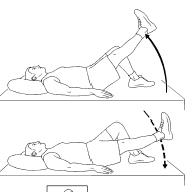
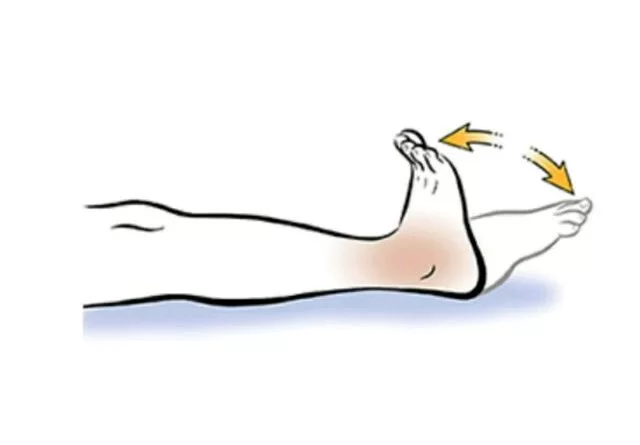
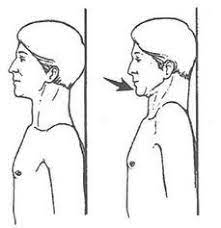
Best Sternocleidomastoid Muscle Stretching Exercise
What is the Sternocleidomastoid stretch? What are the benefits of SCM stretch? There are some common benefits of SCM stretching: Types of Sternocleidomastoid stretch There are some traditional methods to perform SCM stretching: Sternocleidomastoid stretch 1 Sternocleidomastoid stretch 2 Sternocleidomastoid stretch 3 SCM stretch has some variations: Chair leans Neck elongation Head tilts Revolved Triangle…