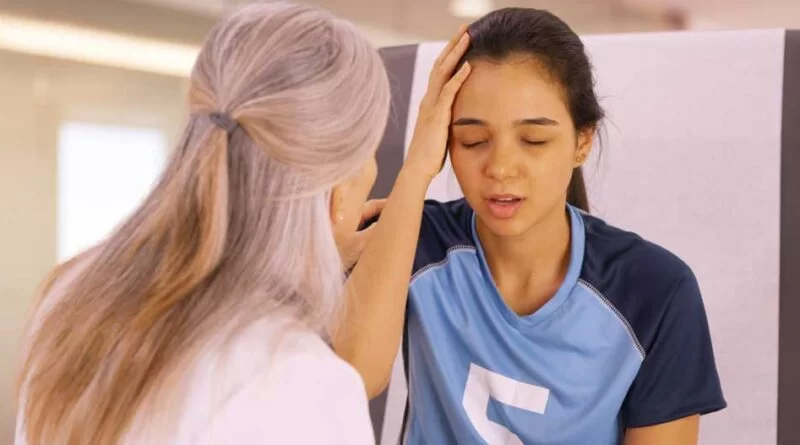
Concussion
Table of Contents
What Is a Concussion?
- The most prevalent & least serious type of traumatic brain injury is called a concussion. The word comes from the Latin concutere, which means “to shake violently.” A concussion is most frequently caused by a sudden direct blow & bumps to the head.
- According to the CDC, between 2001 & 2009, an estimated 173,285 people under age 19 were treated in hospital emergency rooms for concussions related to sports and recreation activities. Other causes include car & bicycle accidents, work-related injuries, falls, and fighting.
What are the causes and risk factors of concussion?
- The brain is made of soft tissue. It’s cushioned by spinal fluid & encased in the protective shell of the skull. When you have a blow or bump to the head, the impact can jolt the brain. Sometimes, it accurately causes it to move around in the head. Traumatic brain injuries can cause by bruising, damage to the blood vessels, & injury to the nerves.
- The result is the brain doesn’t function as it should. If you’ve had a concussion, your vision might be disturbed, you may lose equilibrium, & you may fall unconscious. In short, the brain is confused.
Some things increase the risk of a concussion, including:
- Falls, particularly in children & older adults
- Playing a contact sport
- Lack of proper safety gear & supervision for contact sports
- Car, motorcycle, bicycle, & other accidents that cause a blow to the head
- Being hit, struck with an object, & other physical abuse
- Military service
- An earlier concussion
What are the Symptoms of Concussions?
- Concussions can be tricky to diagnose. Though a person may have a visible cut or bruise on the head, you can’t see a concussion. Signs may not appear for days & weeks after the injury. Some symptoms last for just seconds; others may be longer.
- Concussions are fairly common. Some evaluations observe a mild brain trauma is sustained every 21 seconds in the U.S. But it’s important to recognize the signs of a concussion so a person can take the proper steps to treat the injury.
Signs of traumatic brain injury
There are some common physical, mental, & emotional symptoms a person may display following a concussion.
- Confusion or feeling dazed
- Clumsiness
- Slurred speech
- Nausea or vomiting
- Headache
- Balance problems or dizziness
- Blurred vision
- Sensitivity to light
- Sensitivity to noise
- Sluggishness
- Ringing in ears
- Irritability or other behavior or personality changes
- Difficulty concentrating
- Loss of memory
- Fatigue or sleepiness
- Loss of consciousness
- Forgetfulness such as repeating yourself
- Slowed response to questions
- Problems with sleep
- Depression
- Problems with taste or smell Related
Concussions in Children
- Because their heads are disproportionately large compared to the rest of their body, concussions frequently occur in young children. As kids enter adolescence, they experience brisk rapid height & weight gain. Both are components that make them more prone to accidents than adults.
- If a child has a concussion, an adult should monitor or observe them for the first 24 hours. Don’t give medications, including ibuprofen or aspirin, which might cause bleeding, to a child without talking to a doctor first.
What are the symptoms?
