Endomorph Body Type
Table of Contents
Introduction
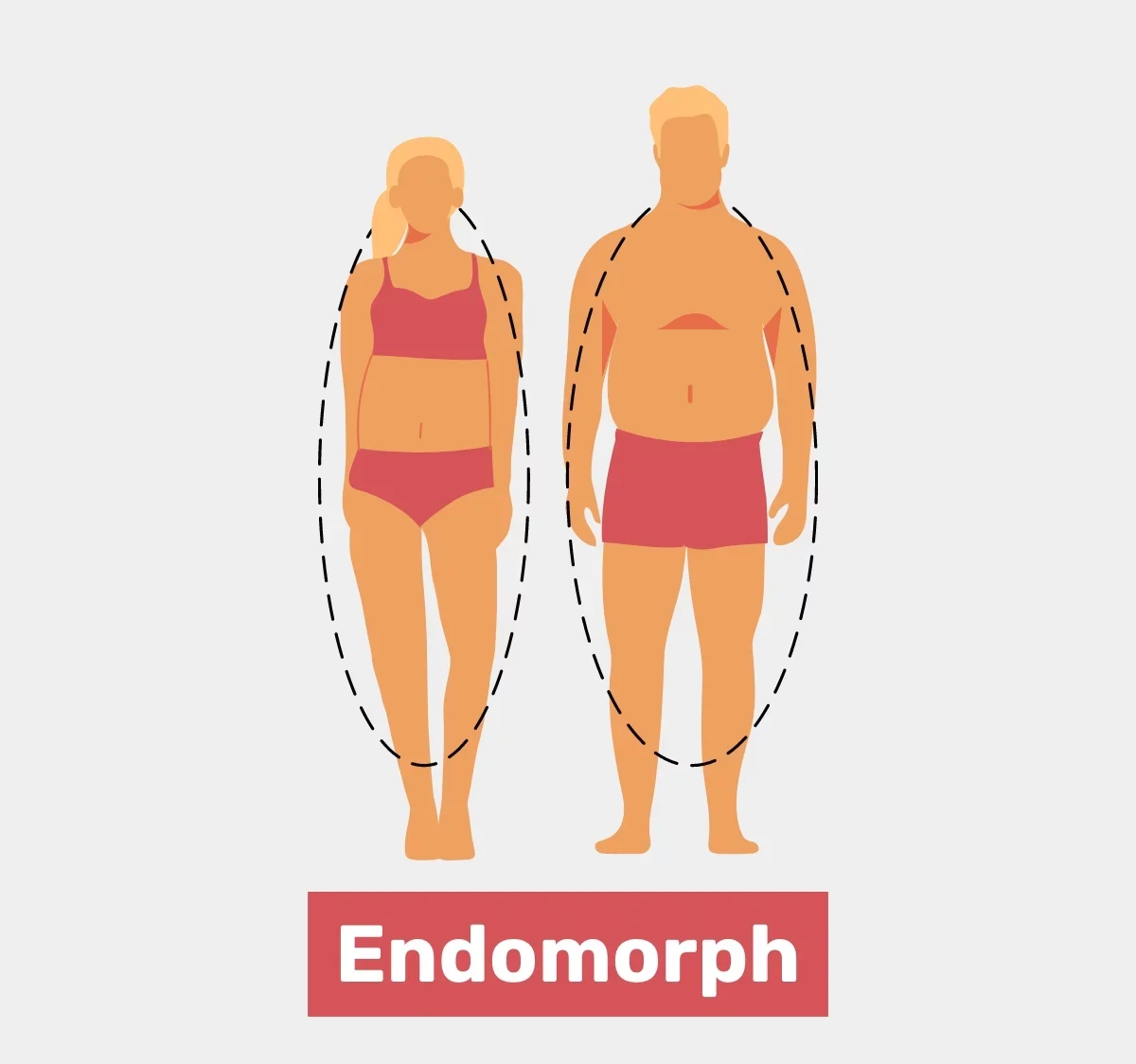
The endomorph body type is characterized by a naturally higher percentage of body fat and a rounder physique. People with this body type often have a larger bone structure, broader hips, and a tendency to gain weight more easily, especially in the lower body.
