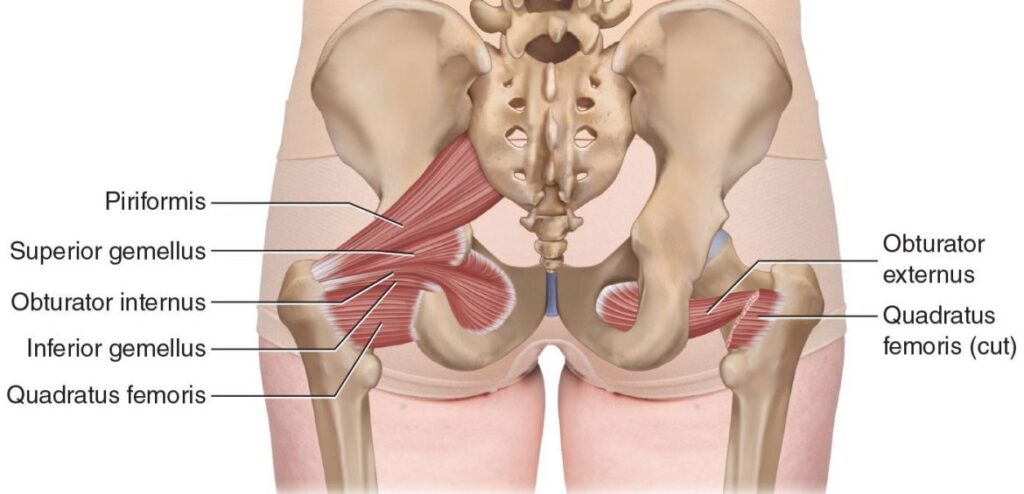
Obturator internus Muscle is a deep hip rotator that arises from the medial surface of the ischium and inserts into the femur. It is used to adduct the hip. It is innervated by the anterior division of the obturator nerve (L2, L3). The obturator nerve also innervates muscles of the medial compartment of the thigh (obturator externus and adductors longus and brevis), and the knee (sartorius).
Main function of the muscle is Laterally rotate the Hip, also helps in Abduction and play part of stabilizier of Hip joint.
Causes :
Following one or more causes are responsible for Obturator Internus syndrome
- The obturator internus muscle tightness mainly due to sedentary life style
- muscle imbalances may cause over-pressure on obturator internus muscle which lead to muscle pain and spasm
- injuries around Hip area. eg. Slip or fall on hip may cause injury to muscle
- Postural changes. eg. as you ages your leg gradually externally rotated and muscle become weak and tight and gradually reduce elasticity property in muscle
- Muscle Spasticity due to stroke or other cerebral disease.
Symptom’s:
Obturator internus syndrome symptoms are :
- Pain in the hip with painful sitting, and with muscle tightness are most common symptoms.
- Hips that feel tight and your feet always seem to be rotated
- Pain on the lateral side of their hip or the pain is in the buttock region. Lateral hip pain, can be mistaken for IT band syndrome/bursitis
- Pain in the tailbone
- Pain in the groin area
- Burning-type of pain at the “sit bone”- Sit bone pain
- Compression of of the pudendal nerve by obturator fascia can lead to refereed pain symptoms like burning, itching, cold, and tingling sensations in groin, legs, abdomen, and buttocks.
- Obturator strain is associated with the kicking sports due to overuse in young male athletes with initial complain of groin pain.
- The pudendal nerve is the only nerve with both autonomous and somatic fibers, meaning that pressure to the nerve can lead to the above issues with other associated increased heart rate, high blood pressure, constipation, and discomfort.
- The obturator internus muscle should be considered as a other possible cause of sciatica pain. However, the diagnosis of the obturator internus syndrome can only be made by differentiate with other possible causes of sciatic pain, which is similar to the piriformis syndrome is diagnosed.
The obturator internus has many pain referral sites. So symptoms can vary from one day to the next.
Other associated symptoms in the pelvic muscles are :
- Urinary urgency
- Urinary frequency
- Urinary incontinence
- Painful intercourse
There are sportsperson have also tightness in the obturator internus muscle. Gymnasts, horseback riders, spin class cyclers,runners, and dancers tend to have spasms here. In any post-operative hip surgery in which Hip rotation is limited, as with a hip replacement, this muscle can be a source of pain or contribute to the onset of urinary incontinence.
Diagnosis :
There are number of causes for Hip pain, in and around the hip joint and understanding the anatomy of the hip joint and it’s associated bursae will help solve some less common causes of hip pain.
X-Ray, MRI, CT Scan are helpful in Differential diagnosis of Hip pain.
MRI : Obturator internus bursa is one of the less commonly visualized bursa among the 20 odd bursae around the hip joint. It is typified by it’s classical ‘boomerang’ appearance on axial images and appears on MRI only when it is inflamed.
Physical Examination :
Examination of Leg position in Supine position. Area of pain, also examine muscle tightness by stretching the muscle.
Obturator internus syndrome treatment :
Treatment of OIS are mainly Medical and Physiotherapy treatment and last option is Surgery.
Medical Treatment :
Pain relieving analgesics mainly NSAIDs are prescribed mostly by Physician and asl recommended to start Physiotherapy treatment and exercise.
Bupivacaine (Marcaine) injection
Surgical treatment :
- Surgical release of the internal obturator muscle can result relieve in pain in patients with retro-trochanteric pain syndrome and should be recommended only if medical/physiotherapy treatment fails.
- Other Surgical treatment are Neuroplasty release of the nerve to the obturator internus and the pudendal nerve.
Physiotherapy Treatment in Obturator internus syndrome :
Symptomatic Pain relieving Electrotherapy modalities.
IFT (Interferential Therapy), TENS, Ultrasound Helps relieving pain.
You can also use Hot Pack / Ice Pack at Home.
Exercise :
Gentle Stretching exercise of obturator internus muscle and other related tight muscle from day 1 is recommended.
These muscles can be gradually stretched and released, and the muscle imbalances will restored.
Initially active movement and then strengthening exercise also helps to improve muscle power.