Rectus abdominis muscle pain
When you feel pain lower region of the belly & tenderness in the abdominal area it is indicated as rectus abdominal muscle pain which is part of the abdominal muscle. you also feel pain or discomfort when you are touching the abdomen.
This pain is due to many reasons like muscle injury which leads to muscle strain & ruptures or tears this injury also triggers bleeding & the formation of an abdominal hernia. this pain is reduced by to RICE principle, pain medication & physiotherapy treatment.
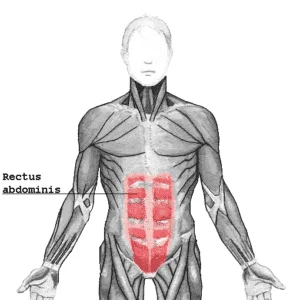
Table of Contents
What is Anatomy of rectus abdominis muscle?
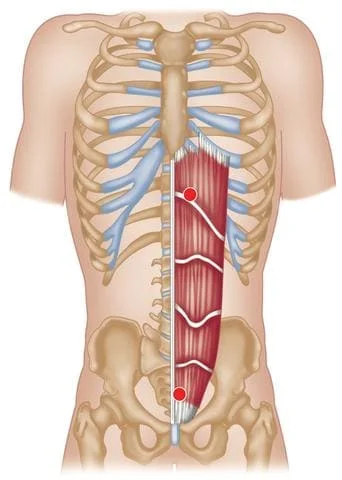
- This rectus abdominis is a large muscle in the center of the abdomen that extends from the ribs to the front of the pubic bone.
- This rectus abdominis muscle spans from the pubic bone to the 5th – 7th rib & the xiphoid process, which is the lowest part of the breastbone.
- The function of The rectus abdominis muscle is the flexion of the spine & increase the intraabdominal pressure, which is created during coughing.
- The purpose of this muscle is to allow to you move the portion of the body between the pelvis & rib cage.
What are the Causes of the rectus abdominis muscle pain?
Muscle strain:
- It is possible that strain occurs in the other muscles of the abdomen but most abdominal strains occur in the rectus abdominis muscle of the abdominal muscle.
- This strain occurs in physical labor & athletic activities.
- The Labor-related causes of the strain include sudden twisting motions & the lifting of heavy objects.
- The Athletics-related causes of the strain include weightlifting, engaging in skating or hockey, pole-vaulting, performing sit-ups & swimming the breaststroke.
- When you are overweight & out of shape, you also develop abdominal strain when you are performing physical activities without proper preparation.
- In some & rare cases, prolonged, coughing & energetic sneezing are also triggered to an abdominal strain.
- Levels of the muscle strain Injury:
- This muscle strain comes in the three levels & degrees.
- First-degree muscle strain = rectus abdominis muscle is abnormally stretched but intact.
- Second-degree muscle strain = stretching is severe enough when occurs to trigger a partial muscle tear.
- Third-degree muscle strain = occurs to complete tear which is frequently involved in the separation of the muscle from associated tendons.
- When occur to third-degree strain is associated with a tear in the abdominal wall, which leads to developing a hernia.
Postural stress:
- Some postures are given to stress on the rectus abdominis muscle which produces pain in the. muscle.
- In the Sitting position – bent forward position this occurs mostly due to a lack of back support.
- “Victim posture” = crouched & slouched back & bent forward position.
Emotional stress:
- This stress increases the tension of the muscles in general, mostly in all the flexors because the emotional stress is related to fear, which is caused mostly unconsciously
- So the body’s response to fear is always the activation of the flexor muscle groups or at least an increased tension in the muscle.
- Common reasons for emotional stress…
- If You are in an unfulfilling relationship.
- When You pursue a career you don’t like this career but can’t & don’t have the guts to quit.
- When you feel Huge financial problems.
- When occurs to Serious disease & death of a close friend/ family member.
- All these examples put massive amounts of stress on the rectus abdominis muscle.
Active stress & trauma:
- Below are some points that put strong mechanical forces on the rectus abdominal muscle.
- Excessive training of the abs
- Surgery on the abdomen
- Heavy weightlifting
- Strong activation of the abs on stool due to constipation
- Some causes that produce Trigger points of muscle pain :
- Weak core muscle strength & poor posture
- Pain coming from organs (as a secondary symptom)
- Severe period pain in women
- Endometriosis
What are the Symptoms of the rectus abdominis muscle injury?
- Injury always leads to pain in the injury area.
- This pain is also produced by stiffness in the muscle after prolonged sitting.
- This pain is also felt during sneezing, coughing & laughing.
- This muscle pain is felt in the lower region of the belly as well as in the lower & mid-back.
- You feel too impaired & painful movements mostly of which activity need to strong activation of the rectus abdominal muscles.
- When you try to lean forward.
- You also feel swellings & spam in the area of the pain.
- You always feel trigger points in the muscle pain area.
- Other Symptoms which feel very very in people include :
- Indigestion
- Feeling of fullness
- Heartburn
- Stomach cramping
- Vomiting
- Cardiovascular chest pain which leads to heart attack
- Dysmenorrhea & (excessive) menstrual pain
- Acute appendicitis
What is treatment for the rectus abdominis muscle pain?
RICE principle:
When you feel pain doctor advises to RICE principle in the starting phase as a primary treatment.
- R – rest = When the pain occurs doctor is always advised to rest for sometimes for release to muscle pain & swelling.
- I – ice = You can apply ice on the area of pain for 20 minutes release to swellings & muscle pain but always apply the ice with the help of a towel between the skin & ice prevent to ice burn, you can also be used to ice pack & frozen peas for ice therapy.
