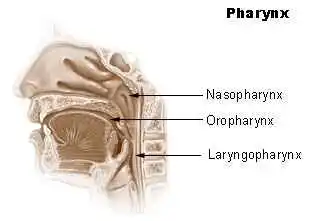
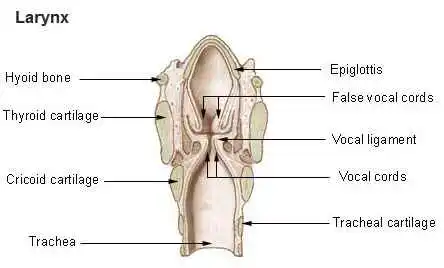
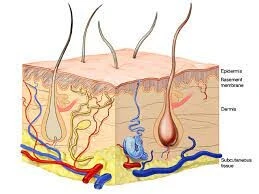
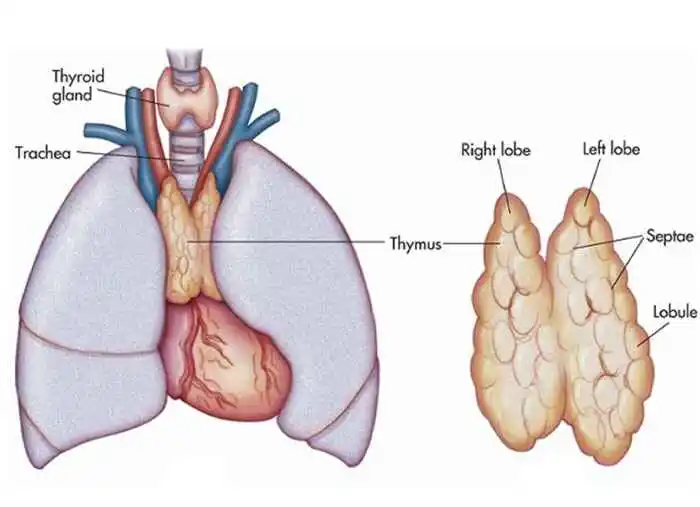
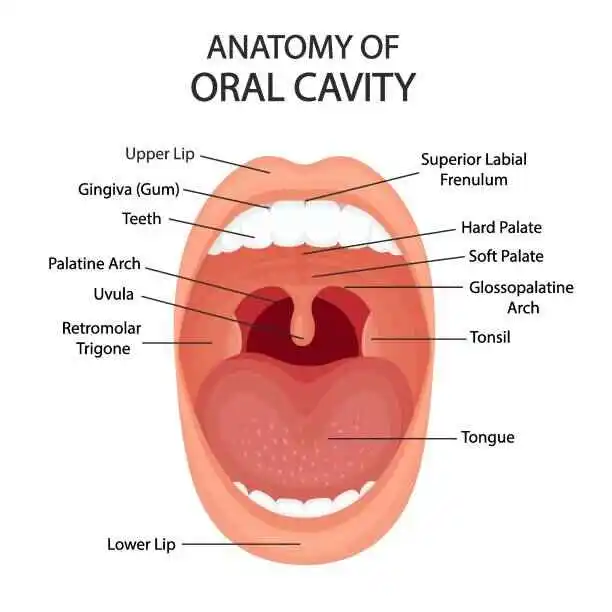
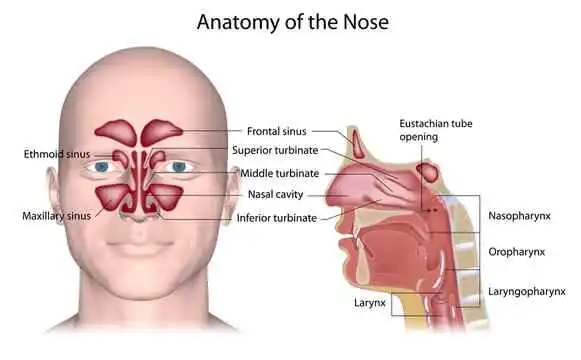
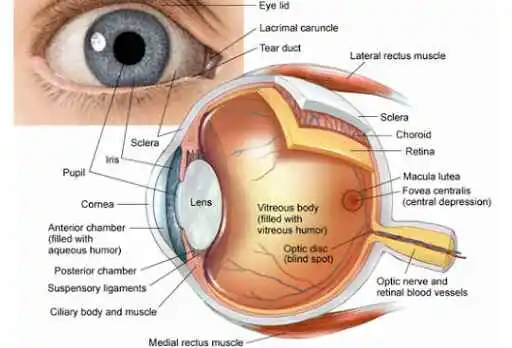
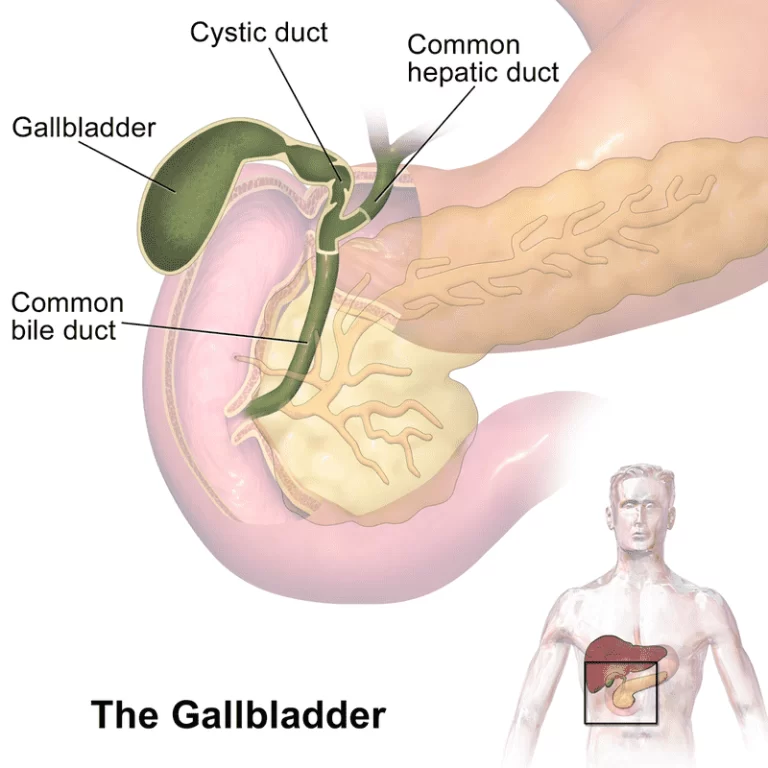
Broca’s Area
What Is Broca’s Area? The capacity to speak is related to a part of the frontal lobe’s dominant hemisphere, which is often the left hemisphere of the brain. Speaking and language comprehension tasks depend on Broca’s region of the brain. It is believed to use sensory information and interact with the motor cortex to coordinate…