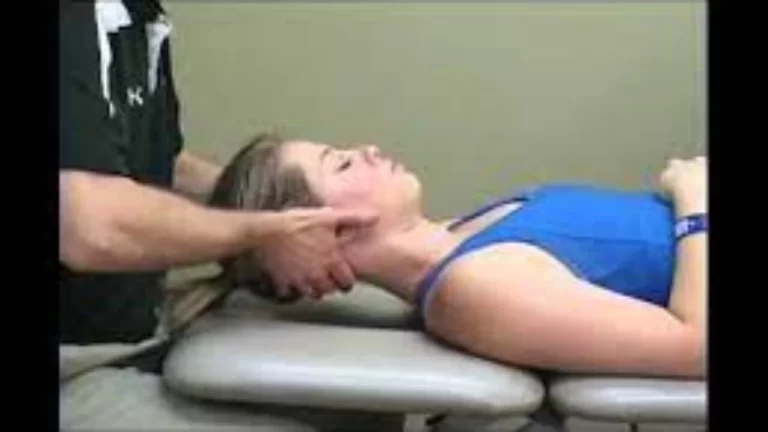
Sitting Root Test
Table of Contents
What is a Sitting Root Test?
The Sitting Root Test is a diagnostic tool used in physiotherapy to assess nerve tension, particularly involving the sciatic nerve. It helps identify nerve root irritation or compression by evaluating the flexibility and response of the lower limb nerves in a seated position.
This test is commonly used to diagnose conditions like sciatica, herniated discs, or other lumbar spine issues, providing valuable information to guide treatment and rehabilitation plans for patients experiencing lower back and leg pain.
Overview:
- The Siting root test is also called the modified slump test.
- In the clinic, the Siting root test is used to evaluate neurological dysfunction.
- The therapist uses this clinical test when a patient complains of back and radicular pain in the leg.
Objective:
- The goal of this test is to provide tension to the sciatic nerve’s dural sheath.
Procedure of Sitting Root Test
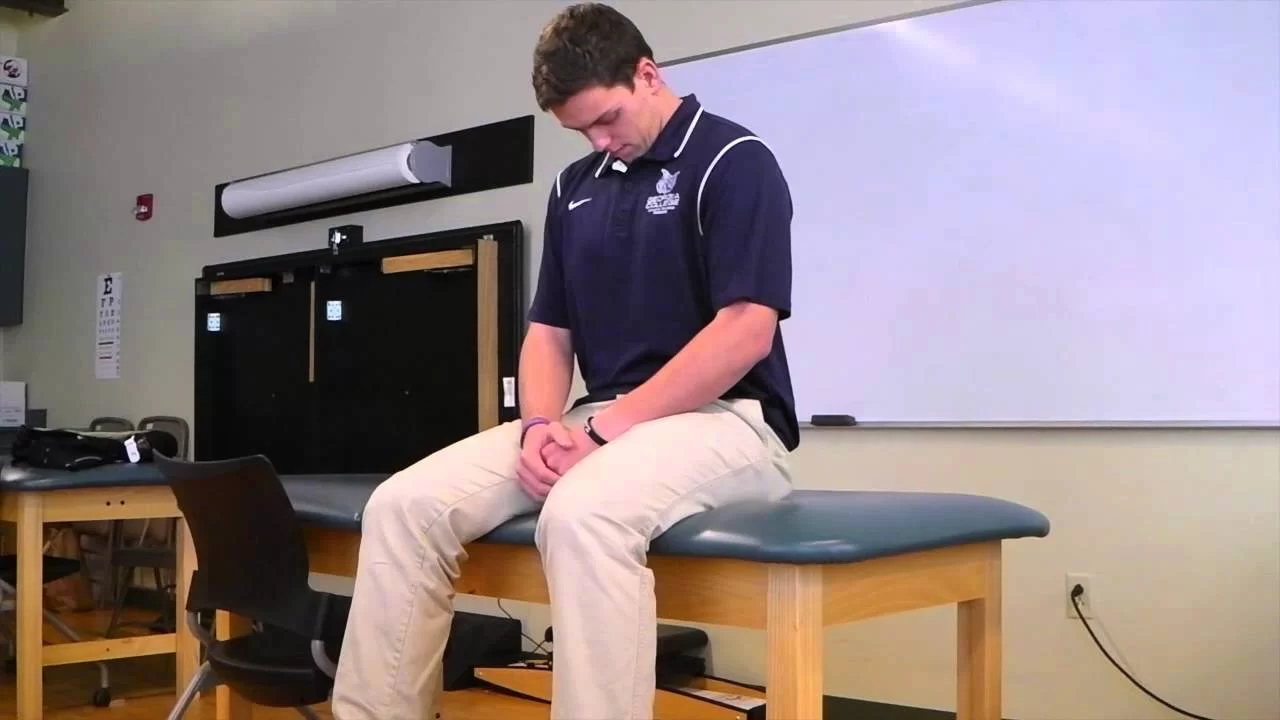
- The first sitting position of the patient during the examination.
- With their neck extended, the patient sits.
- The therapist directs the patient to extend the knee while maintaining a 90-degree flexion of the hip joint.
- If the patient is experiencing additional discomfort, it may indicate sciatic nerve strain.
- The examiner in the above case, a therapist, passively stretches the knee joint while Performing as though to inspect the foot.
Mechanism:
- As the patient shifts postures, the dural sheath surrounding the sciatic nerve is either stretched or strained.
Outcomes:
- Any sciatic pain (sharp, shooting, radiating pain) or recurrence of other neurological problems is a positive sign. This suggests that the spinal cord, dural lining, sciatic nerve, or nerve roots are impinged upon.
FAQs
What is a sitting root test?
In the sitting SLRT (Bechterew test): the patient is instructed to flex both their hips and knees while sitting at a table’s edge. After that, they are told to extend or elevate their extended knee, which simulates radicular pain. While they might be able to stretch each leg on its own, doing so simultaneously results in radicular pain.
What does a positive SLR test mean?
Its goal is to evaluate for irritation of the lumbosacral nerve root. Numerous disorders can result in a positive test; the most frequent one is lumbar disc herniation.
What does a positive slump test indicate?
The therapist will watch the patient for any lower back, hamstring, or sciatic nerve pain, discomfort, or restricted movement during the Slump Test. In the event of a positive test result, more testing or medical intervention may be necessary to address neural stress, disc herniation, or other nerve-related issues.
References:
Ladva, V. (2023, September 7). Siting Root Test – Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. Mobile Physiotherapy Clinic. https://mobilephysiotherapyclinic.in/siting-root-test/