This body type is also associated with a slower metabolism, making it challenging to lose weight. However, with the right approach to diet, exercise, and lifestyle, individuals with an endomorph body type can achieve a healthy and fit physique.
Somatotypes are based on the concept that all people have a certain body type from birth. Body type, or somatotype, is inherited and manifests as skeletal structure and body composition. The endomorph body type has more muscle and fat. These folks are overweight but not necessarily obese. If you have an endomorph body type, you know how simple it is to acquire weight yet how difficult it is to remove it and develop muscle. Special diet and exercise routines can help you attain peak health and fitness.
Endomorphs typically have a solid, soft body shape. Endomorphs acquire weight quickly. Endos are often shorter in stature, having thick arms and legs. Muscles are powerful, especially in the upper legs. Endomorphs are naturally powerful in leg workouts such as the squat.
Endomorph characteristics include the following:
- Body is round and soft.
- Gains muscle and fat quickly.
- Is often a short “Stocky” build
- Fat loss is difficult for those with round bodies.
- Slow metabolic rate
- Muscles that are not adequately defined
What is an endomorph?
Depending on his studies, he determined that we each have a genetic body type, or somatotype, that determines whether we’re leaner, heavier, or somewhere in between, depending on our skeletal frame and body composition. Because of this hereditary body type, achieving weight reduction and exercise objectives frequently needs an individualized plan.
It is believed that endomorphs have less muscle mass and a higher percentage of body fat. They are frequently heavier and rounder, although they are not always obese. persons with endomorphic bodies are more sensitive to calorie consumption than persons with other body types due to their physical structure.
Endomorphs must carefully monitor their food intake to avoid consuming more calories than they expend. Another feature is a bigger frame and an unwillingness to reduce weight.
These traits distinguish the ectomorph from the mesomorph and vice versa. Because of their quicker metabolisms, ectomorphs can eat more food with no weight gain. They also have smaller joints, a smaller frame, and a smaller body size.
As opposed to this, the mesomorph somatotype is halfway between the ectomorph and the endomorph. These people may have a bigger skeletal structure, but they have a smaller amount of body fat. They may readily acquire muscle and shed weight.
What should an endomorph eat?
If you have an endomorphic physique and want to reduce weight or develop muscle definition, you should explore a body-type-specific training regimen and nutrition.
Endomorphs have a slower metabolism. Because you don’t burn calories as quickly as ectomorphs and mesomorphs, extra calories are more likely to be stored as fat.
Some believe endomorphs are also less able to tolerate carbs, thus the paleo diet may be the optimal diet for your body type, with greater fat and protein consumption and a lower carbohydrate intake. This diet can assist you in losing body fat while maintaining your energy level.
Good fat and protein sources include:
- Macadamia seeds
- Egg yolks beef olive oil
- Seafood that is rich in fat
- Walnuts with cheese
You do not, however, have to forgo carbs. Carbohydrates are a great source of energy. When you cut carbohydrates out of your diet, you may experience weariness.
If carried too far, a low-carb diet might create gastrointestinal problems. The key is to choose the proper carbohydrates. Pay special attention to complex carbohydrates found in fruits, whole grains, legumes, and vegetables, especially starchy vegetables like potatoes and tubers.
Consume less simple carbs. These meals include a lot of sugar and calories, which can lead to fat accumulation. Simple carbohydrates include things like cakes, cookies, spaghetti, white bread, and white rice.
