Phalen’s Test and Reverse Phalen’s Test
Phalen’s Test and Reverse Phalen’s Test are two physical examination maneuvers used to assess for carpal tunnel syndrome, a condition characterized by compression of the median nerve at the wrist. These tests are commonly performed by healthcare professionals, such as physicians or physical therapists, to help diagnose carpal tunnel syndrome.
Table of Contents
The Phalen’s Test
- Phalen’s test is also known as the wrist flexion test.
- This test is used in a clinic to examine the wrist joint for neurological impairment.
- When a patient complains of hand numbness, the therapist performs this clinical examination.
Clinically Relevant Anatomy
- Median Nerve is formed by the spinal roots C6, C7, C8, and T1.
- C6 innervates the wrist extensors on the lateral side of the arm.
C7 innervates the wrist flexors via the middle finger.
Similar to how T1 innervates the medial side of the upper arm, C8 innervates the medial side of the forearm, ring finger, and little fingers.
Lumbricals 1 and 2 are innervated, Pronator teres, longus palmaris, flexor carpi radialis, and profundus flexor digitorum (lateral half), Opponens pollicis, Pronator quadratus, Flexor pollicis longus, Abductor pollicis brevis, Flexor pollicis, and Flexor pollicis brevis.
What is the purpose of Phalen’s test investigation?
- This Phalen’s test is used to study carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS).
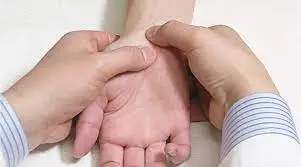
How do you perform the Phalen’s Test?

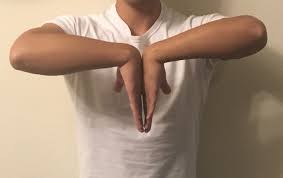
1.Phalen’s Test and 2.Reverse Phalen’s Test
- Another way to explain the standard Phalen’s test is that the patient holds their elbows bent between 0 and 30 degrees. The patient is then instructed by the therapist to supinate their forearm. Following that, the therapist maintains maximal palmar flexion of the wrist for 60 seconds. Every 15 seconds during the test, the patient will be asked to describe his/her feelings.
Reverse Phalen’s Test
Another name for the reverse Phalen’s test is the praying test.
What is the importance of the reverse Phalen’s test?
- This reverse Phalen’s test is used to examine the pathophysiology of the median nerve.
- Reverse Phalen’s test For two minutes, the patient holds a fully extended wrist and finger position. After 10 seconds, the pressure on the carpal tunnel rises (as opposed to 20–30 seconds for the traditional Phalen test). The strain on the wrist and carpal tunnel increase the longer the position is maintained.
- In comparison to the reverse Phalen test, which saw pressure changes of 34 mmHg at one minute and 42 mmHg at two minutes, the average pressure change for the Phalen test was 4 mmHg in two minutes. according to research comparing the variations in pressure between the two tests. Therefore, the reverse Phalen’s test could be a better clinical test for really compressing the carpal tunnel and inducing CTS symptoms.
What is the result of Phalen’s test and the reverse of Phalen’s test?
- A result of the reverse Phalen’s Test and the Phalen’s Test: If the patient’s symptoms are recreated in both tests, they are both considered positive.
- This test produces paresthesias, or sensations of numbness, burning, and tingling along the median nerve’s distribution, similar to those of carpal tunnel syndrome.
- Even if an action is prolonged for three minutes or more, the Phalen’s Test and reverse Phalen’s Test are both regarded as negative tests if the patient develops no pain or other symptoms.
What is the evidence of Phalen’s Test and of the reverse Phalen’s Test?
- The intra-rate reliability standard is standard, according to one study.
- The dependability between the raters appears to be great.
- The Phalen test has the following indicators: 0.64 for sensitivity, 0.75 for specificity, and 2.54 for a positive probability ratio.
- The Phalen test’s negative probability ratio was 0.49.
- Therefore, it is more likely that these alterations are related to nerve conduction studies in line with carpal tunnel syndrome (CTS) when a positive Phalen’s test is discovered.
- Reverse Phalen’s Test Sensitivity = 77
- Reverse Phalen’s Test Specificity = 40
Summary
The Phelan’s test is a provoking test used in the diagnosis of CTS. This happens when the median nerve at the wrist is pinched or crushed. It frequently hurts the worst at night. Driving and typing are two common daily tasks that may make the symptoms worse. The most frequent complaints are tingling and discomfort in the fingers and hands. discomfort at or around the wrist and numbness in the fingers, particularly the thumb, forefinger, and a portion of the middle finger, and arm ache that occurs less frequently. Due to blood vessel compression in the carpal tunnel, skin lesions in the area of the median nerve are possible.
FAQ
If the patient suffers pain and paresthesias along the median nerve’s distribution, which includes the thumb, index finger, and middle finger, the test is positive.
The Phalen’s test is a physical examination method used to determine whether carpal tunnel syndrome is present. Phalen’s test should not be performed if you have recently had wrist or hand surgery or had an accident.
In order to increase pressure inside the carpal tunnel and exhaust CTS paresthesia symptoms, the patient is typically actively examined for 60 seconds (the patient performs movements on their own). This could result in either it may positive or negative results.
The “Reverse Phalen’s Test” is another test that your doctor could advise you to do. The standard procedure for this reverse Phalen’s test is to maintain full wrist and finger extension for two minutes. Within 10 seconds following the wrist position shift in this test, the pressure in the carpal tunnel significantly increased.
Reverse Phalen’s Test is performed by placing the palms together to create bilateral wrist extension, which also increases pressure in the carpal tunnel.
This test is also known as Wormser’s Test.

One Comment