- C – compression = You can also apply compression bandage release to muscle pain, and swelling but it is not possible for this muscle.
- E – elevation = You must be elevated to the injured part for release to muscle pain & swelling with the help of a pillow placed under the feet.
Pain medication:
- You can also take non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs = NSAIDs like aspirin & ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) which help to release the muscle pain.
- You can also apply pain relieve gel & spray like volini gel & spray on the area of muscle pain release to muscle pain & swelling.
What is Physiotherapy treatment for rectus abdominis muscle pain?
Physiotherapy treatment helps you release pain, swelling, spam & tightness of the muscle pain.
The physiotherapy treatment includes massage, electrotherapy, stretching exercise & strengthening exercise
Massage:
When you try to massage the rectus abdominis muscle, the first difference to pain created by to intestines.
- To check the different pain contract the muscle, but the fingers on the area you want to massage & then loosen it up again.
- Now slowly palpate the area of pain & press into the belly & try to search for tender spots.
- When you find a painful location then exert only as much pressure as needed to initiate to pain.
- Then contract to the abs muscle again while increasing the pressure on the muscle.
- When the pain becomes worse, it is a sign that this pain is created by the rectus abdominis muscle.
- When the pain decreases, it is indicated to visceral problem.
- The best way to massage the rectus abdominis is by lying on the back & using the finger technique.
- This means, you are searching for the tender spots & then do the massage each of them with very short & slow strokes.
- Make sure to keep the muscle relaxed & only focus on the tender spots.
- Always use a maximum of 15 strokes on each tender spot.
- For treating the trigger points, it is better to keep the massage sessions short & repeat them frequently.
Electrotherapy treatment:
To relieve the swellings, spasms & pain therapist is advised to you electrotherapy treatment.
In electrotherapy, the treatment therapist is used to many machines.
- When the trigger & tender points are present therapists apply US = ultrasound therapy for the release of muscle pain.
- This treatment is applied with the help of gel & applied for 5 to 10 minutes on the area of pain.
- This therapy helps you release pain & swelling.
- Reduce to pain therapist is applied to SWD = short wave diathermy, IFT = Interferential Therapy, TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation on the area of pain.
- SWD = Short wave diathermy is hot therapy for release to spams on the area of pain.
- IFT = Interferential Therapy & TENS = Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation is applied with the help of gel & electrodes on the area of pain.
- This therapy is applied for 10 minutes to the area of pain.
Exercise therapy:
After following the RICE principle for 2- 3 days & with the help of pain medication, you feel released from pain.
when you feel too comfortable & release your pain then the physiotherapist advises to you exercise therapy reduce to muscle weakness & tightness.
The exercise therapy includes Stretching & strengthening Exercises.
Stretching exercise is help to you relive to muscle tightness & strengthening Exercises is help to you relive to muscle weakness.
Stretching exercise:
After the follow of electrotherapy for release to muscle pain by physiotherapist then the therapist is advised to stretch for release to muscle tightness.
This stretching is applied when your pain is release .
Stretching exercise is help to you for release to muscle pain & tightness .
- Basic Standing Stretch
- Belly Down Stretch
- Stability Ball Back bend
Basic Standing Stretch:
- This stretching is the most basic stretch for the rectus abdominis muscle.
- You are Standing tall with your feet together & raise your arms over your head.
- Your fingers are extended so the palms of your hands are facing the ceiling.
- Lift the chest as you arch your back.
- Must be Keep the arms extended toward the ceiling as you move the arms behind the head.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds & rest for 30 seconds.
- Perform 3 times in 1 time & 3 times per day.
Belly Down Stretch:
- This stretching is commonly known as the Cobra pose in yoga.
- You are lying on the stomach means in a prone position with the legs extended behind you so that the tops of the feet are in contact with the floor.
- Bend the elbow joint & place the palms close to the body or flat on the ground even with the chest.
- While must keep the front of the pelvis in close contact with the floor.
- Then extend the elbow joint so that the back arches & the front of the body raises from the floor.
- Pull the shoulder joint back as you push your chest up.
- Must be head remains in a neutral position as the eyes directly face the wall in front of you.
- Arms help support the body, so be sure to keep the abdominals & back relaxed for the duration of the stretch.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds & rest for 30 seconds.
- Perform 3 times in 1 time & 3 times per day.