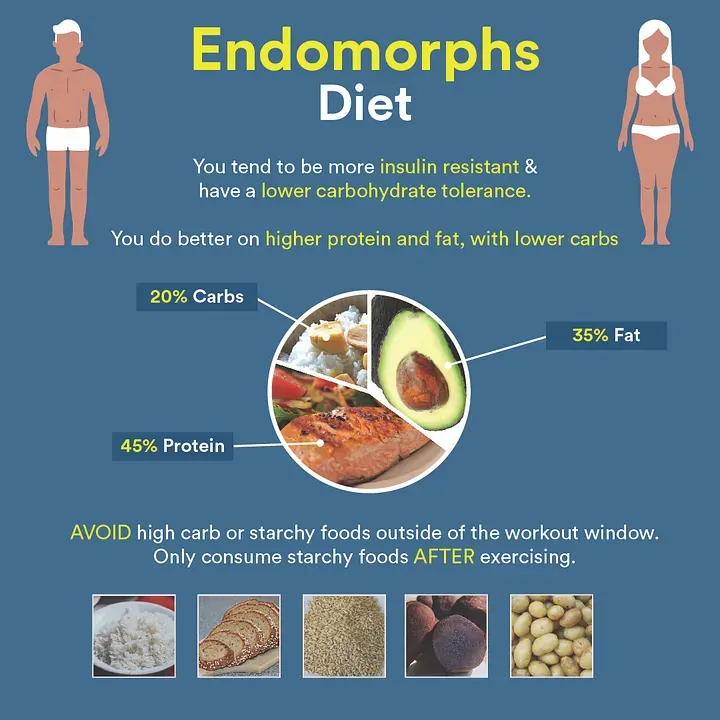
Fruit is a nutritious supplement to any diet. Fruit should be consumed in moderation if you are carbohydrate-sensitive. When planning your daily meals, the American Council on Exercise recommends using the following formula:
- 30% of carbs
- Protein content of 35%
- 35% body fat
Portion management is also essential when it comes to losing body fat as an endomorph. This assists you in avoiding excessive calorie consumption. Eating 200 to 500 less calories than you typically do can also aid in your weight reduction efforts.
Dieting alone, say proponents of the plan, may not be enough to lose weight since endomorphs have a tougher time shedding body fat. Physical activity should also be incorporated into your everyday routine. This is a popular suggestion for anybody trying to enhance their general health.
An excellent fitness regimen incorporates both weight training and aerobic training.
Endomorph Hybrid Varieties
A hybrid body type is also possible. Some people are skewed meso-endomorphs, which have bigger bodies that are powerful but lack developed muscles. If this is you, he offers a combination of strength training and cardio for exercise, as well as a fat-loss eating plan.
You might also be a mesomorph or an ectomorph with a bigger waist, which some people call an apple shape. This may increase your risk of metabolic issues, thus Catudal suggests monitoring carbs in the same way as the endomorph suggestions below.
Popular Diets That Endomorphs May Benefit From
Because endomorphs are more likely to develop insulin resistance and carry more body fat, Catudal recommends a balanced diet low in carbohydrates to aid in fat reduction.
Indeed, one study found that cutting carbohydrates from your meals can enhance insulin function within a day and may be a potent approach to minimize your risk of prediabetes. Furthermore, because fat burns fewer calories than muscle, an endomorph’s metabolism is likely to be slower than that of a naturally strong mesomorph, implying that you should eat fewer calories at the start of the diet.
Catudal mostly indicates paleo-diet-style regimens (also known as a caveman diet), which emphasize fruits, vegetables, meats, seafood, nuts and seeds, and oils. Though most paleo diets avoid legumes, he recommends beans and lentils, which are high in weight-friendly and digestion-slowing fibre. But grains are part of an endomorph diet.
List of Endomorph Foods
Endomorphs, according to conventional wisdom, perform best when they focus on lowering calorie consumption while increasing protein, healthy fats, and low-carb diets. According to Catudal, this strategy will help individuals lose weight, slim down, and improve their insulin resistance.
you can eat the following items.
- Cod Salmon
- Yogurt
- Milk
- Vegetables and fruits
- Berries
- Apples
- Pears
- Asparagus
- Zucchini
- Tomatoes
- Onions
- Spinach, kale, and romaine lettuce
- Seeds and nuts
- Butter made from nuts and seeds
- Almonds
- Pistachios
- Seeds of sunflower
- Cauliflower seeds
- Grains and root vegetables
- sweet potatoes
- Quinoa Squash
- Brown rice, beans, and oats
- Meat and seafood
- Turkey Chicken
Appropriate dishes consist of:
- Chicken breasts
- Seafood, which includes fish and shellfish;
- Fruits;
- Vegetables, which include raw root vegetables;
- Nuts and seeds;
- Herbs and spices;
- Natural sugars, like honey, maple sugar
- Oil
Foods to remain out of:
Paleo diets contend that the human body is incapable of metabolizing food.
