Manual Muscle Testing of Knee
Manual muscle testing of the knee is a procedure used to assess the strength and function of specific muscles around the knee joint. It involves applying resistance against the movement of a muscle group to determine its strength. Here’s a general guide on how to perform manual muscle testing for the major muscle groups around the knee:
Table of Contents
Knee flexion
Testing muscles
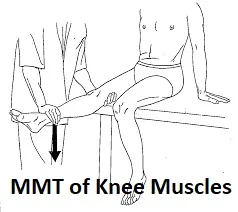
The knee flexors muscles involved the group of hamstrings muscle, sartorius, gastrocnemius, plantaris, gracilis, and popliteus muscles. The Hamstrings group of muscles are the chief knee flexors
- Biceps femoris
- Semitendinosus
- Semimembranosus
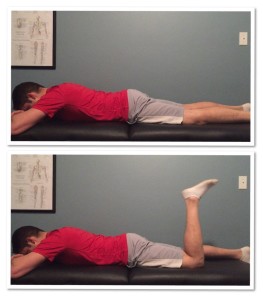
Patient’s position
The patient has to be in a comfortable position.
Patients suppose to wear comfortable clothes in which he or they can do complete movement without any restrictions.
to assess grades 3 to 5 Patients should be lying on their stomachs, knees in extension.
For assessing grades 0-2 Patient should be in a side-lying position, knee in extension.
Therapist’s position
The therapist is supposed to stand at examine side in the prone position of the Patient.
While the patient is in a side-lying position, the therapist has to stand behind the patient and give support to the lower limb with movement as required.
How to test?
The patient himself does the knee flexion in the available range.
To assess grades 4 to 5 give resistance force with the distal tibia and fibula in the opposite direction to knee flexion
The therapist should then grade the strength of the knee flexors according to the criteria listed above, ranging from grade 0 (no evidence of muscle contraction) to grade 5 (able to fully flex the knee against maximal resistance).
The grading system is as follows:
- Grade 0: No contraction felt
- Grade 1: A visible flicker or trace of contraction felt, but no movement
- Grade 2: Movement with gravity eliminated (i.e., horizontal)
- Grade 3: The movement should be against gravity but not resistance
- Grade 4: The movement should be against gravity and mild to moderate resistance
- Grade 5: Normal strength against full resistance
The therapist needs to ensure that the patient is using only their knee flexors to perform the movement, and not compensating with other muscles such as the hip flexors or back muscles. The therapist should also ensure that the patient is not experiencing any pain or discomfort during the test.
Overall, knee flexor manual muscle testing can provide valuable information about a patient’s muscle strength and function, which can help guide treatment and rehabilitation plans.
Knee extensions
Testing muscles
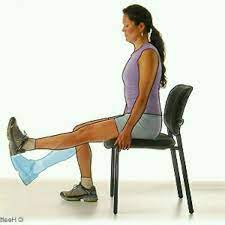
Patient’s position
The patient has to be comfortable sitting.
Patients have to wear comfortable clothes so that he or they can do the complete movement without any restrictions.
For assessing grades 3 to 5 Patient should be in a short sitting position.
For examination, grades 0-2 Patient is supposed to be in a side-lying position.
Therapist’s position
The therapist should kneel near the patient and fix the femur on the examined side.
When a patient is in a side-lying position, the therapist to give support the lower limb with movement as necessary.
How to test?
Stabilize the thigh: The therapist should place one hand under the patient’s thigh to stabilize it.
Place hand on lower leg: The therapist should place the other hand on the lower leg just above the ankle.
Ask the patient to straighten their knee: The therapist should ask the patient to straighten their knee by pushing their foot towards the ceiling.
The patient himself does the extension of the knee
For assessing grades 4 to 5 give resistance force with the distal tibia and fibula in an opposite direction to knee extensions.
Resist the movement: The therapist should resist this movement by pushing down on the lower leg.
Increase resistance: Gradually increase the resistance until the therapist feels that the patient is exerting maximum effort.
Grade the strength: The therapist should grade the strength of the knee extensors according to the criteria listed above, ranging from grade 0 to grade 5.
The grading system is as follows:
- Grade 0: No contraction can feel
- Grade 1: A visible flicker or trace of contraction can feel, but no movement occurs
- Grade 2: Movement with gravity eliminated, ex., Horizontal
- Grade 3: The movement should be against gravity but not resistance
- Grade 4: The movement should be against gravity with mild to moderate resistance
- Grade 5: Normal strength against full resistance
Ensure proper technique: Ensure that the patient is using only their knee extensors to perform the movement, and not compensating with other muscles such as the hip extensors or back muscles.
Check for pain or discomfort: Ensure that the patient is not experiencing any pain or discomfort during the test
Precaution
- Check for contraindications: Before performing the knee manual muscle testing, the therapist should check for any contraindications such as recent surgery, acute injury, or inflammation in the knee joint.
- Warm-up: The therapist should ensure that the patient’s muscles are properly warmed up before performing the test to prevent any injury.
- Proper positioning: The patient should be in a comfortable position with proper support to prevent any unnecessary stress on the knee joint.
- Gradual increase in resistance: The therapist should gradually increase the resistance during the test to prevent any sudden movements that may cause injury.
- Communication with the patient: The therapist should communicate with the patient throughout the test to ensure that they are not experiencing any pain or discomfort.
- Safety precautions: The therapist should take necessary safety precautions such as using proper equipment and ensuring a safe environment to prevent any accidents or injuries during the test.
FAQ
The quadriceps, hamstrings, and gastrocnemius muscles are typically tested during knee manual muscle testing.
Knee manual muscle testing is important for diagnosing and monitoring conditions that affect the muscles surrounding the knee joint, such as knee injuries, arthritis, and neurological disorders. It can also help guide treatment planning and rehabilitation efforts.
Knee manual muscle testing should only be performed by trained healthcare professionals who have been properly trained in the technique. Additionally, it is important to consider any contraindications or precautions before performing the test on a patient.