Squeeze Test of Ankle
Table of Contents
Introduction
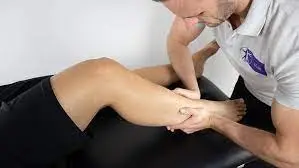
The squeeze test is a physical assessment test used to evaluate the integrity of the syndesmosis, a joint between the tibia and fibula bones of the lower leg. Syndesmotic sprains, or injury to the ligaments supporting the syndesmosis, are frequently diagnosed with it.
Purpose
The squeeze test is intended to assist in the diagnosis of ankle sprains that are syndesmotic. The literature that is currently accessible suggests doing the squeeze test, also referred to as the fibular compression test, in conjunction with the ankle external rotation test.
Technique
The purpose of the squeeze test is to evaluate the strength of the bones, syndesmotic ligaments, and interosseus membrane by compressing the proximal fibula against the tibia. When a fracture or diastasis occurs, pain is viewed as a good.
Diagnostic Precision:.75 ppm.
What Does the Ankle Squeeze Test Indicate?
The squeeze test’s reliability can be reported as moderate, with a kappa value of 0.50.
Alonso et al. describe a study that, in accordance with the results described by César PC et al.
The outcome of this test reveals:
30% is the sensitivity of the ankle squeeze test.
Specificity of the ankle squeeze test = 93.5%
which suggests a high sprain of the ankle.
Importance of the Test:
A tibiofibular syndesmosis injury is referred to as a “high ankle sprain” when it occurs independently. Ten to twenty percent of all ankle sprains result in syndesmotic sprains. Excessive dorsiflexion and external rotation of the foot, which frequently occur during skiing, football, soccer, and other turf sports, are the most frequent mechanisms of injury. The anterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (AITFL), the posterior inferior tibiofibular ligament (PITFL), the interosseous ligament, and the inferior transverse ligament are particularly important for the stability of the syndesmosis. After an injury, applying compression force in this area will frequently cause pain.
FAQ
What is the ankle squeeze test?
A clinical examination known as the “squeeze test” is used to identify “stable” syndesmosis injuries. When pain is felt in the region of the distal tibiofibular and interosseous ligaments with proximal compression of the calf, the test is considered positive.
What does a positive squeeze test indicate?
The squeeze test (or compression test) is often utilized to fast screen for arthritis in MCP and MTP joints. A positive test is traditionally assumed to show the presence of synovitis.
it identifies a sprain of the syndesmosis or a fibular fracture. applied by putting pressure on the tibia and fibula above the lesion. The (+) test If it’s a syndesmosis sprain, pain will be replicated throughout the distal tibiofibular junction and along the fibular shaft. Moderate interrater value of 0.5.
Reference
- Squeeze Test. (n.d.). Physiopedia. https://www.physio-pedia.com/Squeeze_TestSqueeze Test. (n.d.). The Student? Physical Therapist.
- https://www.thestudentphysicaltherapist.com/squeeze-test.htmlSqueeze Test | Special Tests. (2016, March 5). Special Tests. https://special-tests.com/ankle-foot-tests/squeeze-test/
- Ladva, V. (2022, February 8). Squeeze Test of the Ankle: Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/squeeze-test-of-ankle/



One Comment