- Grain and flour legumes, such as cashews, peanuts, beans, peas, and tofu;
- Processed sugars; root vegetables such as potatoes, tapioca, parsnips, sweet potatoes, and yam that shouldn’t be eaten uncooked
- Meals that include sodas, coffee alcohol, and yeast juices
- Dairy items
- Processed meats
- Salt
Two examples of the many paleo diet variations are the Autoimmune Paleolithic diet and the Paleolithic ketogenic diet.
Exercise for Endomorph Body Type
Physical activity is essential for optimum health. Because endomorphs struggle to shed weight and have a tendency to store fat, this is especially true for them. To achieve your health objectives and an ideal weight, you may require a specialized food plan and workout regimen.
Endomorphs have narrow shoulders and excess fat in the lower belly, hips, and thighs. This distribution of body weight and fat makes losing weight difficult and necessitates specific exercise approaches. To lose weight, you must, of course, combine these with a healthy diet.
Endomorphs require a lot of exercise. It promotes muscular growth and metabolism. The endomorph somatotype has a slower metabolism and more fat. You must dedicate yourself to a lifelong workout program in order to achieve and maintain lean body mass.
Endomorph exercises
Weight training and aerobics are essential components of any endomorph’s fitness regimen. Muscle building is not difficult, but you must avoid overtraining. Because your body type is prone to gaining weight quickly, your workout plan should burn calories while creating a negative calorie balance.
Cardiovascular exercise.
This is an essential component of your fitness routine. You should do 30 to 60 minutes of aerobic workouts at least twice a week. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) is an excellent alternative for increasing stamina and burning calories.
Aside from these regular workouts, you should make it a habit to move throughout the day. Seek out ways to stay active rather than just rest. Getting up earlier, watching less television, and making a list of workout objectives will enhance your health.
Weight lifting.
It provides you with three benefits:
- Increasing lean muscle mass
- Body fat reduction
- Increasing your metabolism
Increased muscle mass raises your resting metabolic rate and boosts the usage of fat for energy production. Your primary muscle groups—your legs and back—would be the focus of an appropriate training regimen. Each exercise should include at least 15 repetitions (reps). You should do circuit training with brief rest periods between sessions.
Here is some exercise should try the following moves:
Lunges followed by a lateral rise-
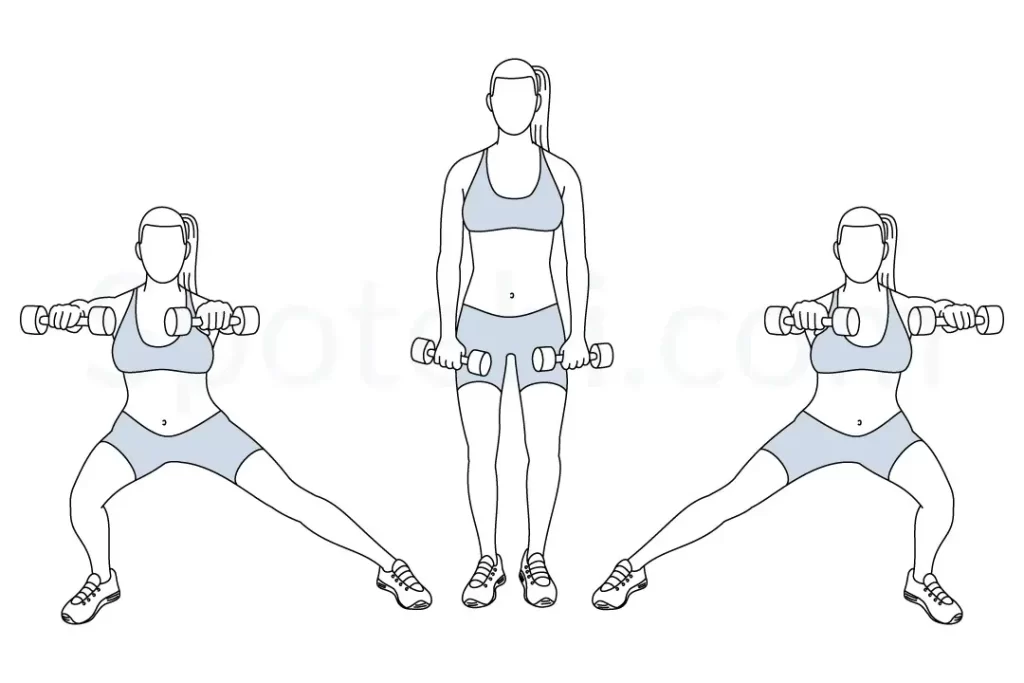
- Begin by placing your arms at your sides and your feet shoulder-width apart.