It’s important to watch for behavioral changes. Youngsters, especially, might not be able to fully communicate what they’re feeling, so it is critical to watch them closely or nearly. Symptoms of concussions in children include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Problems with balance
- Upset stomach or vomiting
- Fatigue
- Sensitivity to light & noise
- Mental fogginess & slowed thinking
- Problems with memory, concentration, or focus
- Feeling more irritable, sad, nervous, & emotional than usual
- Problems with sleep
What is the Diagnosis of concussion?
- Most people with concussions fully recover with suitable treatment. But because a concussion can be serious, protecting yourself is important. Here are a few steps to assess the patient which includes:
- Seek medical attention. A healthcare professional can decide how serious the concussion is & whether the person requires treatment.
- They’ll ask how the head injury happened & discuss the symptoms or chief complaint. The doctor may also interrogate some simple questions to the patient such as “Where do you live?” “What is your name?,” &” Who is the president of our country?” The doctor (provider) asks these questions to assess memory & concentration skills & capability.
- The doctor may conduct tests for the coordination & reflexes, which are both functions of the central nervous system. The doctor might also conduct a CT scan or an MRI to prevent bleeding & other serious brain injuries.
Concussion Treatment & Home Remedies
- If you don’t need hospitalization, the doctor will give you instructions or a protocol to follow. Experts suggest follow-up medical attention or under observation within 24 to 72 hours if symptoms worsen. To recover at home, you should:
- Take a break. If the concussion was sustained during athletic activity, stop play & sit it out. the brain requires some time to get heal properly so rest is key. Definitely do not start play on the same day. Athletes & children should be properly monitored by coaches upon resuming play. If they resume playing too soon, they risk a greater chance of having a second concussion, which can compound the destruction.
- Guard against repeat concussions. Repeat concussions cause aggregating effects on the brain. Successive concussions can have destructing consequences, including brain swelling, permanent brain damage, long-term disabilities, or even death. Don’t r go back to normal activities if you still have symptoms? Get a doctor’s permission so you can return to work or play with confidence.
- Treat pain with aspirin-free medications. the doctor will prescribe a medication to relieve pain & recommend an over-the-counter option.
What is the Prevention of Concussion?
A concussion is unexpected, so it is resilient to prevent. But there are several commonest precautions you can take to lessen or reduce the possibility of traumatic brain injury.
- Wear protective equipment. Participation in high-contact, high-risk sports such as football, hockey, boxing, & rugby can increase the likelihood of a concussion. Skateboarding, snowboarding, horseback riding, & rollerblading are also a threat to your brain’s health. Wearing headgear, padding, & mouth & eye guards can help to protect against traumatic head injuries. Wearing a bike helmet can lower or decrease the risk of traumatic head injury by 85%. There is also a new C-shaped collar-like apparatus called Q-Collar which can be exhausted by athletes. It applies compressive force to the neck & increases blood volume to help reduce or decrease the movement of the brain, which may occur because of hits to or on the head. Make sure that any equipment fits you properly/correctly & is well-maintained.
- Drive and ride smart. Always wear a seatbelt, obey posted speed limits, & don’t use drugs & alcohol, because they can impair reaction time.
- Don’t fight. Concussions are frequently sustained during an assault, & more men than women report traumatic head injuries.
- Reduce trip & fall hazards in the home. Clear clutter from floors & hallways & make sure that the home is well-lighted.
- Exercise regularly. It can give you stronger leg muscles & better balance, which can help stave off falls.
- Use home safety measures to protect your children. Install window guards & block stairways.
What is Post-Concussion Syndrome?
- Post-concussion syndrome is a condition that is typically correlated with a head injury. The head injury may be classified as a concussion or a mild traumatic brain injury. In general terms, post-concussion syndrome, or Post-concussion syndrome, is a medical problem that preserves for a period of time after a head injury has occurred. This period of time can compass from weeks to months.