Stability Ball Back-bend:
- This stretch allows you to perform a back-bend while offering body-weight support.
- For stability, this stretch is performed with the ball next to a wall.
- You are lying with the back over the stability ball so both the upper & lower back is touching the ball.
- Legs are spread, which provides greater balance during the stretch & increases the size of your base.
- Then Stretch the arms behind so that palms touch the floor &fingers are facing the stability ball.
- Allow the body to fall deeper into the stretch by relaxing the abdominals & back as they take the shape of the ball.
- Hold this stretching position for 30 seconds & rest for 30 seconds.
- Perform 3 times in 1 time & 3 times per day.
Strengthening Exercises:
After the follow-up electrotherapy, massage releases muscle pain by physiotherapist then the therapist advises to you do strengthening exercises release to muscle weakness.
This strengthening exercise is always advised when you feel to release of pain.
This all-strengthening exercise will help you with muscle weakness & pain.
- Abdominal crunch
- Plank
- Abdominal roller
- Forearm Plank
- Reverse Crunch
- Scissor Flutter Kicks
- Toe Taps
- Jack Knife Crunch
Abdominal crunch:
- The patient is lying on the back with the knee joint bent.
- Place the hands behind the neck but don’t pull the neck forward.
- Then Lift the head, neck & shoulders off the ground & slide the hands up, towards the knee joint.
- Must be Try to keep the same gap between the chin & chest to avoid straining the neck.
- Then Slowly return to the starting position.
- Do the 5 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Plank:
- This exercise starts with a push-up position& raises the body so that the elbows and joints are completely straight.
- The hands should be facing directly forward.
- Inhale & engage the core.
- As of exhale position, float one leg upwards so that it is in line with the back.
- Then toes on the raised leg should be pointing away from the body.
- Then Return the leg to the start position after one breath & repeat with the opposite leg.
- Do the 5 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Abdominal roller:
- It is an advanced exercise & should only be done later in the exercise program.
- The athlete is pushed the roller out whilst on hands & knees.
- Then hold the stretched-out position briefly then return to the starting position.
- Do the 5 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Forearm Plank:
- You are lying down with your forearms on the floor.
- The elbow joint beneath the shoulders & legs is extended behind you.
- Rise on the toes so that only the forearms & toes touch the floor.
- Put the body in a straight line a few inches off the floor.
- Bring to belly button to the spine, by contracting the deep abdominal muscles & tightening the buttocks & upper body.
- Do the 5 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Reverse Crunch:
- You are lying down on the back with the knee joint bent & thighs perpendicular to the ground, hands at the sides & feet on the floor.
- Contract the abdominal muscles & raise the hips toward your rib cage.
- Then lift the tailbone off the ground & bring the knee joint towards the chest.
- Hold this position for 10 counts & Slowly lower back to the starting position.
- Do the 5 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Scissor Flutter Kicks:

- You are lying down on the back with your legs extended & arms by your sides.
- Using an exercise mat helps reduce the pressure on the lower back.
- Press the lower back into the mat & tuck the pelvis.
- Lift both legs off the mat, about 6 inches to 10 inches from the floor.
- You should not feel pain in the lower back & Lower leg toward the floor.
- When the leg gets close to the floor then lift the other leg.
- Then Continue scissoring the legs by slowly switching them up & down.
- Do the 5 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.
Toe Taps:

- You are lying down on the back with the knees bent & feet lifted into a tabletop position.
- Press the lower back into the mat & engage the core.
- Then Slowly lower the right foot till the toe taps the floor.
- The foot is put in a flexed position.
- Contract the abdominal muscles & raise the right foot back up to the table top.
- Do the 5 times in 1 session & 3 sessions per day.

Jack Knife Crunch:
- You are Lie flat on an exercise mat & extending the arms straight back behind the head.
- Bend the spine & at the same time, raise the legs & arms to meet in a closed jackknife position.
- Exhale on the way up & inhale on the way down
- Make sure not to arch the back when lowering the leg
- Then Try to keep the neck in one line with the back.


One Comment