- Step forward with your right leg while bending your right knee, pausing until your thigh is parallel to the floor. Make sure your right knee stays inside your right foot.
- Step up off your right foot and take a step back to the beginning. Continue with your left leg. This counts as one rep. Also the same as lateral side lunges.
- Do three sets of ten repetitions.
Squats combined with an overhead press-

- Step one: Get up and place your feet shoulder-width apart or slightly apart. Choose a modest weight set of dumbbells (we recommend starting with 10 pounds). To get the floor parallel to your upper arms, raise the weights above your head.
- Sustain core stability as you push up until your arms are fully stretched above your head. Maintain a still head and neck.
- When you feel that your triceps muscle is parallel to the floor again, take a brief rest, bend your elbows, and then bring the weight back to the beginning position.
- Finish three sets of twelve reps.
Push-ups / Knee drives with push-ups-

- Take a plank position to begin. Shoulders drawn back and down, neck neutral, and core tight.
- As you start to lower your body to the floor, bend your elbows. Stretch your elbows until your chest touches it, then start over again. Throughout this entire workout, keep your elbows tight to your torso.
- Complete as many repetitions as possible in three sets.
- A modified stance where you can push yourself to your knees is an option if you struggle to perform a pushup with good form. You will still get strength from this and get many of the same advantages.
Burpees

We both love and despise burpees as a full-body, extremely effective workout. They are also a great way to build muscle and cardiovascular endurance.
- To begin, stand erect, place your feet shoulder-width apart, and keep your arms by your sides.
- As you extend your hands in front of you, begin to squat. Straighten your legs back into a pushup position as soon as your hands touch the ground.
- Lift your feet to your palms with a hip swing. If needed, place your feet outside of your hands and bring them as close to your hands as possible.
- Make a leap by bending forward and lifting your arms above your head.
- This counts as one rep. Commence with three sets of 10 reps.
Planks/Planks with dumbbell extensions for the triceps-
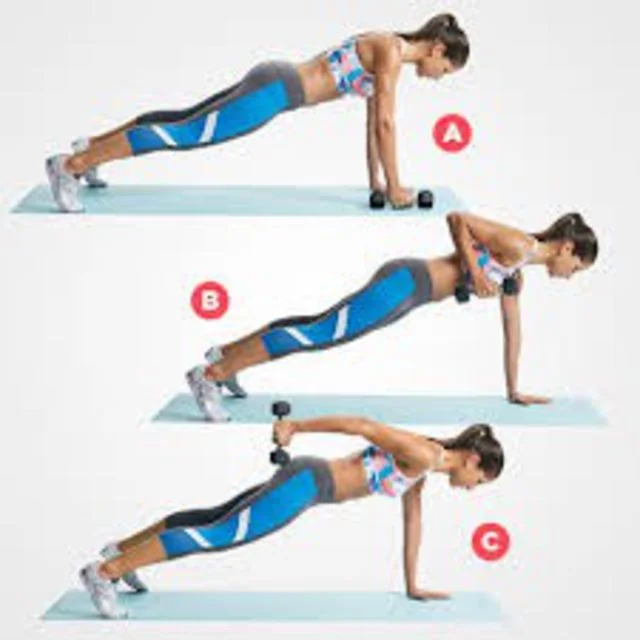
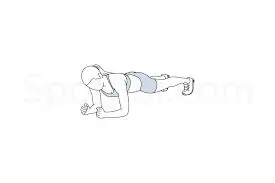

- Start in the push-up position, keeping your back straight, your core tight, and your hands and toes firmly planted on the ground.
- Maintain a slight tuck in your chin and look directly in front of your hands.