Causes of Post-Concussion Syndrome
- In general, post-concussion syndrome follows the happening of an injury or trauma to the head. Not every people who suffer mild traumatic head injury experience post-concussion syndrome. This syndrome might be worse in people who have had previous concussions or head trauma. It may also be more severe or critical in those who have early symptoms of headache after injury, or who have mental changes such as amnesia, fogginess, or fatigue. Other risk factors include younger age & previous history of headaches. Women & older patients appear or are seen to be more susceptible to the development of post-concussion symptoms.
What is the Diagnosis of Post-Concussion Syndrome?
- Since symptoms can be vague & attributable to other reasons, it can be difficult to diagnose post-concussion syndrome. There is no positive test for post-concussion syndrome. Diagnosis is mainly based on a history of head injury & reported symptoms. A physical exam, & possibly a CT or MRI scan of the head, may be done to evaluate symptoms. Other tests might be given to rule out or to prevent other causes of symptoms, such as infection, bleeding injury to the brain, or poisoning.
What are the Symptoms of Post-Concussion Syndrome?
- Symptoms of post-concussion syndrome are frequently vague & non-specific.
- Commonly reported symptoms to include:
- Headache
- Dizziness
- Sleep problems
- Psychological symptoms like a depressed mood, irritability, & Anxiety
- Cognitive problems involving memory, concentration, & thinking
- Treatment of Post-Concussion Syndrome
- Most people with post-concussion syndrome are able to recover with rest & by minimizing stress.
- Most healthcare providers will also treat symptoms of post-concussion syndrome. For example, migraine or pain medications may be prescribed for those with headaches. A specialist such as a neurologist & /or psychiatrist may also be involved to treat mental health symptoms associated with post-concussion syndrome. Antidepressants and psychotherapy might be recommended.
- The Role of Education About Concussions
- For some patients, the best post-concussion treatment is education, as patients might experience anxiety about their long-term health. Patients need to be reassured that symptoms are frequently worse in the first week or two after the injury, but typically improve over a few weeks and resolve within a few months.
FAQ
Rest (for 1–2 days after the concussion)
Relax at home
Avoid or cut down on screen time
Don’t drive.
Avoid all sports & any activities (such as roughhousing with friends, or riding a bike or skateboard) that could lead to another head injury.
proper sleep
While most children & teens with a concussion feel better within a couple of weeks, some will have symptoms for months or longer. Talk with the children’s or teen’s health care provider if their concussion symptoms do not go away or if they get worse after they return to their regular activities.
Return to normal activities of daily living & normal social interchange is encouraged to speed recovery. Stress can make symptoms worse. Help calm yourself by resting in a quiet place & imagining a peaceful scene. Relax the muscles by soaking in a hot bath or taking a hot shower.
Physical & mental rest will help to heal
In the first few days after a concussion, relative rest is the most appropriate way to allow the brain to recover. the doctor will recommend that that person or patient physically & mentally rest to recover from a concussion.
During the first 24 hours, the person should avoid medications that can increase the risk of bleeding. These include or comprise aspirin, ibuprofen (Advil), & naproxen sodium (Naprosyn, Aleve). During the first 24 hours, acetaminophen (Tylenol) can be used to reduce or relieve the pain.
The 4-Step Concussion Recovery Protocol
Step 1: Get evaluated for assets as soon as possible after the injury.
Step 2: The patient should take Rest for one to two days after the injury.
Step 3: Start therapy & light activities.
Step 4: Gradually return to work or school & normal exercise.
Concussion tests help to assess brain function after a head injury. Most concussion tests consist of questionnaires & symptom checklists. Concussion tests check for things like alertness, memory, focus, how fast you think & the ability to solve problems. They also check the balance & coordination.
After experiencing a concussion, careful monitoring is required. This is normally for 48 hours. This is because the symptoms of concussion could also be symptoms of a more serious condition, such as subdural hematoma – bleeding between the skull & the brain.
Symptoms might include Mild head injury: Raised or increased, swollen area from a bump or a bruise.
Moderate to severe head injury (requires immediate medical attention)symptoms may include raised, swollen area from a bump or a bruise, plus:
Loss of consciousness.
Severe headache that does not go away.
Repeated nausea & vomiting.



One Comment