- Engage your stomach, shoulders, triceps, glutes, and quads as you take deep, purposeful breaths while maintaining a taut complete body.
- Try two or three sets of thirty-second holds at first.
Side planks
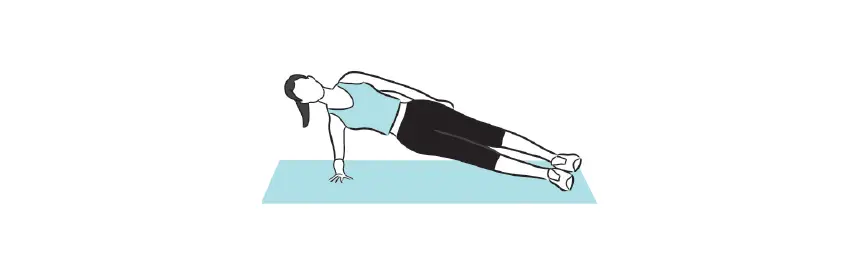
- Placing your left foot and leg on top of your right foot and leg, lie on your right side. Place your right forearm on the floor with your elbow exactly under your shoulder to raise your upper body.
- To make your spine stiffen and to raise your hips and knees off the floor so that your body forms a straight line, contract your core.
- Return in a controlled manner to the beginning. Switch after three sets of ten to fifteen repetitions on one side.
Glute bridge

- Beginning on the floor, position your feet flat on the floor, bend your knees, and keep your arms straight at your sides with your palms facing downward.
- Push through your heels and raise your hips off the ground by using your hamstrings, glutes, and core. Your upper back, shoulders, and core should all remain in contact with the ground. Your core should then form a straight line that ends at your knees.
- At the top, pause for one or two seconds before going back to the beginning.
- Perform 3 sets of 10–12 repetitions.
Single-leg deadlifts
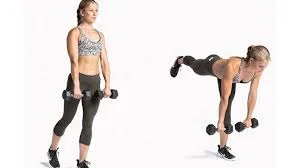
- With your knees slightly bent, start by holding a dumbbell in your right hand.
- Lower the dumbbell towards the floor by kicking your left leg straight back behind you while hinging at the hips.
- Once you have raised your left leg to a comfortable height, slowly and methodically lower yourself back to the beginning position while tightening your right glute. Make sure your pelvis stays square to the ground the entire time you perform the exercise.
- After completing 10 to 12 repetitions, switch the weight to your left hand and repeat the same movements with your left leg. Three sets of ten to twelve repetitions per side are advised.
Endomorph Workout and Diet Advantages
There may be some advantages to eating and exercising for your body type, but don’t anticipate miracles. An overall healthy diet and frequent exercise help everyone.
Alter Your Body Composition
Endomorphs have more fat, accumulate fat more readily, and have a more difficult time reducing it. Your body composition can be altered by addressing these issues, resulting in the loss of fat and the gain of muscle.
Increase Weight Loss
Weight loss and maintenance are the same. Endomorphs acquire weight rapidly and lose weight slowly. Some changes in your diet and exercise routine might help you lose weight or maintain a healthy weight.
Improve Your Health
Endomorphs with impaired insulin sensitivity are more likely to experience blood sugar rises and the associated health concerns. When your body does not handle sugar well, you are more likely to develop metabolic syndrome, type II diabetes, and other chronic health issues. Taking care of this issue can significantly enhance your long-term health and reduce your chances of chronic illness.
Endomorph Advantages
It’s not all horrible to be an endomorph. Endomorphs have broad and wide bones and may quickly gain muscular mass with correct exercise and nutrition. Being strongly built and powerful has various advantages, especially in sports.
The endomorph appearance is very popular in the arts and entertainment industries. Marilyn Monroe and Oprah Winfrey are two examples of endomorphs who have excelled in a variety of fields.
Endomorphs are also emotionally and mentally well-adjusted since they are gregarious, emotionally stable, outgoing, easy to converse with, and respectful to others.
A proper training routine will help you gain strength, endurance, and abilities.
The endomorph body type’s sluggish metabolism is frequently caused by sedentary behaviors and long-term positive calorie balance. Your determination and qualified instruction can improve your behaviours as well as your health. Consistency and diligence go a long way towards obtaining excellent health and an attractive body shape.
Disadvantages of endomorph body type
- Weight Management Challenges
- Metabolic Considerations
- Social and Cultural Influences
- Potential Health Risks
Tendency for Higher Body Fat:
Endomorphs are often associated with a higher percentage of body fat. Regarding the health risks that come with having too much body fat, like type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and other disorders linked to obesity, this could be a drawback.
Metabolic Difficulties:
Endomorphs may struggle with their metabolism, which makes it simpler for them to put on weight and more difficult for them to lose it. A slower metabolic rate in comparison to other body types could be the cause of this.
Having and Sustaining a Lean Body: A Challenge
Endomorphs may find it more difficult to attain and maintain a lean body type than those with other body types. To properly manage their weight, they might have to work harder at exercising and eating a healthy diet.
Social Perception and Body Image:
Because leaner body types are typically preferred by society, endomorphic people may experience difficulties with their body image and social perception. Psychological strain and a decline in self-worth may result from this.
Possibility of Health Problems Linked to Weight:
The endomorph body type is linked to a higher percentage of body fat, which can raise the risk of obesity-related health problems like joint issues, sleep apnea, and a higher chance of developing chronic diseases.
Conclusion
When your efforts do not provide results, losing weight might appear to be an uphill fight. Understanding your own body type, as well as the specific problems that endomorphs experience, may help you lose weight and achieve your exercise objectives.
Cardiovascular activity is a crucial part of a person’s fitness routine. A home workout can consist of a variety of activities with varying degrees of difficulty.
While designing a cardiovascular program, people can want to include a variety of obstacles.
Maintain a modest refined carbohydrate consumption, gain lots of frequent physical activity, and practice portion management. All of these are healthy practices that are advised for the majority of individuals. Sticking to this practice may help you lose excess weight – and keep it off.
FAQs
How do people who are endomorphs lose weight?
An endomorphic body type may find it helpful to follow a paleo-style diet that emphasizes veggies, protein, and healthy fats in each meal to help them lose weight. It could also be advantageous to include strength and cardiovascular training in their regimen.
What is an endomorph body type?
Having a rounder shape, a larger percentage of body fat, and an inclination to acquire weight quickly, an endomorph is one of the three main body types.
What are the typical characteristics of an endomorph?
Endomorphs usually have a slower metabolism, shorter limbs, and a tendency to store fat. They may find it easier to gain muscle but also face challenges in losing excess body fat.
Is it possible to change from an endomorph body type to another?
While body types are largely genetic, lifestyle factors such as diet and exercise can influence body composition. Endomorphs can achieve a healthier body by adopting a balanced approach to nutrition and regular physical activity.
What are the best exercises for endomorphs?
Endomorphs benefit from a combination of cardiovascular exercises to burn calories and resistance training to build muscle. A mix of strength and endurance exercises is ideal.
How should endomorphs approach their diet?
A balanced diet with a focus on portion control and nutrient-dense foods is crucial. Endomorphs may need to be mindful of carbohydrate intake and prioritize lean protein sources.
Can endomorphs lose weight effectively?
Yes, endomorphs can lose weight with a diet and exercise regimen that is consistent and customized for them. It’s essential to adopt sustainable habits rather than resorting to extreme diets.
Are there specific challenges for endomorphs in fitness?
Endomorphs may find it challenging to lose weight quickly and may need to be patient with their progress. It’s important to set realistic goals and focus on overall health rather than rapid weight loss.
Should endomorphs focus more on cardio or strength training?
A balanced approach is key. Strengthening and aerobic exercise are equally important for overall fitness. Combining these elements helps improve metabolism, burn calories, and build muscle.
How can endomorphs boost their metabolism?
Regular physical activity, particularly high-intensity interval training (HIIT), can help boost metabolism. Additionally, ensuring an adequate intake of water, proper sleep, and managing stress are important factors.
Is there a recommended meal plan for endomorphs?
While individual needs vary, a balanced diet with an emphasis on whole foods, lean proteins, and controlled portions is beneficial. Consulting with a nutritionist can help tailor a meal plan to specific requirements.